Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a/ Hai hàm số có đồ thị // với nhau khi
\(\hept{\begin{cases}m-2=1\\3\ne0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow m=3\)
b/ Tọa độ giao điểm 2 đường thẳng là nghiệm của hệ
\(\hept{\begin{cases}y=x+3\\y=2x+1\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=2\\y=5\end{cases}}\)
c/ Gọi điểm mà đường thẳng luôn đi qua là M(a,b) ta thế vào hàm số được
\(b=ma+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow ma+3-b=0\)
Để phương trình này không phụ thuôc m thì
\(\hept{\begin{cases}a=0\\3-b=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}a=0\\b=3\end{cases}}\)
Tọa độ điểm cần tìm là M(0, 3)
d/ Ta có khoản cách từ O(0,0) tới (d) là 1
\(\Rightarrow=\frac{\left|0-0m-3\right|}{\sqrt{1^2+m^2}}=\frac{3}{\sqrt{1+m^2}}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{1+m^2}=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}m=2\sqrt{2}\\m=-2\sqrt{2}\end{cases}}\)

a) (d) // (d') khi m - 3 = 1
m = 1 + 3
m = 4
Vậy m = 4 thì (d) // (d')
b) Với m = 4 ⇒ (d): y = x + 2
Đồ thị:
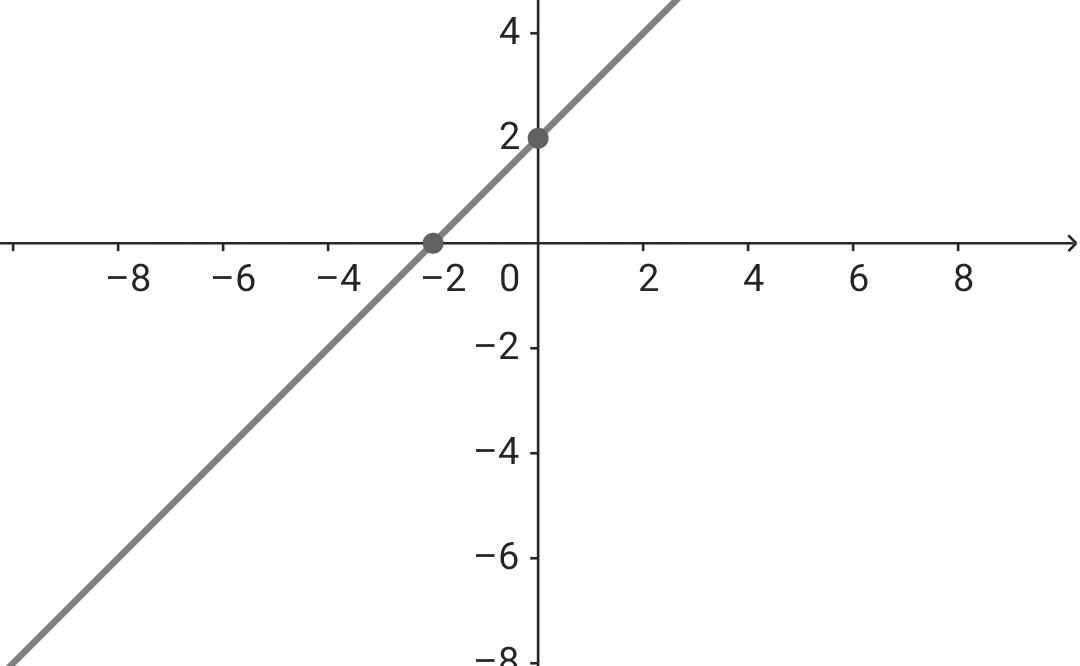

b: Để hai đường song song thì m-2=2
=>m=4
c: Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=\dfrac{-2}{m-2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow OA=\dfrac{2}{\left|m-2\right|}\)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow OB=2\)
SAOB=1
=>1/2*4/|m-2|=1
=>4/|m-2|=2
=>|m-2|=2
=>m=4 hoặc m=0

a) Để đồ thị 2 hàm số đã cho cắt nhau thì:
\(m-1\ne3-m\Leftrightarrow m\ne2\)
Vậy khi m\(\ne\)2 thì đồ thị của hai hàm số đã cho cắt nhau
b) Khi m=0 ta đc hàm số y = -x+2 và y=3x -2
* hàm số y=-x +2, cho x =0 thì y=2 => A(0;2)
, cho y=0 thì x=2 => B(2;0)
*Hàm số y =3x-2, cho x=0 thì y= -2 => C(0;-2)
cho y=0 thì x=2/3 => D(2/3; 0)
2 1 2 1 -2 y=3x-2 y=-x+2 O ^ > x y

a: Thay x=2 và y=-3 vào (d), ta được:
\(2\left(2m-1\right)-2m+5=-3\)
=>\(4m-2-2m+5=-3\)
=>2m+3=-3
=>2m=-6
=>\(m=-\dfrac{6}{2}=-3\)
b: Để (d)//(d') thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2m-1=2\\-2m+5\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2m=3\\-2m\ne-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=\dfrac{3}{2}\\m\ne2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>m=3/2
Thay m=3/2 vào (d), ta được:
\(y=\left(2\cdot\dfrac{3}{2}-1\right)x-2\cdot\dfrac{3}{2}+5=2x+2\)
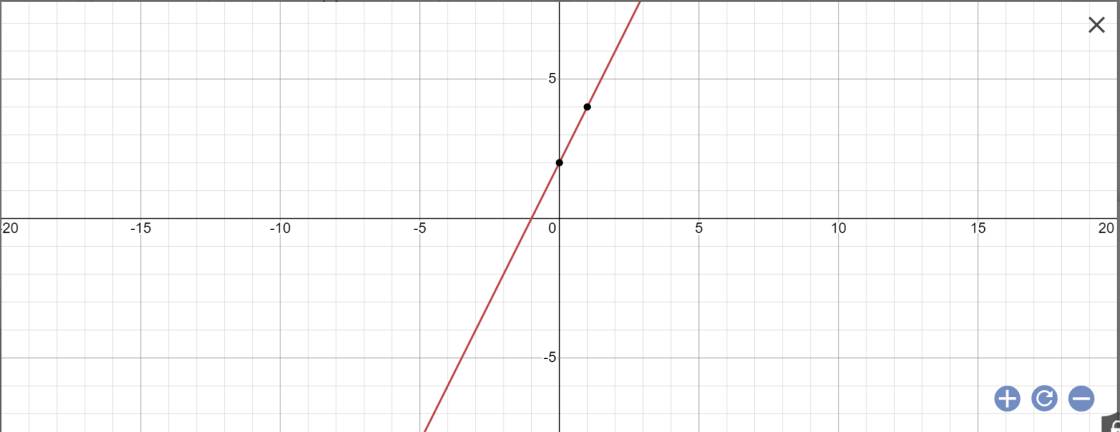
y=2x+2 nên a=2
Gọi \(\alpha\) là góc tạo bởi (d) với trục Ox
\(tan\alpha=2\)
=>\(\alpha\simeq63^026'\)

a) (d) // (d') khi m - 3 = 1
m = 1 + 3
m = 4
Vậy m = 4 thì (d) // (d')
b) Với m = 4 ⇒ (d): y = x + 2
Đồ thị:


1: Để (d)//(d') thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-3=1\\2\ne-5\left(đúng\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>m-3=1
=>m=4
Thay m=4 vào (d), ta được:
\(y=\left(4-3\right)x+2=x+2\)
Vẽ đồ thị:
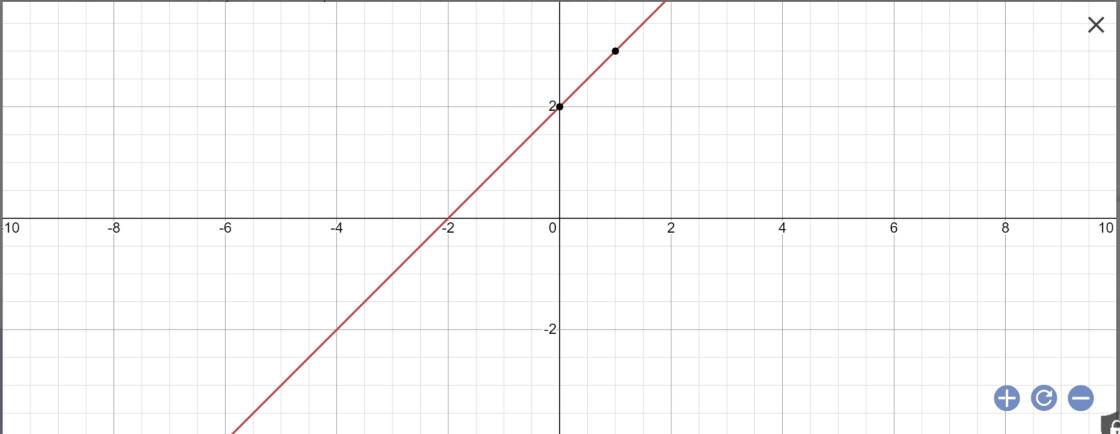
2: Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\left(m-3\right)x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x\left(m-3\right)=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{2}{m-3}\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(A\left(-\dfrac{2}{m-3};0\right)\)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=\left(m-3\right)\cdot x+2=0\left(m-3\right)+2=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy: B(0;2)
\(OA=\sqrt{\left(-\dfrac{2}{m-3}-0\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}\)
\(=\sqrt{\left(-\dfrac{2}{m-3}\right)^2+0^2}=\dfrac{2}{\left|m-3\right|}\)
\(OB=\sqrt{\left(0-0\right)^2+\left(2-0\right)^2}=2\)
Vì Ox\(\perp\)Oy
nên OA\(\perp\)OB
=>ΔOAB vuông tại O
=>\(S_{OBA}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot OA\cdot OB=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot2\cdot\dfrac{2}{\left|m-3\right|}=\dfrac{2}{\left|m-3\right|}\)
Để \(S_{OAB}=2\) thì \(\dfrac{2}{\left|m-3\right|}=2\)
=>|m-3|=1
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}m-3=1\\m-3=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=4\\m=2\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(a,\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-1=1\\3-2m\ne-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=2\\m\ne\dfrac{7}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m=2\\ \Leftrightarrow y=x-1\\ b,\text{PT giao Ox và Oy: }y=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{2m-3}{m-1}\Leftrightarrow OA=\left|\dfrac{2m-3}{m-1}\right|\\ x=0\Leftrightarrow y=3-2m\Leftrightarrow OB=\left|2m-3\right|\\ \text{Gọi H là chân đường cao từ O \rightarrow}\left(d\right)\Leftrightarrow\Leftrightarrow OH=1\\ \text{Áp dụng HTL: }\dfrac{1}{OA^2}+\dfrac{1}{OB^2}=\dfrac{1}{OH^2}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(m-1\right)^2}{\left(2m-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{1}{\left(2m-3\right)^2}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2-2m+2=4m^2-12m+9\\ \Leftrightarrow3m^2-10m+7=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=\dfrac{7}{3}\\m=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bn tự vẽ đồ thị nha (khá dễ mà :v)
b, Vì đường thẳng y = (m - 1)x + m + 3 // với đường thẳng y = x - 2 nên:
\(\Rightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=a'\\b\ne b'\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-1=1\\m+3\ne-2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=2\\m\ne-5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) m = 2
Vậy m = 2
Chúc bn học tốt!
Cảm ơn bạn ạ>3