K
Khách
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.
Các câu hỏi dưới đây có thể giống với câu hỏi trên

12 tháng 5 2023
a: 
b: Phương trình OA có dạng là y=ax+b
Theo đề, ta có hệ:
0a+b=0 và a+b=1
=>b=0 và a=1
=>y=x
Vì (d)//OA nên (d): y=x+b
Thay x=2 và y=0 vào (d), ta được:
b+2=0
=>b=-2
=>y=x-2
PTHĐGĐ là:
-x^2-x+2=0
vì a*c<0
nên (P) luôn cắt (d) tại hai điểm phân biệt

22 tháng 12 2021
b: Tọa độ giao điểm là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+2=x\\y=x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=y=-2\)

13 tháng 11 2021
b: Tọa độ giao điểm là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=-x+2\\y=-x+2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{4}\\y=2-\dfrac{3}{4}=\dfrac{5}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)

DT
11 tháng 2 2022
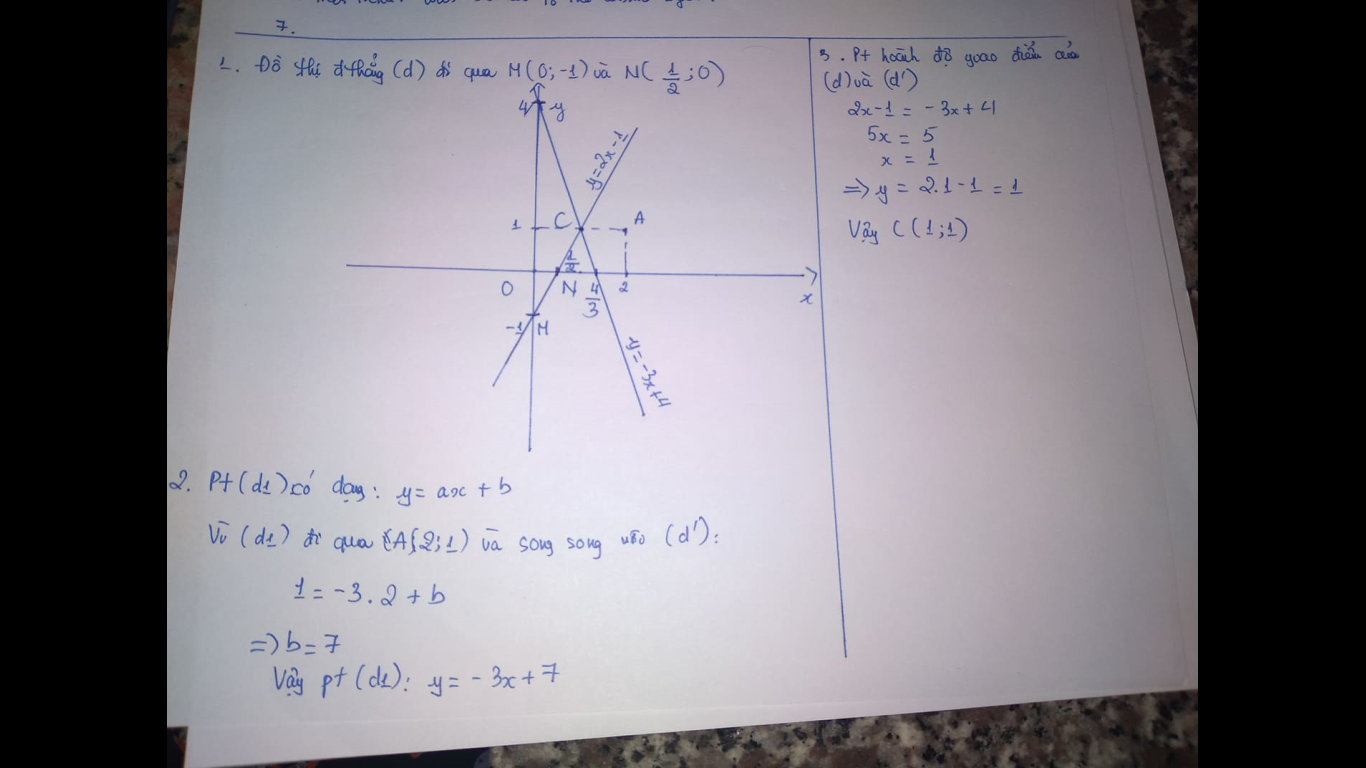
c1:
Vì (d')//d nên pt đường thẳng của (d') là:y=-3x+b
đường thẳng (d') có tung độ gốc =2 => b=2
Vậy : pt đường thẳng của (d') là:y=-3x+2
a:
b: (d1)//(d')
=>(d1): y=-2x+b
Thay x=0 và y=5 vào (d1), ta được:
b-2*0=5
=>b=5
c: Tọa độ giao điểm là;
x=-2x+3 và y=x
=>3x=3 và y=x
=>x=1 và y=1(ĐPCM)