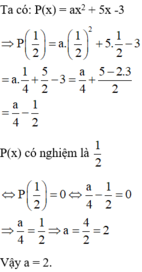Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a/ \(M\left(x\right)=-x^2+5\)
Có \(-x^2\le0\forall x\)
=> \(M\left(x\right)\le5\forall x\)
=> M(x) không có nghiệm.
2/
Thay \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\) vào đa thức M(x) có
\(M\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=\dfrac{1}{4}a+\dfrac{5}{2}-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{4}a=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a=2\)
Vậy...

a) Ta có f(7) = a7 + b và f(2) + f(3) = (a2+ b) + (a3 + b) = 5a + 2b. Vậy để f(7) = f(2) + f(3), ta cần giải phương trình:
a7 + b = 5a + 2b
Simplifying, ta được: 2a = b.
Vậy điều kiện của a và b để f(7) = f(2) + f(3) là b = 2a.
b) Để tìm nghiệm của P(x), ta cần giải phương trình (x-2)(2x+5) = 0:
(x-2)(2x+5)= 0
→ X-2 = 0 hoặc 2x+5 = 0
→ x = 2 hoặc x = -5/2
Vậy nghiệm của P(x) là x = 2 hoặc x =-5/2.
c) Ta biết rằng đa thức P(x) có 1 nghiệm là -2, vậy ta có thể viết P(x)
dưới dạng:
P(x) = (x+2)(x^3 - 2x^2 + ax - 2)
Từ đó suy ra:
P(-2) = (-2+2)(8 - 4a - 2) = 0
⇔-8a= 16
⇔a = -2
Vậy hệ số a của P(x) là -2.

Vì đa thức \(M_{\left(x\right)}=ax^2+5-3\) có nghiệm là \(\frac{1}{2}\) nên:
\(M\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)=0\Leftrightarrow a\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+5-3=0\)
\(\Rightarrow a.\frac{1}{4}+2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow a.\frac{1}{4}=-2\)
\(\Rightarrow a=-2\div\frac{1}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow a=-8\)

1) \(\left(x^2-4x+3\right)f\left(x+1\right)=\left(x-2\right)f\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)f\left(x+1\right)=\left(x-2\right)f\left(x-1\right)\)
Với \(x=1\): \(0=-1f\left(0\right)\Leftrightarrow f\left(0\right)=0\)do đó \(0\)là một nghiệm của đa thức \(f\left(x\right)\).
Tương tự xét \(x=2,x=3\)có thêm hai nghiệm nữa là \(3\)và \(2\).
2) \(f\left(2\right)=4a-2+b=0\Leftrightarrow4a+b=2\)
Tổng hệ số cao nhất và hệ số tự do là \(a+b\)suy ra \(a+b=-7\).
Ta có hệ:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}4a+b=2\\a+b=-7\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}3a=9\\b=-7-a\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}a=3\\b=-10\end{cases}}\).

Ta có f(x)=ax^2+5x-6 (1)
Thay x=-2 vào (1) ta đc
f(-2)=a(-2)^2+5(-2)-6
= 4a-10-6
=4a-16
Mà x=-2 là 1 nghiệm của f(x)
suy ra 4a-16=0
4a=16
a=4
Vậy a=4

Ta có P(0,5)=0
=>a0,5^2+5.0,5-3=0
=>0,25a+2,5-3=0
=>0,25a-0,5=0
=>0,25a=0,5
=>a=0,5-0,25
a=0,25
Vậy hệ số a là 0,25

Bài 3:
\(x=1-\sqrt{2}\Leftrightarrow x^2=3-2\sqrt{2}=2-2\sqrt{2}+1\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2=2x+1\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow P\left(x\right)=ax^2+bx+c=x^2-2x-1\\ \Leftrightarrow a=1;b=-2;c=-1\\ \Leftrightarrow11a+3b+2x=11-6-2=3⋮3\)