Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Đặt \(x+y=t,t\in\left[-2;2\right]\)
Biến đổi được \(P=-2t^3+6t\)
Xét \(f\left(t\right)=-2t^3+6t\) trên \(\left[-2;2\right]\)
Lập bảng biến thiên
Ta có \(P_{Max}=4\) khi t=1
\(P_{Min}=-4\) khi t= -1

Từ gt ta có x^2+y^^2=xy+1
=>P=(x^2+y^2)^2-2x^2y^2-x^2y^2
=(xy+1)2-2x2y2-x2y2
=x2y2+xy+1-3x2y2=-2x2y2+xy+1
=......
\(1=x^2+y^2-xy\ge2xy-xy=xy\Rightarrow xy\le1\)
\(1=x^2+y^2-xy\ge-2xy-xy=-3xy\Rightarrow xy\ge-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow-\dfrac{1}{3}\le xy\le1\)
\(P=\left(x^2+y^2\right)^2-2\left(xy\right)^2-\left(xy\right)^2=\left(xy+1\right)^2-3\left(xy\right)^2=-2\left(xy\right)^2+2xy+1\)
Đặt \(xy=t\in\left[-\dfrac{1}{3};1\right]\)
\(P=f\left(t\right)=-2t^2+2t+1\)
\(f'\left(t\right)=-4t+2=0\Rightarrow t=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(f\left(-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)=\dfrac{1}{9}\) ; \(f\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=\dfrac{3}{2}\) ; \(f\left(1\right)=1\)
\(\Rightarrow P_{max}=\dfrac{3}{2}\) ; \(P_{min}=\dfrac{1}{9}\)

Đáp án C.
Ta có

Khi đó, giả thiết trở thành:
log 3 x + y x 2 + y 2 + x y + 2 = x 2 + y 2 + x y + 2 - 3 x + y - 2
⇔ log 3 x + y - log 3 x 2 + y 2 + x y + 2 = x 2 + y 2 + x y + 2 - 3 x + y - 2
⇔ 3 x + y + log 3 3 x + y = x 2 + y 2 + x y + 2 + log 3 x 2 + y 2 + x y + 2
Xét hàm số f t = t + log 3 t trên khoảng 0 ; + ∞ , có f ' t = 1 + 1 t ln 3 > 0 ; ∀ t > 0 .
Suy ra f(t) là hàm số đồng biến trên 0 ; + ∞ mà f[3(x + y)] = f(x2 + y2 + xy + 2)


Do x+ y= 1 nên
S = 16 x 2 y 2 + 12 ( x + y ) ( x 2 - x y + y 2 ) + 34 x y = 16 x 2 y 2 + 12 ( x + y ) 2 - 3 x y + 34 x y , d o x + y = 1 = 16 x 2 y 2 - 2 x y + 12
Đặt t= xy . Do x≥ 0 ; y≥0 nên
0 ≤ x y ≤ ( x + y ) 2 4 = 1 4 ⇒ t ∈ 0 ; 1 4
Xét hàm số f(t) = 16t2- 2t + 12 trên [0 ; 1/4].
Ta có f’ (t) = 32t- 2 ; f’(t) =0 khi t= 1/ 16 .
Bảng biến thiên
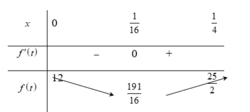
Từ bảng biến thiên ta có:
m i n 0 ; 1 4 f ( t ) = f ( 1 16 ) = 191 16 ; m a x 0 ; 1 4 f ( t ) = f ( 1 4 ) = 25 2
Vậy giá trị lớn nhất của S là 25/2 đạt được khi
x + y = 1 x y = 1 4 ⇔ x = 1 2 y = 1 2
giá trị nhỏ nhất của S là 191/ 16 đạt được khi
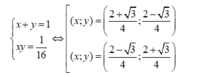
Chọn A.

a. Đề bài em ghi sai thì phải
Vì:
\(x+y=2\left(\sqrt{x-3}+\sqrt{y-3}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3-2\sqrt{x-3}+1\right)+\left(y-3-2\sqrt{y-3}+1\right)+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x-3}-1\right)^2+\left(\sqrt{y-3}-1\right)^2+4=0\) (vô lý)
b.
Xét hàm \(f\left(x\right)=x^3+ax^2+bx+c\)
Hàm đã cho là hàm đa thức nên liên tục trên mọi khoảng trên R
Hàm bậc 3 nên có tối đa 3 nghiệm
\(f\left(-2\right)=-8+4a-2b+c>0\)
\(f\left(2\right)=8+4a+2b+c< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(-2\right).f\left(2\right)< 0\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) luôn có ít nhất 1 nghiệm thuộc (-2;2)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow+\infty}f\left(x\right)=x^3\left(1+\dfrac{a}{x}+\dfrac{b}{x^2}+\dfrac{c}{x^3}\right)=+\infty.\left(1+0+0+0\right)=+\infty\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Luôn tồn tại 1 số thực dương n đủ lớn sao cho \(f\left(n\right)>0\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(2\right).f\left(n\right)< 0\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) luôn có ít nhất 1 nghiệm thuộc \(\left(2;n\right)\) hay \(\left(2;+\infty\right)\)
Tương tự \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-\infty}f\left(x\right)=-\infty\Rightarrow f\left(-2\right).f\left(m\right)< 0\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) luôn có ít nhất 1 nghiệm thuộc \(\left(-\infty;-2\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) có đúng 3 nghiệm pb \(\Rightarrow\) hàm cắt Ox tại 3 điểm pb





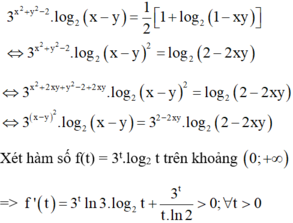

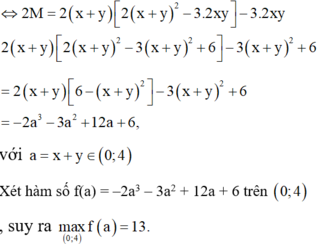

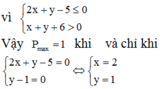

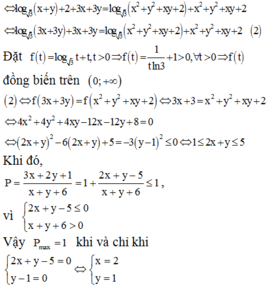
Ta có: \begin{aligned} (x-y)^2+(x^3+y^2)+7xy & = 49+(y^2-x^3)^2 \ \Leftrightarrow x^2-2xy+y^2+x^3+y^2+7xy & = 49+y^4-2y^2x^3+x^6 \ \Leftrightarrow x^2+x^3+3xy+y^2 & = y^4+(x^3-3xy)^2+49 \end{aligned} Chú ý rằng $(x^3-3xy)^2\geqslant 0$ nên: \begin{aligned} y^4+(x^3-3xy)^2+49 & \geqslant 49 \ \Rightarrow x^3+x^2+3xy+y^2 & \geqslant 49 \end{aligned} Từ đó, ta có: A = xy = \dfrac{1}{2}[(x-y)^2+x^2+y^2]\leqslant \dfrac{1}{2}[2x^2+2y^2]=x^2+y^2 Do đó, ta có: $A\leqslant x^2+y^2\leqslant\dfrac{(x^3+x^2+3xy+y^2)+(y^4+(x^3-3xy)^2+49)}{2}=49$ Vậy $A\leqslant 49$ và $A=49$ đạt được khi và chỉ khi $(x, y)=(-3, -4)$ hoặc $(x, y)=(4, 3)$.