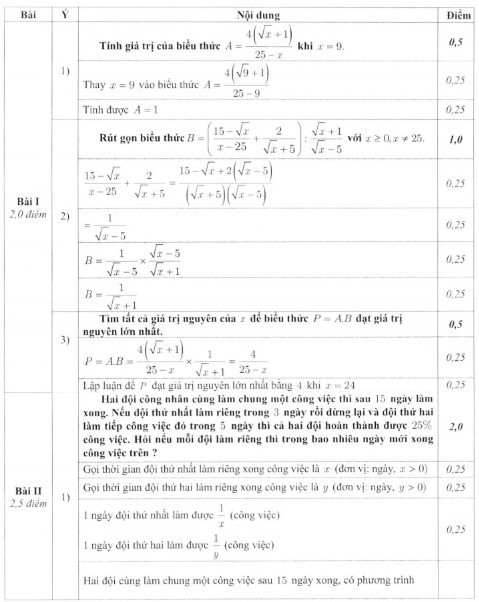
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Câu 4:
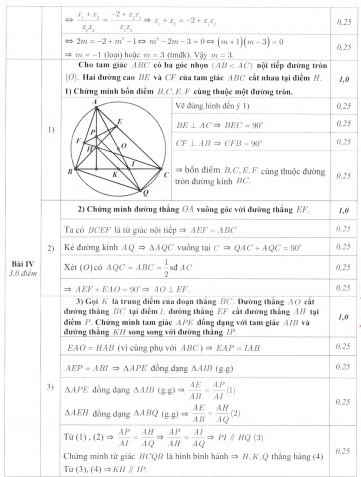
A B C E F H O I P K Q x
a) Vì BE,CF là các đường cao của \(\Delta\)ABC nên ^BEC = ^CFB = 900
=> ^BEC và ^CFB cùng nhìn đoạn BC dưới một góc 900
=> Bốn điểm B,C,E,F cùng thuộc đường tròn đường kính BC (Theo quỹ tích cung chứa góc) (đpcm).
b) Gọi Ax là tia tiếp tuyến tại A của đường tròn (O), khi đó OA vuông góc Ax
Từ câu a ta thấy tứ giác BFEC nội tiếp đường tròn (BC) => ^AFE = ^ACB
Mà ^ACB = ^BAx (Tính chất góc tạo bởi tiếp tuyến và dây) nên ^AFE = ^BAx
=> EF // Ax (2 góc so le trong bằng nhau)
Do OA vuông góc Ax nên OA vuông góc EF (Quan hệ song song, vuông góc) (đpcm).
c) +) Ta dễ có ^OAC = 900 - ^AOC/2 = 900 - ^ABC = ^BAH => ^OAC + ^OAH = ^BAH + ^OAH => ^BAI = ^EAP
Xét \(\Delta\)APE và \(\Delta\)AIB: ^EAP = ^BAI, ^AEP = ^ABI (Tứ giác BFEC nội tiếp) => \(\Delta\)APE ~ \(\Delta\)AIB (g.g) (đpcm).
+) Gọi AO cắt đường tròn (O) lần thứ hai tại Q. Khi đó AQ là đường kính của (O)
Nên ta có: ^ABQ = ^ACQ = 900 hay BQ vuông góc AB, CQ vuông góc AC. Mà CH vuông góc AB, BH vuông góc AC
Nên BQ // CH, BH // CQ (Quan hệ song song vuông góc) => Tứ giác BHCQ là hình bình hành
Từ đó HQ đi qua trung điểm K của BC hay H,K,Q thẳng hàng (1)
Cũng dễ thấy ^QBC = ^HCB (Vì BQ // CH) = ^FEH (Vì B,C,E,F cùng thuộc một đường tròn)
Hay ^QBI = ^HEP. Kết hợp với ^BQI = ^BQA = ^ACB = ^AHE (Cùng phụ ^CAH) = ^EHP
Suy ra \(\Delta\)BIQ ~ \(\Delta\)EPH (g.g) => \(\frac{HP}{QI}=\frac{EP}{BI}\). Lại có \(\frac{EP}{BI}=\frac{AP}{AI}\)nên \(\frac{HP}{QI}=\frac{AP}{AI}\)
Áp dụng ĐL Thales đảo vào \(\Delta\)AQH ta có IP // HQ (2)
Từ (1) và (2) ta thu được KH // IP (đpcm).


Nếu ko nhìn rõ thì bn có thể tham khảo tại:
https://vietnamnet.vn/vn/giao-duc/tuyen-sinh/dap-an-mon-toan-thi-tuyen-sinh-lop-10-ha-noi-2019-cua-so-gd-dt-ha-noi-539465.html
https://vnexpress.net/giao-duc/so-giao-duc-va-dao-tao-ha-noi-cong-bo-dap-an-thi-vao-lop-10-3934904.html
https://vietnamnet.vn/vn/giao-duc/tuyen-sinh/dap-an-mon-toan-thi-tuyen-sinh-lop-10-ha-noi-2019-cua-so-gd-dt-ha-noi-539465.html
https://tin.tuyensinh247.com/dap-an-de-thi-vao-lop-10-mon-toan-ha-noi-nam-2019-c29a45461.html

Gọi thời gian đội A đội B hoàn thành công việc khi làm một mình lần lượt là a,b
Theo đề, ta có: 16/a+16/b=1 và 4/a+3/b=11/48
=>a=24 và b=48

Mấy bài này dài vật vã ghê =)))))))))))))
1, a, \(\frac{3+4\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{5}}\)
= \(\frac{\left(3+4\sqrt{3}\right)\left(\sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{5}\right)}{\left(\sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{5}\right)\left(\sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{5}\right)}\)
=\(\frac{\left(3+4\sqrt{3}\right)\left(\sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{5}\right)}{\left(\sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2}\right)^2-5}\)
=\(\frac{\left(3+4\sqrt{3}\right)\left(\sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{5}\right)}{8+4\sqrt{3}-5}\)
= \(\frac{\left(3+4\sqrt{3}\right)\left(\sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{5}\right)}{3+4\sqrt{3}}\)
=\(\sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{5}\)
b, M = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}\left(x-1\right)}{\sqrt{x^2}-x+1}\)(ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge0\))
= \(\frac{\sqrt{3}\left(x-1\right)}{x-x+1}\)
= \(\sqrt{3}\left(x-1\right)\)
Thay x = \(2+\sqrt{3}\)(TMĐK) vào M ta có:
M = \(\sqrt{3}\left(2+\sqrt{3}-1\right)=\sqrt{3}\left(1+\sqrt{3}\right)=3+\sqrt{3}\)
Vậy với x = \(2+\sqrt{3}\)thì M = \(3+\sqrt{3}\)
2, Mình chỉ giải câu a thôi nhé:
\(\sqrt{1+b}+\sqrt{1+c}\ge2\sqrt{1+a}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{1+b}+\sqrt{1+c}\right)^2\ge\left(2\sqrt{1+a}\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1+b+2\sqrt{\left(1+b\right)\left(1+c\right)}+1+c\ge4\left(1+a\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2+b+c+2\sqrt{\left(1+b\right)\left(1+c\right)}\ge4\left(1+a\right)\left(1\right)\)
Vì \(\left(\sqrt{1+b}-\sqrt{1+c}\right)^2\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow2+b+c\ge2\sqrt{\left(1+b\right)\left(1+c\right)}\left(2\right)\)
Từ \(\left(1\right),\left(2\right)\Rightarrow4+2\left(b+c\right)+2\sqrt{\left(1+b\right)\left(1+c\right)}\ge4\left(1+a\right)+2\sqrt{\left(1+b\right)\left(1+c\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4+2\left(b+c\right)\ge4\left(1+a\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4+2\left(b+c\right)\ge4+4a\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(b+c\right)\ge4a\)
\(\Leftrightarrow b+c\ge2a\)
4*. Thật ra cái này mình xài làm trội, làm giảm là được mà
Đặt A = \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}+....+\frac{1}{\sqrt{n}}\)
\(\frac{1}{2}A=\frac{1}{2\sqrt{2}}+\frac{1}{2\sqrt{3}}+....+\frac{1}{2\sqrt{n}}\)
\(\frac{1}{2}A=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{2}}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{3}}+....+\frac{1}{\sqrt{n}+\sqrt{n}}\)
Ta có: \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{2}}>\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{2}}\)
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{3}}>\frac{1}{\sqrt{4}+\sqrt{3}}\)
+ .........................................................
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{n}+\sqrt{n}}>\frac{1}{\sqrt{n+1}+\sqrt{n}}\)
Cộng tất cả vào
\(\Rightarrow\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{2}}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{3}}+...+\frac{1}{\sqrt{n}+\sqrt{n}}>\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{2}}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{4}+\sqrt{3}}+...+\frac{1}{\sqrt{n+1}+\sqrt{n}}\)\(\frac{1}{2}A>\frac{\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{2}}{3-2}+\frac{\sqrt{4}-\sqrt{3}}{4-3}+...+\frac{\sqrt{n+1}-\sqrt{n}}{n+1-n}\)
\(\frac{1}{2}A>\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{4}-\sqrt{3}+...+\sqrt{n+1}-\sqrt{n}\)
\(\frac{1}{2}A>\sqrt{n+1}-\sqrt{2}\)
\(A>2\sqrt{n+1}-2\sqrt{2}>2\sqrt{n+1}-3\)
\(A+1>2\sqrt{n+1}-3+1\)
\(A+1>2\sqrt{n+1}-2\)
\(A+1>2\left(\sqrt{n+1}-1\right)\)
Vậy ta có điều phải chứng minh.

1,
\(D=\frac{1}{\sqrt{h+2\sqrt{h-1}}}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{h-2\sqrt{h-1}}}\)
\(=\frac{1}{\sqrt{h-1+2\sqrt{h-1}+1}}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{h-1-2\sqrt{h-1}+1}}\)
\(=\frac{1}{\sqrt{h-1}+1}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{h-1}-1}\)
\(=\frac{\sqrt{h-1}-1+\sqrt{h-1}+1}{h-1-1}\)
\(=\frac{2\sqrt{h-1}}{h-2}\)
Thay \(h=3\)vào D ta có:
\(D=\frac{2\sqrt{3-1}}{3-2}=2\sqrt{2}\)
Vậy với \(h=3\)thì \(D=2\sqrt{2}\)
2,
a, \(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{4x-4}-\sqrt{25x-25}+2=0\)(ĐK: \(x\ge1\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-1}+2\sqrt{x-1}-5\sqrt{x-1}+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2\sqrt{x-1}=-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-1}=1\Leftrightarrow x=2\left(TM\right)\)
Vậy PT có nghiệm là \(x=2\)
b, \(\sqrt{9x^2+18}+2\sqrt{x^2+2}-\sqrt{25x^2+50}+3=0\)(ĐK: \(-\sqrt{2}\le x\le\sqrt{2}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow3\sqrt{x^2+2}+2\sqrt{x^2+2}-5\sqrt{x^2+2}=-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0=-3\)(vô lí)
Vậy PT đã cho vô nghiệm.

Bài 6:
a: \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2+4}=\sqrt{12}\)
=>x^2+4=12
=>x^2=8
=>\(x=\pm2\sqrt{2}\)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow4\sqrt{x+1}-3\sqrt{x+1}=1\)
=>x+1=1
=>x=0
c: \(\Leftrightarrow3\sqrt{2x}+10\sqrt{2x}-3\sqrt{2x}-20=0\)
=>\(\sqrt{2x}=2\)
=>2x=4
=>x=2
d: \(\Leftrightarrow2\left|x+2\right|=8\)
=>x+2=4 hoặcx+2=-4
=>x=-6 hoặc x=2

a/ \(P=12\)
b/ \(Q=\frac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)
c/ Ta có:
\(\frac{P}{Q}=\frac{\frac{x+3}{\sqrt{x}-2}}{\frac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}}=\frac{x+3}{\sqrt{x}}\ge\frac{2\sqrt{3x}}{\sqrt{x}}=2\sqrt{3}\)
Dấu = xảy ra khi x = 3 (thỏa tất cả các điều kiện )
a. Thay x = 3 vào biểu thức P ta được :
\(p=\frac{x+3}{\sqrt{x}-2}=\frac{9+3}{\sqrt{9}-2}=12\)
b, \(Q=\frac{\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}+2}+\frac{5\sqrt{x}-2}{x-4}\)
\(=\frac{\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}+2}+\frac{5\sqrt{x}-2}{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(=\frac{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)+5\sqrt{x}-2}{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x-3\sqrt{x}+2+5\sqrt{x}-2}{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x+2\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(=\frac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(=\frac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)
c, Ta có :
\(\frac{P}{Q}=\frac{\frac{x+3}{\sqrt{x}-2}}{\frac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}}=\frac{x+3}{\sqrt{x}}\ge\frac{2\sqrt{3x}}{\sqrt{x}}=2\sqrt{3}\)
Vậy GTNN \(\frac{P}{Q}=2\sqrt{3}\) khi và chỉ khi \(x=3\)

Bài 1. ĐKXĐ thêm x ≠ 1 nữa ạ
1) Với x = 9 tmđk, thay vào A ta được : \(A=\dfrac{2\sqrt{9}+1}{9^2}=\dfrac{7}{81}\)
2) \(B=\left[\dfrac{4x}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\right]\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-1}{x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{4x-1}{\sqrt{x}-1}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-1}{x^2}=\dfrac{4x-1}{x^2}\)
3) Để B < A thì \(\dfrac{4x-1}{x^2}< \dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+1}{x^2}\)
<=> \(\dfrac{4x-1}{x^2}-\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+1}{x^2}< 0\)
<=> \(\dfrac{4x-2\sqrt{x}-2}{x^2}< 0\)
Vì x2 > 0 ∀ x
=> \(4x-2\sqrt{x}-2< 0\)
<=> \(2x-\sqrt{x}-1< 0\)
<=> \(\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(2\sqrt{x}+1\right)< 0\)
Vì \(2\sqrt{x}+1\ge1>0\forall x\ge0\)
=> \(\sqrt{x}-1< 0\)<=> x < 1
Vậy với x < 1 thì B < A
Câu 3 :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2y+\dfrac{1}{2x+3y}=2\\2x-4y+\dfrac{3}{2x+3y}=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2y+\dfrac{1}{2x+3y}=2\\2\left(x-2y\right)+\dfrac{3}{2x+3y}=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đặt \(x-2y=t;\dfrac{1}{2x+3y}=z\)
Hệ phương trình tương đương
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}t+z=2\\2t+3z=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}t=2-z\left(1\right)\\2t+3z=3\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thế (1) vào (2) ta được : \(2\left(2-z\right)+3z=3\Leftrightarrow4-2z+3z=3\Leftrightarrow z=-1\)
\(\Rightarrow t=2-z=3\)
hay \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2y=3\\\dfrac{1}{2x+3y}=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3+2y\left(3\right)\\\dfrac{1}{2x+3y}=-1\left(4\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thế (3) vào (4) ta được : \(\dfrac{1}{2\left(3+2y\right)+3y}=-1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{6+7y}=-1\Rightarrow-6-7y=1\Leftrightarrow-7y=7\Leftrightarrow y=-1\)
\(\Rightarrow x=3-2=1\)
Vậy \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(1;-1\right)\)