
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a.
\(A=\left(\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}{x\left(x-1\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{x\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{x-2}{x}\right):\dfrac{x+1}{x}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x^2+x+1}{x}+\dfrac{x+2}{x}+\dfrac{x-2}{x}\right):\dfrac{x+1}{x}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x^2+3x+1}{x}\right).\dfrac{x}{x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+3x+1}{x+1}\)
2.
\(x^3-4x^3+3x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-4x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(loại\right)\\x=1\left(loại\right)\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với \(x=3\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{3^2+3.3+1}{3+1}=\dfrac{19}{4}\)



Bài 4:
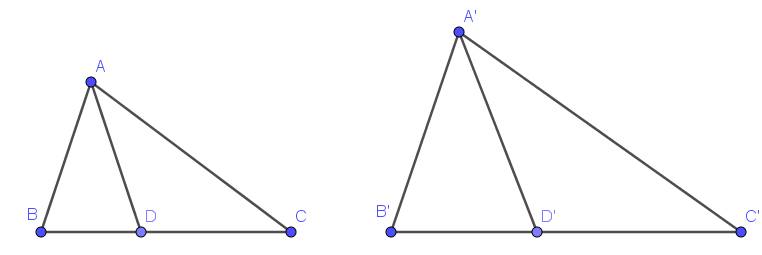
a. Vì $\triangle ABC\sim \triangle A'B'C'$ nên:
$\frac{AB}{A'B'}=\frac{BC}{B'C'}=\frac{AC}{A'C'}(1)$ và $\widehat{ABC}=\widehat{A'B'C'}$
$\frac{DB}{DC}=\frac{D'B'}{D'C}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{BD}{BC}=\frac{D'B'}{B'C'}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{BD}{B'D'}=\frac{BC}{B'C'}(2)$
Từ $(1); (2)\Rightarrow \frac{BD}{B'D'}=\frac{BC}{B'C'}=\frac{AB}{A'B'}$
Xét tam giác $ABD$ và $A'B'D'$ có:
$\widehat{ABD}=\widehat{ABC}=\widehat{A'B'C'}=\widehat{A'B'D'}$
$\frac{AB}{A'B'}=\frac{BD}{B'D'}$
$\Rightarrow \triangle ABD\sim \triangle A'B'D'$ (c.g.c)
b.
Từ tam giác đồng dạng phần a và (1) suy ra:
$\frac{AD}{A'D'}=\frac{AB}{A'B'}=\frac{BC}{B'C'}$
$\Rightarrow AD.B'C'=BC.A'D'$


ĐKXĐ: \(\left|x-2\right|-1\ne0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|x-2\right|\ne1\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2\ne1\\x-2\ne-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne3\\x\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\)






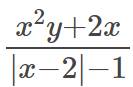
17:
a: Gọi hai số tự nhiên liên tiếp là a;a+1
Hiệu bình phương của chúng là 209 nên ta có:
\(\left(a+1\right)^2-a^2=209\)
=>\(a^2+2a+1-a^2=209\)
=>2a+1=209
=>2a=208
=>a=104
vậy: Hai số cần tìm là 104;104+1=105
b: Gọi hai số tự nhiên lẻ liên tiếp là 2k+1;2k+3
Hiệu lập phương của chúng là 1178 nên ta có:
\(\left(2k+3\right)^3-\left(2k+1\right)^3=1178\)
=>\(8k^3+36k^2+54k+27-8k^3-12k^2-6k-1=1178\)
=>\(24k^2+48k+26-1178=0\)
=>\(24k^2+48k-1152=0\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}k=6\left(nhận\right)\\k=-8\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hai số cần tìm là \(2\cdot6+1=13;2\cdot6+3=15\)
19:
a: \(A=x^2-4x+10\)
\(=x^2-4x+4+6\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)^2+6>=6>0\forall x\)
=>ĐPCM
b: \(B=2x^2-2x+3\)
\(=2\left(x^2-x+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\)
\(=2\left(x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{5}{4}\right)\)
\(=2\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{5}{2}>=\dfrac{5}{2}>0\forall x\)
=>ĐPCM
c: \(C=x^4-3x^2+5\)
\(=x^4-3x^2+\dfrac{9}{4}+\dfrac{11}{4}\)
\(=\left(x^2-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{11}{4}>=\dfrac{11}{4}>0\forall x\)
=>ĐPCM
d: \(D=\dfrac{1}{4}x^4+\dfrac{2}{5}x^2+2\)
\(=x^2\left(\dfrac{1}{4}x^2+\dfrac{2}{5}\right)+2>=2>0\forall x\)
=>ĐPCM
e: \(E=x^2+\left(x+1\right)^2\)
\(=x^2+x^2+2x+1=2x^2+2x+1\)
\(=2\left(x^2+x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=2\left(x^2+x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)\)
\(=2\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{1}{2}>=\dfrac{1}{2}>0\forall x\)
=>ĐPCM
f: \(F=\left(x-2\right)^2+\left(x-4\right)^2\)
\(=x^2-4x+4+x^2-8x+16\)
\(=2x^2-12x+20=2\left(x^2-6x+10\right)\)
\(=2\left(x^2-6x+9+1\right)=2\left[\left(x-3\right)^2+1\right]>=2\cdot1=2>0\forall x\)
g: \(G=x^2+y^2+2x-6y+11\)
\(=x^2+2x+1+y^2-6y+9+1\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)^2+\left(y-3\right)^2+1>=1>0\forall x,y\)
=>ĐPCM