
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(x^2-\sqrt{x^2-5}=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2-5}=x^2-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x^2-5}\right)^2=\left(x^2-7\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5=\left(x^2\right)^2-2.x^2.7+7^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5=x^4-14x^2+49\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^4+x^2+14x^2-5-49=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^4+15x^2-54=0\)
Đặt : \(t=x^2\left(t\ge0\right)\) , ta có :
\(-t^2+15t-54=0\)
\(\left(a=-1;b=15;c=-54\right)\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac\)
\(=15^2-4.\left(-1\right).\left(-54\right)\)
\(=225+4.\left(-54\right)\)
\(=225-216\)
\(=9>0\)
\(\sqrt{\Delta}=\sqrt{9}=3\)
\(t_1=\frac{-15+3}{2.\left(-1\right)}=6\) ( nhận )
\(t_2=\frac{-15-3}{2.\left(-1\right)}=9\) ( nhận )
Vs : \(t_1=6\Rightarrow x^2=6\Rightarrow x=\pm\sqrt{6}\)
Vs : \(t_2=9\Rightarrow x^2=9\Rightarrow x=\pm3\)
Vậy phương trình có 4 nghiệm : \(x_1=3;x_2=-3;x_3=6;x_4=-6\)
Cái đề có gì đó sai sai
\(\)

Ta có: \(\frac{x-x^2+1}{x-x^2-1}< 1\Leftrightarrow\frac{x-x^2+1}{x-x^2-1}-1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x-x^2+1}{x-x^2-1}-\frac{x-x^2-1}{x-x^2-1}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2}{x-x^2-1}< 0\Leftrightarrow x-x^2-1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x+1>0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}>0\)(đúng với mọi x)
Suy ra đpcm.

Điều kiện x \(\ge\frac{1}{4}\)
Đặt a = \(\sqrt{x-\frac{1}{4}}\)(a \(\ge0\))
=> x = a2 + \(\frac{1}{4}\)
=> PT <=> 2a2 + \(\frac{1}{2}\)+ \(\sqrt{a^2+\frac{1}{4}+a}\)= 2
<=> \(\sqrt{a^2+\frac{1}{4}+a}\)= \(\frac{3}{2}-2a\)
<=> a2 + 0,25 + a = 4a4 + 2,25 - 6a2
<=> 4a4 - 7a2 - a + 2 = 0
<=> (a + 1)(2a - 1)(2a2 - a - 2) = 0
<=> a = 0,5
<=> x = 0,5

a: \(x=\dfrac{6^2}{3}=12\left(cm\right)\)
\(y=\sqrt{6^2+12^2}=6\sqrt{5}\)
b: \(x=\sqrt{4\cdot9}=6\)
c: \(x=5\cdot\tan40^0\simeq4,2\left(cm\right)\)

\(\Leftrightarrow n^5+n^2-n^2+1⋮n^3+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-n^3+n⋮n^3+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow n=1\)

1) Vì x=25 thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ nên Thay x=25 vào biểu thức \(A=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{x+1}\), ta được:
\(A=\dfrac{\sqrt{25}-2}{25+1}=\dfrac{5-2}{25+1}=\dfrac{3}{26}\)
Vậy: Khi x=25 thì \(A=\dfrac{3}{26}\)
2) Ta có: \(B=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-3}{\sqrt{x}+1}+\dfrac{2x+8\sqrt{x}-6}{x-\sqrt{x}-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}+\dfrac{2x+8\sqrt{x}-6}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-5\sqrt{x}+6+2x+8\sqrt{x}-6}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x+3\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)

đây là bài lớp 10 chứ nhỉ
ta có \(AC=20\times2=40\text{ hải lí}\), \(AB=15\times2=30\text{ hải lí}\)
áp dụng định lý cosin ta có :
\(BC=\sqrt{AB^2+AC^2-2AB.AC\text{c}osA}=\sqrt{40^2+30^2-2\times30\times40\times cos60^o}\simeq36.06\text{ hải lí}\)
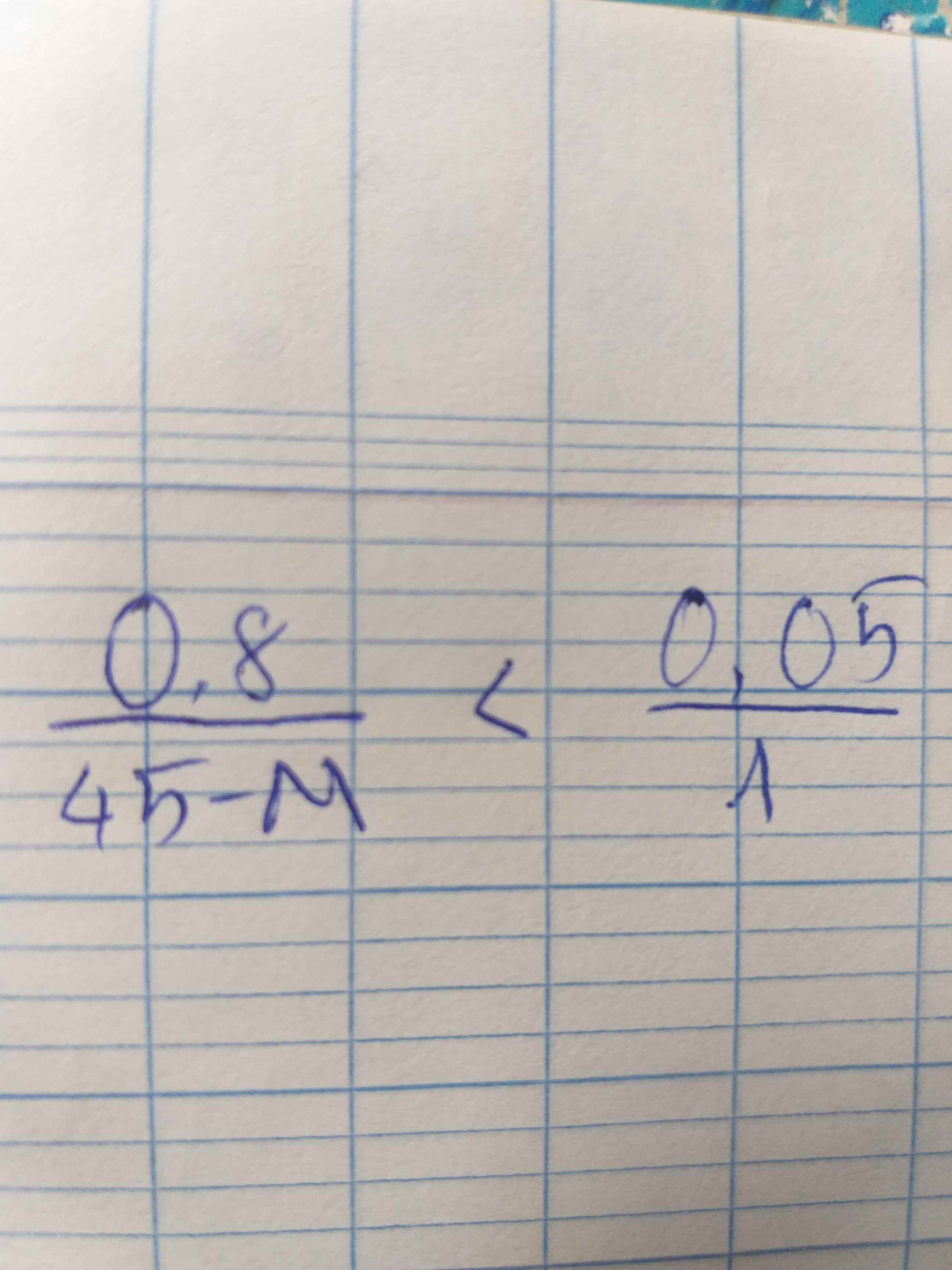

 Giải giúp mình với ạ, cần gấp lắm, cảm ơn
Giải giúp mình với ạ, cần gấp lắm, cảm ơn