Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(a,\) Bn tự vẽ
\(b,\) PT hoành độ giao điểm của \(\left(d_1\right);\left(d_2\right)\) là
\(-\dfrac{1}{2}x=\dfrac{1}{2}x+3\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-3\\ \Leftrightarrow y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(-3\right)=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Vậy tọa độ giao điểm \(\left(d_1\right);\left(d_2\right)\) là \(A\left(-3;\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\)
\(c,\) Gọi \(B\left(m;-m\right)\) là tọa độ giao điểm của \(\left(d_2\right);\left(d_3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-m=\dfrac{1}{2}m+3\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{2}m=3\\ \Leftrightarrow m=2\)
Vậy tọa độ giao điểm của \(\left(d_2\right);\left(d_3\right)\) là \(B\left(2;-2\right)\)
Khi đó \(-2=2\cdot2+b\Leftrightarrow b=-6\)

a: 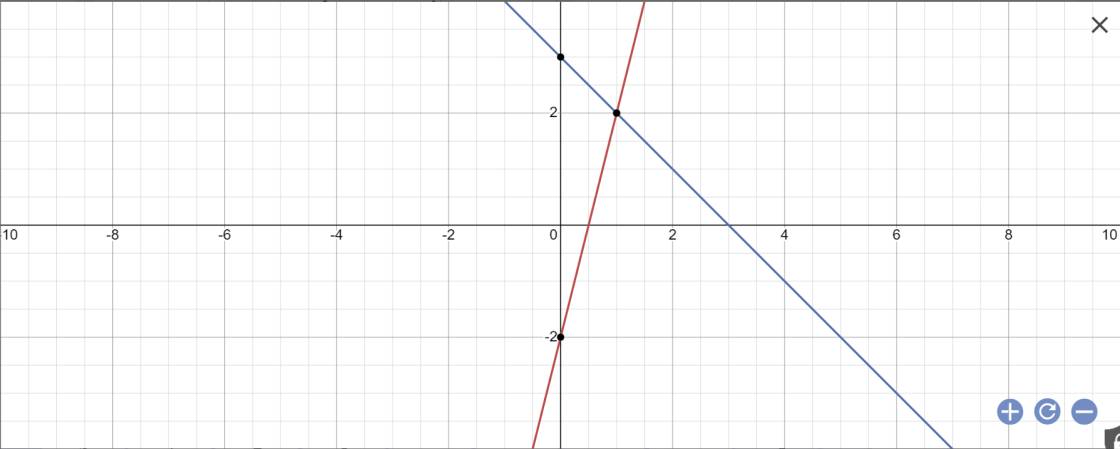
b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
4x-2=-x+3
=>4x+x=3+2
=>5x=5
=>x=1
Thay x=1 vào y=-x+3, ta được:
\(y=-1+3=2\)
Vậy: M(1;2)
c: Gọi \(\alpha;\beta\) lần lượt là góc tạo bởi (d1),(d2) với trục Ox
(d1): y=4x-2
=>\(tan\alpha=4\)
=>\(\alpha=76^0\)
(d2): y=-x+3
=>\(tan\beta=-1\)
=>\(\beta=135^0\)
d: Thay y=6 vào (d1), ta được:
4x-2=6
=>4x=8
=>x=2
=>A(2;6)
Thay x=6/2=3 vào (d2), ta được:
\(y=-3+3=0\)
vậy: B(3;0)
Vì (d):y=ax+b đi qua A(2;6) và B(3;0) nên ta có hệ phương trình:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2a+b=6\\3a+b=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2a+b-3a-b=6-0\\3a+b=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-a=6\\b=-3a\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-6\\b=-3\cdot\left(-6\right)=18\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: (d): y=-6x+18
e: A(2;6); B(3;0); M(1;2)
\(AM=\sqrt{\left(1-2\right)^2+\left(2-6\right)^2}=\sqrt{17}\)
\(BM=\sqrt{\left(1-3\right)^2+\left(2-0\right)^2}=2\sqrt{2}\)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(3-2\right)^2+\left(0-6\right)^2}=\sqrt{37}\)
Chu vi tam giác AMB là:
\(C_{AMB}=\sqrt{17}+2\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{37}\)
Xét ΔAMB có
\(cosAMB=\dfrac{MA^2+MB^2-AB^2}{2\cdot MA\cdot MB}=\dfrac{17+8-37}{2\cdot2\sqrt{2}\cdot\sqrt{17}}=\dfrac{-3}{\sqrt{34}}\)
=>\(\widehat{AMB}\simeq121^0\) và \(sinAMB=\sqrt{1-\left(-\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{34}}\right)^2}=\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{34}}\)
Xét ΔAMB có
\(\dfrac{AB}{sinAMB}=\dfrac{AM}{sinABM}=\dfrac{BM}{sinBAM}\)
=>\(\dfrac{\sqrt{17}}{sinABM}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{2}}{sinBAM}=\sqrt{37}:\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{34}}\)
=>\(sinABM\simeq0,58;\widehat{BAM}\simeq0,4\)
=>\(\widehat{ABM}\simeq35^0;\widehat{BAM}\simeq24^0\)

b, PT hoành độ giao điểm là \(\dfrac{3}{2}x-2=-2x+5\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{7}{2}x=7\Leftrightarrow x=2\Leftrightarrow y=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A\left(2;1\right)\)
Vậy A(2;1) là tọa độ giao điểm 2 đths

a:
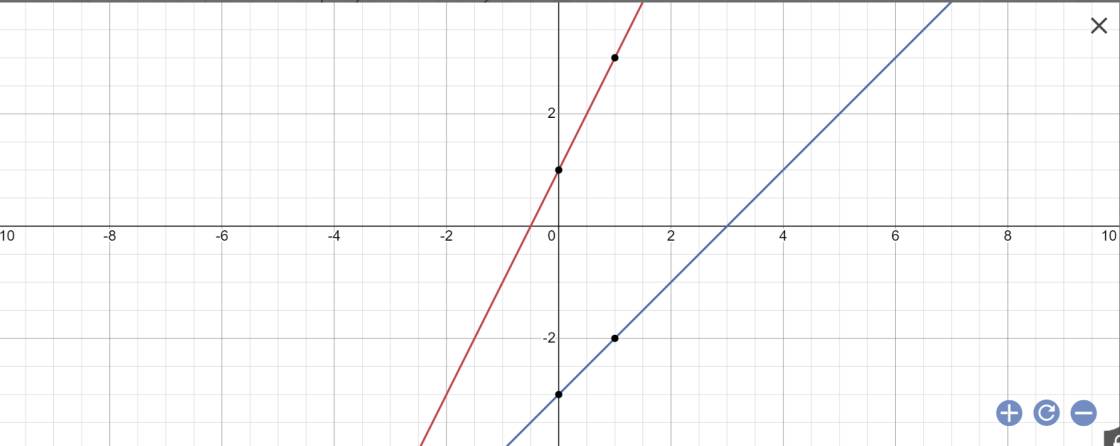
b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(2x+1=x-3\)
=>\(2x-x=-3-1\)
=>x=-4
Thay x=-4 vào y=x-3, ta được:
\(y=-4-3=-7\)
Vậy: Tọa độ giao điểm của (D1) và (D2) là B(-4;-7)
c: Đặt phương trình đường thẳng (d3): y=ax+b
Vì (d3)//(d1) nên \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2\\b< >1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: y=2x+b
Thay x=1 và y=0 vào y=2x+b, ta được:
\(b+2\cdot1=0\)
=>b+2=0
=>b=-2
Vậy: (d): y=2x-2

a: 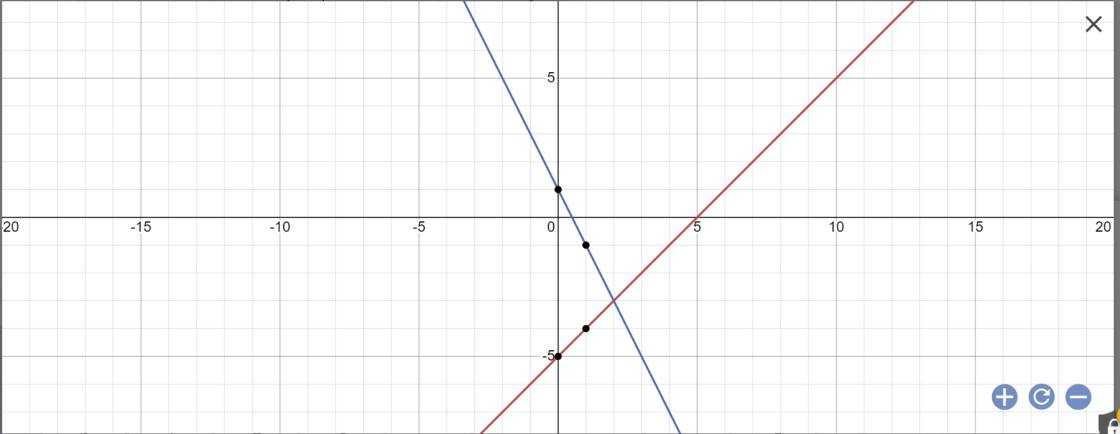
b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
-2x+1=x-5
=>-2x-x=-5-1
=>-3x=-6
=>x=2
Thay x=2 vào y=x-5, ta được:
\(y=2-5=-3\)
Vậy: (d1) cắt (d2) tại A(2;-3)
c: (d1): y=x-5
=>x-y-5=0
Khoảng cách từ O(0;0) đến (d1) là:
\(d\left(O;\left(d1\right)\right)=\dfrac{\left|0\cdot1+0\cdot\left(-1\right)-5\right|}{\sqrt{1^2+\left(-1\right)^2}}=\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{2}}\)
(d2): y=-2x+1
=>y+2x-1=0
=>2x+y-1=0
Khoảng cách từ O đến (d2) là:
\(d\left(O;\left(d2\right)\right)=\dfrac{\left|0\cdot2+0\cdot1-1\right|}{\sqrt{2^2+1^2}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\)

a: 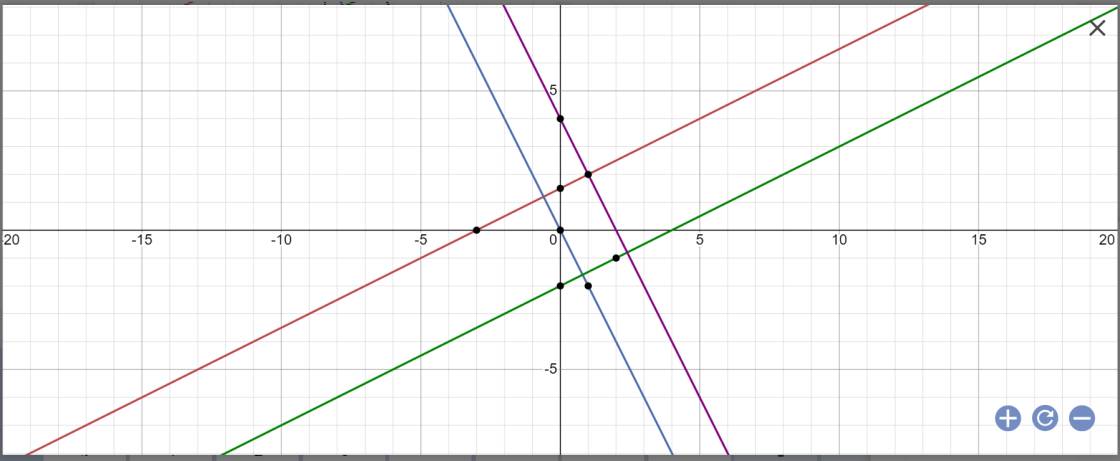
b: (d1): y=1/2x+3/2; (d2): y=-2x; (d3): y=1/2x-2; (d4): y=-2x+4
=>(d1) vuông góc (d2), (d1) vuông góc (d4); (d2) vuông góc (d3); (d2)//(d4)
=>ABCD là hình chữ nhật
=>A(-3/5;6/5); B(2/5;16/5); C(4/5;-8/5); D(12/5;-4/5)

b: Tọa độ giao điểm là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x=-2x+5\\y=3x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(b,\) Tọa độ giao điểm 2 đường thẳng là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-2x+4\\y=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1=-2x+4\\y=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow A\left(1;2\right)\)
Tọa độ giao điểm 2 đường thẳng với trục hoành là
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=-2x+4\\y=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}4-2x=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow B\left(2;0\right),C\left(-1;0\right)\)
\(b,\) PT hoành độ giao điểm: \(-2x+5=x+2\Leftrightarrow x=1\Leftrightarrow y=3\Leftrightarrow M\left(1;3\right)\)