
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



a) \(\dfrac{13}{20}+\dfrac{3}{5}+x=\dfrac{5}{6}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{5}{4}+x=\dfrac{5}{6}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{6}-\dfrac{5}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-5}{12}\)
b) \(x+\dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{2}{5}-\dfrac{-1}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow x+\dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{11}{15}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{11}{15}-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2}{5}\)
c)\(\dfrac{-5}{8}-x=\dfrac{-3}{20}-\dfrac{-1}{6}\)
\(\dfrac{-5}{8}-x=\dfrac{1}{60}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-5}{8}-\dfrac{1}{60}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-77}{120}\)
d) \(\dfrac{3}{5}-x=\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{7}{10}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{3}{5}-x=\dfrac{19}{20}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{5}-\dfrac{19}{20}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-7}{20}\)
e) \(\dfrac{-3}{7}-x=\dfrac{4}{5}+\dfrac{-2}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{-3}{7}-x=\dfrac{2}{15}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-3}{7}-\dfrac{2}{15}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-59}{105}\)
g) \(\dfrac{-5}{6}-x=\dfrac{7}{12}+\dfrac{-1}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{-5}{6}-x=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-5}{6}-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-13}{12}\)

a) \(\dfrac{x}{5}=\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow5x=10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Vậy x = 2
b) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne0\)
\(\dfrac{3}{-8}=\dfrac{6}{-x}\)
\(\Rightarrow-3x=-48\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=16\)
Vậy x = 16
c) \(\dfrac{1}{9}=\dfrac{-2x}{10}\)
\(\Rightarrow-18x=10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{5}{9}\)
Vậy \(x=-\dfrac{5}{9}\)
d) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne0\)
\(\dfrac{3}{x}-5=\dfrac{-9}{x}+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3-5x}{x}=\dfrac{-9+2x}{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow3-5x=-9+2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7x=12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{12}{7}\)
Vậy \(x=\dfrac{12}{7}\)
e) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne0\)
\(\dfrac{x}{-2}=\dfrac{-8}{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\pm4\)
Vậy \(x=\pm4\)
a) Ta có: \(\dfrac{x}{5}=\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{2\cdot5}{5}=2\)
Vậy: x=2
b) Ta có: \(\dfrac{3}{-8}=\dfrac{6}{-x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x=\dfrac{6\cdot\left(-8\right)}{3}=-16\)
hay x=16
Vậy: x=16

a) \(\dfrac{1}{2}-\left(x+\dfrac{1}{3}\right)=\dfrac{5}{6}\)
\(\Rightarrow x+\dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{5}{6}\)
\(\Rightarrow x+\dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{-1}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-1}{3}-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-2}{3}\)
b)\(\dfrac{3}{4}-\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=\dfrac{4}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow x+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{3}{4}-\dfrac{4}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow x+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{-1}{20}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-1}{20}-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-11}{20}\)
c) \(\dfrac{3}{35}-\left(\dfrac{3}{5}+x\right)=\dfrac{2}{7}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{3}{5}+x=\dfrac{3}{35}-\dfrac{2}{7}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{3}{5}+x=\dfrac{-1}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-1}{5}-\dfrac{3}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-4}{5}\)
d)\(\dfrac{2}{3}.x=\dfrac{4}{27}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4}{27}:\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2}{9}\)
e) \(\dfrac{-3}{5}.x=\dfrac{21}{10}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{21}{10}:\dfrac{-3}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-7}{2}\)

a, 3/x=5/6-y/3=5/6-2y/6=5-2y/6
Do đó: x(5-2y)=18=2.3^2
Do x và y là các số nguyên nên 5-2y là ước của 18, mặt khác 5-2y là số lẻ. Ưowcs lẻ của 18 là :1,-1,3,-3,9,-9. Ta có:
| 5-2y | 1 | -1 | 3 | -3 | 9 | -9 |
| 2y | 4 | 6 | 2 | 8 | -4 | 14 |
| y | 2 | 3 | 1 | 4 | -2 | 7 |
| x | 18 | -18 | 6 | -6 | 2 | -2 |
Có 6 cặp số x, y ở bảng trên thõa mãn bài toán

Hai bài bị trùng nhau nên các bạn nhìn ảnh hay văn bản đều như nhau ạ
c: =>x+2>0
hay x>-2
d: =>-4<=x<=3
e: =>\(x\in\varnothing\)
f: \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>4\\x< -6\end{matrix}\right.\)

A. x = 2
B. \(\dfrac{3}{8}=\dfrac{6}{x}\)\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{6.8}{3}=16\)
C. x = 3
D. \(x=\dfrac{4.6}{8}=3\)
E. \(x=\dfrac{7}{3}\)
G.\(\dfrac{14}{13}=\dfrac{28}{10-x}\)
<=>\(14\left(10-x\right)=364\)
<=> 10 - x = 26
<=> x = -16
H. \(3\left(x+2\right)=4\left(x-5\right)\)
<=> 3x + 6 = 4x - 20
<=> -x = -26
<=> x = 26
K. \(\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{8}{x}\)
<=> \(x^2=16\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
M. \(\left(x-2\right)^2=100\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=10\\x-2=-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=12\\x=-8\end{matrix}\right.\)
a=2
b=16
c=3
d=3
mik chỉ biết thế này thôi(ko chắc đúng=3)

đặt A = 2/2 + 2/6 + 2/12 + .... + 2/ x(x+1)
A = 2 . ( 1/2 + 1/6 + 1/12 + ...+ 1/x(x+1) )
A = 2 . ( 1/ 1.2 + 1/2.3 + .......+ 1/ x(x+1) )
A = 2 . ( 1 - 1/2 + 1/2 - 1/3 + ....+ 1/x - 1/x+1 )
A = 2 . ( 1 - 1/x+1) = 2 . x / x+1 = 2x/ x+1
thay A vào đề bài ta có
2x/x+1 = 8/5 => 2x . 5 = 8 . (x+1)
<=> 10x = 8x+8
<=> 10x -8x = 8 => 2x = 8 => x=4
vậy x = 4 ( cách làm là vậy đó ko biết có đúng ko, ủng hộ mik nha)

a) 2/5 < x < 6/5
=> x = 1 ( =5/5 ) (vì x thuộc Z)
Vậy x = 1
b) 3/5 < 3/x < 3/2
=> 5 > x > 2
=> x thuộc { 4 ; 3 } (vì x thuộc Z)
Vậy ...
c) 3/8 + -11/8 < x < 22/9 + 5/18
=> -8/8 < x < 49/18
=>-1 < x < 2+13/18
=> x thuộc {0; 1; 2} ( vì x thuộc Z )
Vậy...

Bài 1:
a: x/-2=-18/x
=>x2=36
=>x=6 hoặc x=-6
b: x/2+x/5=17/10
=>7/10x=17/10
hay x=17/7
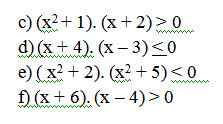 Giúp mình với, mình cần gấp ạ
Giúp mình với, mình cần gấp ạ
\(-\frac{1}{5}\)\(+\)\(\frac{2}{5}\)\(\div x\)\(=\)\(|-6|\)
\(-\frac{1}{5}\)\(+\)\(\frac{2}{5}\)\(\div x\)\(=\)\(6\)
\(\frac{2}{5}\)\(\div x\)\(=\)\(6\)\(-\)\(-\frac{1}{5}\)
\(\frac{2}{5}\)\(\div x\)\(=\)\(6\)\(+\)\(\frac{1}{5}\)
\(\frac{2}{5}\)\(\div x\)\(=\)\(\frac{31}{5}\)
\(x=\)\(\frac{2}{5}\)\(\div\)\(\frac{31}{5}\)
\(x=\)\(\frac{2}{5}\)\(\times\)\(\frac{5}{31}\)
\(x=\)\(\frac{2}{31}\)
\(-\frac{1}{5}+\frac{2}{5}:x=\left|-6\right|\)
\(-\frac{1}{5}+\frac{2}{5x}=6\)
\(\frac{2}{5x}=\frac{31}{5}\)
\(5x=\frac{10}{31}\)
\(x=\frac{2}{31}\)