Tìm x, y thỏa mãn: x2+2x2y2+2y2-(x2y2+2x2)-2=0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bạn vui lòng viết đề đầy đủ, và gõ bằng công thức toán để được hỗ trợ tốt hơn.

\(x^2+2x^2y^2+2y^2-\left(x^2y^2+2x^2\right)-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x^2y^2+2y^2-x^2y^2-2x^2-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2y^2-x^2+2y^2-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2y^2-x^2\right)+\left(2y^2-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(y^2-1\right)+2\left(y^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+2\right)\left(y^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+2\right)\left(y-1\right)\left(y+1\right)=0\)
Dễ thấy: \(x^2+2\ge2>0\forall x\) (vô nghiệm)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}y-1=0\\y+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=1\\y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)

Lời giải:
$x^2+2y^2+x^2y^2-10xy+16=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x^2+y^2-2xy)+(x^2y^2-8xy+16)+y^2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-y)^2+(xy-4)^2+y^2=0$
Vì $(x-y)^2\geq 0; (xy-4)^2\geq 0; y^2\geq 0$ với mọi $x,y$
$\Rightarrow$ để tổng của chúng bằng $0$ thì:
$(x-y)^2=(xy-4)^2=y^2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=y=0$ và $xy=4$ (vô lý)
Vậy không tồn tại $x,y$ thỏa mãn đề nên cũng không tồn tại $T$.

\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^3+2y^2-4y+3=0\\2x^2+2x^2y^2-4y=0\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow}x^3+2y^2-4y-2x^2-2x^2y^2+4y=0\Rightarrow x^3+1-2x^2y^2+2y^2-2x^2+2=0\Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)-2y^2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)-2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1-2xy^2+2y^2-2x+2\right)=0\Rightarrow x=-1\)Thay x=-1 vào (1) ta được y2-2y+1=0⇒ (y-1)2=0⇒y-1=0⇒y=1
Do đó Q=x2+y2=(-1)2+12=2

\(x^2y^2-x^2-3y^2-2x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y^2\left(x^2-3\right)-\left(x+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y^2\left(x^2-3\right)=\left(x+1\right)^2\left(1\right)\)
Vì y2 và (x+1)2 đều là các số chính phương, do đó x2-3 cũng phải là số chính phương.
Đặt \(x^2-3=a^2\) (a là số tự nhiên).
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-a\right)\left(x+a\right)=3\)
Ta có x+a>x-a. Lập bảng:
| x+a | 3 | -1 |
| x-a | 1 | -3 |
| x | 2 | -2 |
Với \(x=2\) . \(\left(1\right)\Rightarrow y^2=9\Leftrightarrow y=\pm3\)
Với \(x=-2\). \(\left(1\right)\Rightarrow y^2=1\Leftrightarrow y=\pm1\)
Vậy các số nguyên \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(2;3\right),\left(2;-3\right),\left(-2;1\right),\left(-2;-1\right)\)

Ta có: \(2x^2+xy+2y^2=\dfrac{3}{2}\left(x^2+y^2\right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left(x^2+2xy+y^2\right)=\dfrac{3}{2}\left(x^2+y^2\right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left(x+y\right)^2\)
Theo BĐT Bunhacopxky: \(\left(x^2+y^2\right)\left(1+1\right)\ge\left(x+y\right)^2\Rightarrow\dfrac{3}{2}\left(x^2+y^2\right)\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\left(x+y\right)^2\\ \Rightarrow2x^2+xy+2y^2=\dfrac{3}{2}\left(x^2+y^2\right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left(x+y\right)^2\ge\dfrac{5}{4}\left(x+y\right)^2\\ \Rightarrow\sqrt{2x^2+xy+2y^2}\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\left(x+y\right)\)
Chứng minh tương tự:
\(\sqrt{2y^2+yz+2z^2}\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\left(y+z\right)\\ \sqrt{2z^2+xz+2x^2}\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\left(x+z\right)\)
Cộng vế theo vế, ta được: \(P\ge\sqrt{5}\left(x+y+z\right)=\sqrt{5}\cdot1=\sqrt{5}\)
Dấu "=" \(\Leftrightarrow x=y=z=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Bạn tham khảo nhé
https://hoc24.vn/cau-hoi/cho-cac-so-duong-xyz-thoa-man-xyz1cmrcan2x2xy2y2can2y2yz2z2can2z2zx2x2can5.182722154737

\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-1=2y^2\)
Do vế phải chẵn \(\Rightarrow\) vế trái chẵn \(\Leftrightarrow x\) lẻ
\(\Rightarrow x=2k+1\)
Pt trở thành: \(\left(2k+1\right)^2-1=2y^2\Leftrightarrow2\left(k^2+k\right)=y^2\)
Vế trái chẵn \(\Rightarrow\) vế phải chẵn \(\Rightarrow y^2\) chẵn \(\Rightarrow y\) chẵn
\(\Rightarrow y=2\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-9=0\Rightarrow x=3\)
Vậy \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(3;2\right)\)

Áp dụng Bunyakovsky, ta có :
\(\left(1+1\right)\left(x^2+y^2\right)\ge\left(x.1+y.1\right)^2=1\)
=> \(\left(x^2+y^2\right)\ge\frac{1}{2}\)
=> \(Min_C=\frac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow x=y=\frac{1}{2}\)
Mấy cái kia tương tự
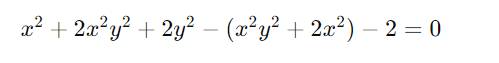
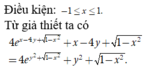
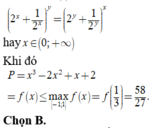
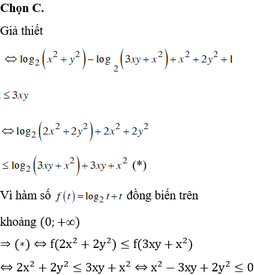
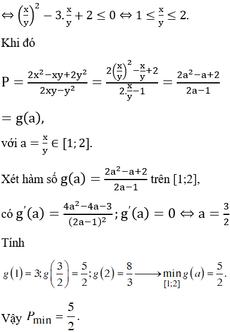
<=> x2 + 2x2y2 + 2y2 - (x2y2 + 2x2) - 2 = 0
<=> x2 + 2x2y2 + 2y2 - x2y2 - 2x2 - 2 = 0
<=> -x2 + x2y2 + 2y2 - 2 = 0
<=> x2 (y2 - 1) + 2 (y2 - 1) = 0
<=> (x2 + 2)(y2 - 1) = 0
Vì x2 + 2 > 0 với mọi x => y2 - 1 = 0 <=> y = ± 1.
Vậy x \(\in\)R, y = ± 1.
_Kik nha!! ^ ^
<=>x2+2x2+2y2-x2y2-2x2-2=0
<=>-x2+x2y2+2y2-2=0
<=>x2(y2-1)+2(y2-1)=0
<=>(x2+2)(y2-1)=0
Vì x2+2>0 với mọi x=>y2-1=0<=>y=1 hoặc (-1)
Vậy x thuộc R,Y = 1 hoặc (-1