Tính tập xác định D của hàm số \(y=\sqrt{4-\log^2_2x}\).
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a, Điều kiện: \(2^x\ne3\Rightarrow x\ne log_23\)
Vậy D = R \ \(log_23\)
b, Điều kiện: \(25-5^x\ge0\Rightarrow5^x\le5^2\Rightarrow x\le2\)
Vậy D = \((-\infty;2]\)
c, Điều kiện: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\lnx\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\x\ne e\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy D = \(\left(0;+\infty\right)\backslash\left\{e\right\}\)
d, Điều kiện: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\1-log_3x\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\log_3x\le1\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\x\le3\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow0< x\le3\)
Vậy D = \((0;3]\)

Chọn B
Xét hàm số y = -log(2x- x 2 )
Điều kiện xác định 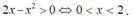
Tập xác định D = (0;2)

Vì \(\dfrac{1}{e}\simeq0,368< 1\)
\(\Rightarrow y=log_{\dfrac{1}{e}}\left(x\right)\) nghịch biến trên D = \(\left(0;+\infty\right)\)
Chọn C.
0<1/e<1
=>\(log_{\dfrac{1}{e}}\left(x\right)\) nghịch biến
=>C

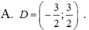
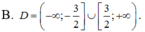
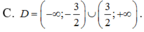
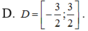
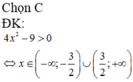

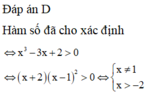

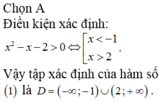
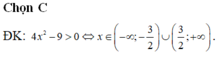
ĐKXĐ: \(4-log_2^2x>=0\)
=>\(log_2^2x< =4\)
=>\(-2< =log_2x< =2\)
=>\(-\dfrac{1}{4}< =x< =4\)