giải phương trình
/x-3/ = 9-2x
2x2-x=3-6x
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Lần sao bạn ấn vào Latex để gõ các công thức như thế nào để câu hỏi được rõ hơn nha. Kí hiệu \(\sum\) ở trên thanh công cụ nhé.
Giải:
ĐKXĐ: \(3-2x\ge0\Leftrightarrow3\ge2x\Leftrightarrow x\le\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\sqrt{x^2-6x+9}=3-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+9=\left(3-2x\right)^2\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+9=9-12x+4x^2\\ \Leftrightarrow3x^2-6x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow3x\left(x-2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(tm\right)\\x=2\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy x = 0

\(\sqrt{x^{ }2-6x+9}=4-x\)
\(\sqrt{\left(x-3\right)^{ }2}=4-x\)
x-3=4-x
x+x=4+3
2x=7
x=\(\dfrac{7}{2}\)
Lời giải:
a.
PT \(\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} 4-x\geq 0\\ x^2-6x+9=(4-x)^2=x^2-8x+16\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} x\leq 4\\ 2x=7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{7}{2}\)
b.
ĐKXĐ: $x\geq \frac{3}{2}$
PT \(\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{(2x-3)+2\sqrt{2x-3}+1}+\sqrt{(2x-3)+8\sqrt{2x-3}+16}=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{(\sqrt{2x-3}+1)^2}+\sqrt{(\sqrt{2x-3}+4)^2}=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow |\sqrt{2x-3}+1|+|\sqrt{2x-3}+4|=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{2x-3}+1+\sqrt{2x-3}+4=2\sqrt{2x-3}+5=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{2x-3}=0\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{3}{2}\)

\(2x^2-6x-3=0\)
\(\Delta'=3^2+3.2=15>0\)
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt.
Theo hệ thức viét có : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=3\\x_1x_2=-\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có : \(A=x_1^2x_2^2-2x_1-2x_2=\left(x_1x_2\right)^2-2\left(x_1+x_2\right)=\left(-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2-2.3=-\dfrac{15}{4}\)
Vậy \(A=-\dfrac{15}{4}\) thì thỏa mãn điều kiện bài ra.

\(pt\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x^4-9\right)+\left(x^3-3x\right)}+\sqrt{\left(x^4-9\right)+\left(2x^3-6x\right)}+\sqrt{x^2-3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x^2-3\right)\left(x^2+x+3\right)}+\sqrt{\left(x^2-3\right)\left(x^2+2x+3\right)}+\sqrt{x^2-3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2-3}\left(\sqrt{x^2+x+3}+\sqrt{x^2+2x+3}+1\right)=0\)
\(\text{Nếu }x=\pm\sqrt{3}\Rightarrow\text{thỏa mãn còn lại thì thừa số số 2}>0\text{ nên không thỏa}\)

\(a)x^2-9x+20=0 \\<=>(x-4)(x-5)=0 \\<=>x=4\ hoặc\ x=5 \\b)x^2-3x-18=0 \\<=>(x+3)(x-6)=0 \\<=>x=-3\ hoặc\ x=6 \\c)2x^2-9x+9=0 \\<=>(x-3)(2x-3)=0 \\<=>x=3\ hoặc\ x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
d: \(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-6x-2x+4=0\)
=>(x-2)(3x-2)=0
=>x=2 hoặc x=2/3
e: \(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x^2-2x-3\right)=0\)
=>x(x-3)(x+1)=0
hay \(x\in\left\{0;3;-1\right\}\)
f: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x-2+x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=6\)
hay \(x\in\left\{\sqrt{6}+2;-\sqrt{6}+2\right\}\)

ĐKXĐ: x ≠ - 1;x ≠ 3.
Ta có: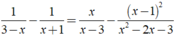
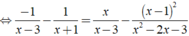
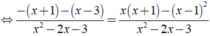
![]()
⇔ -2x + 2 = 3x - 1
⇔ 5x = 3 ⇔ x = 3/5.
Kết hợp điều kiện, vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm là x = 3/5.

/x-3/=9-2x
= (1) x-3 = 9-2x
= 3x=12
x=4
(2) x+3= 9-2x
= 3x= 6
x=2
/x-3/=9-2x