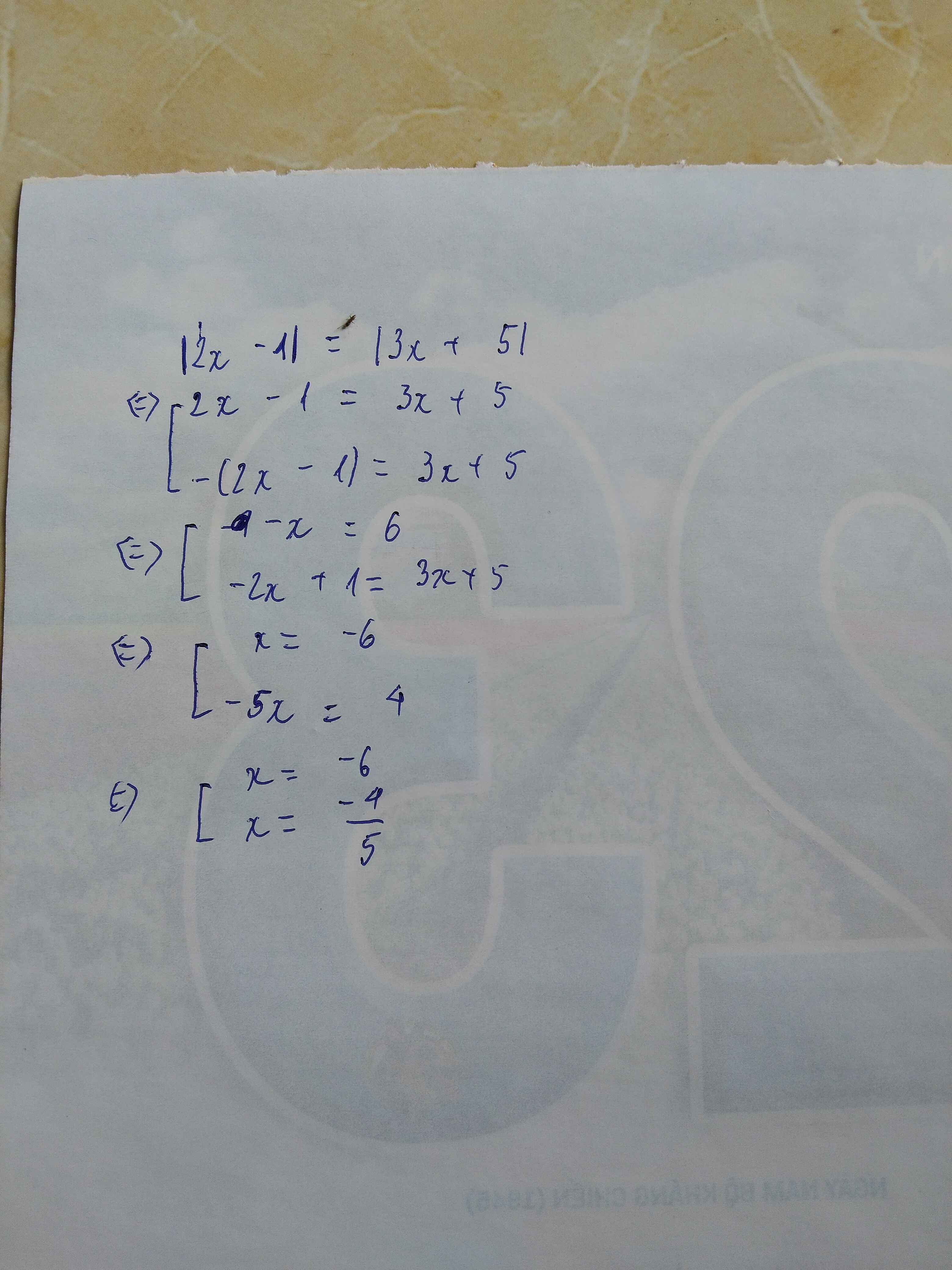Giải phương trình l2x-1l+l2x-5l=4
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a, \(\left|2x-5\right|=4\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x-5=4\\2x-5=-4\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}2x=9\\2x=1\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{9}{2}\\x=\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}}\)
b, \(\left|2x-3\right|-\left|3x+2\right|=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|2x-3\right|=\left|3x+2\right|\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x-3=3x+2\\2x-3=-3x-2\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}-x=5\\5x=1\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-5\\x=\frac{1}{5}\end{cases}}\)
c, \(\left|x+3\right|-\left|3x+2\right|=x+2\)
Ta có: x + 3 = 0 => x = -3
3x + 2 = 0 => x = -2/3
Lập bảng xét dấu:
x x + 3 3x + 2 -2 3 -3 0 0 - + + - - +
Với x < -3
Ta có: -x - 3 + 3x + 2 = x + 2
<=> 2x - 1 = x + 2
<=> x = 3 ( ko t/mãn )
Với -3 ≤ x < -2/3
Ta có: x + 3 + 3x + 2 = x + 2
<=> 4x + 5 = x + 2
<=> 3x = -3
<=> x = -1 ( t/mãn )
Với -2/3 ≤ x
Ta có: x + 3 - 3x - 2 = x + 2
<=> -2x + 1 = x + 2
<=> -3x = 1
<=> x = -1/3 ( t/mãn )
Vậy....
d, \(\left||x-1|-5\right|=x+5\)
Đk: x + 5 ≥ 0 => x ≥ -5
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\left|x-1\right|-5=x+5\\\left|x-1\right|-5=-x-5\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\left|x-1\right|=x+25\\\left|x-1\right|=-x\left(Loai\right)\end{cases}}}\)
Giải \(\left|x-1\right|=x+25\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=-x-25\\x-1=x+25\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x=-24\\0x=26\left(Loai\right)\end{cases}\Rightarrow x}=-12}\)( ko t/mãn )
Vậy x \(\in\varnothing\)

b) |2x - 6| + |x + 2| = 8
1)Với \(x< -2\) ta được: -(2x - 6) + [-(x + 2)] = 8 => -2x + 6 - x - 2 = 8 => -3x = 8 + 2 -6 = 4 => x = \(\frac{-4}{3}\)(loại vì \(\frac{-4}{3}>-2\))
2)Với \(-2\le x< 3\)ta được: (2x - 6) + [-(x + 2)] => 2x - 6 - x - 2 = 8 => x = 8 + 6 +2 => x = 16 (loại vì 16 > 3)
3)Với \(x\ge3\) ta được: (2x - 6) + (x + 2) = 8 => 2x - 6 + x + 2 = 8 => 3x = 8 + 6 - 2 = 12 => x = 4(chọn)
Vậy x = 4
c) |2x - 1| + |2x - 5| = 4
1)Với \(x\le0,5\)ta được: -(2x - 1) + [-(2x - 5)] = 4 => -2x + 1 - 2x + 5 = 4 => -4x = 4 - 1 - 5 => -4x = -2 => x = \(0,5\)(loại)
2)Với \(0,5< x< 2,5\) ta được: 2x - 1 + [-(2x - 5)] = 4 => 2x -1 - 2x + 5 = 4 => 0x = 4 +1 -5 => 0x = 0 => x\(\in R\)
3)Với \(x\ge2,5\)ta được: 2x - 1 + 2x - 5 = 4 => 4x = 4 + 1 + 5 => 4x = 10 => x = \(2,5\) (chọn)
Vậy x = 0,5 hoặc x = 2,5
d) |x + 5| + |x + 3| = 9
1)Với \(x< -5\)ta được: -(x + 5) + [-(x + 3)] = 9 => -x - 5 - x - 3 = 9 => -2x = 9 + 5 + 3 => -2x = 17 => x = -8,5(chọn)
2)Với \(-5\le x< -3\) ta được: x + 5 + [-(x + 3)] = 9 => x + 5 -x - 3 = 9 => 0x = 9 - 5 + 3 => 0x = 7(vô lý)
3)Với \(x\le-3\)ta được: x + 5 + x + 3 = 9 => 2x = 9 - 5 - 3 => 2x = 1 => x = 0,5(chọn)
Vậy x = -8,5 hoặc x = 0,5
a) 7x - |2x - 4| = 3x + 12 => 7x - (2x - 4) = 3x + 12 khi (2x + 4)\(\ge\)0 => x\(\ge\)-0,5 hoặc 7x - [-(2x - 4)] = 3x + 12 khi (2x + 4) < 0 => x < -0,5
1)Với x \(\ge\)-0,5 thì 7x - (2x - 4) = 3x +12 => 7x - 2x + 4 = 3x + 12 => 7x -2x -3x = -4 +12 => 2x = 8 => x = 4(chọn vì 4 > -0,5)
2)Với x < -0,5 thì 7x - [-(2x - 4)] = 3x +12 => 7x + 2x - 4 = 3x + 12 => 7x +2x - 3x = 4 + 12 => 6x = 16 => x = \(\frac{8}{3}\)(loại vì \(\frac{8}{3}\)> -0,5 )
Vậy x = 4

\(a)\left|2x-5\right|=4\)\(\Rightarrow2x-5=\pm4\)
\(Với\)\(2x-5=4\Rightarrow2x=9\Rightarrow x=\frac{9}{2}\)
\(Với\)\(2x-5=-4\Rightarrow2x=1\Rightarrow x=\frac{1}{2}\)
\(Vậy\)\(x=\frac{9}{2};x=\frac{1}{2}\)
\(b)\left|2x-3\right|-\left|3x+2\right|=0\)
\(Vì\)\(\left|2x-3\right|\ge0;\left|3x+2\right|\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2x-3=0\\3x+2=0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2x=3\\3x=-2\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{3}{2}\\x=\frac{-2}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
\(Vậy\)\(x=\frac{3}{2};x=\frac{-2}{3}\)

\(\left|2x-1\right|=\left|3x+5\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=3x+5\\2x-1=-3x-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-6\\x=-\dfrac{4}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(1,|5x|=x-12\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}5x=x-12\\5x=12-x\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}4x=-12\\6x=12\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-3\\x=2\end{cases}}}\)
\(2,|7-x|=5x+1\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}7-x=5x+1\\7-x=-5x-1\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}6x=6\\4x=-8\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=-2\end{cases}}\)
\(3,|2x-3|+x=21\)
\(\Rightarrow|2x-3|=21-x\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x-3=21-x\\2x-3=x-21\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}3x=24\\x=-18\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x=8\\x=-18\end{cases}}\)
\(4,|4+2x|=-4x\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}4+2x=4x\\4+2x=-4x\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}2x=4\\-6x=4\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=-\frac{2}{3}\end{cases}}\)
\(5,|3x-1|+2=x\)
\(\Rightarrow|3x-1|=x-2\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x-1=x-2\\3x-1=2-x\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x=-1\\4x=3\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{1}{2}\\x=\frac{3}{4}\end{cases}}}\)
\(6,|2x-5|+x=2\)
\(\Rightarrow|2x-5|=2-x\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x-5=2-x\\2x-5=x-2\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x=7\\x=3\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{7}{3}\\x=3\end{cases}}}\)

1: |1-5x|-1=3
=>|5x-1|=4
=>5x-1=4 hoặc 5x-1=-4
=>5x=5 hoặc 5x=-3
=>x=1 hoặc x=-3/5
2: 4|2x-1|+3=15
=>4|2x-1|=12
=>|2x-1|=3
=>2x-1=3 hoặc 2x-1=-3
=>x=2 hoặc x=-1
3,\(\left|x+4\right|=2x+1\)
TH1: x+4≥0⇔x≥-4,pt có dạng:
x+4=2x+1⇔-x=-3⇔x=3(t/m)
TH2:x+4<0⇔x<-4,pt có dạng:
-x-4=2x+1⇔-3x=5⇔x=\(\dfrac{-5}{3}\)(loại)
Vậy pt đã cho có tập nghiệm S=\(\left\{3\right\}\)
4,\(\left|3x+4\right|=x-3\)
TH1: 3x-4≥0⇔3x≥4⇔x≥\(\dfrac{4}{3}\),pt có dạng:
3x-4=x-3⇔2x=1⇔x=\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)(loại)
TH2: 3x-4<0⇔3x<4⇔x<\(\dfrac{4}{3}\),pt có dạng:
-3x+4=x-3⇔-4x=-7 ⇔x=1,75(loại)
Vậy pt đã cho vô nghiệm

Lời giải:
a. $|2x+1|=|x-1|$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x+1=x-1$ hoặc $2x+1=1-x$
$\Leftrightarrow x=-2$ hoặc $x=0$
b.
$|2x+1|=|5x-2|$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x+1=5x-2$ hoặc $2x+1=2-5x$
$\Leftrightarrow x=1$ hoặc $x=\frac{1}{7}$
Thay vào đẳng thức xem $|2x+1|=3$ không thì ta thấy $x=1$ thỏa mãn.

\(\left|2x-1\right|=\left|2x+3\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x-1\right|^2=\left|2x+3\right|^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)^2=\left(2x+3\right)^2\) (\(\left|a\right|^2=a^2\) )
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2a-1\right)^2-\left(2a+3\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2a-1-2a-3\right)\left(2a-1+2a+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4\left(4a+2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-\frac{1}{2}\)
Vậy ............

|2x-1| = |2x-3|
<=> \(\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}2x-1=2x+3\\2x-1=-2x-3\end{array}\right.\)
<=> \(\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}0x=4\left(vl\right)\\4x=-2\end{array}\right.\)
<=> \(x=-\frac{1}{2}\)
tao thu may ma may tra loi ngu qua thieu 2th la -2x+1=2x+3
-2x+1=-2x-3