Giải phương trình \(x^4-4x^3+8x-5=0\)
giúp mik với
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\left(x^3-x^2\right)-4x^2+8x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-x^2-4x^2+8x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-5x^2+8x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-x^2-4x^2+4x+4x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)-4x\left(x-1\right)+4\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-4x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\\left(x-2\right)^2=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x-2=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=2\end{cases}}\)
Vậy ...
\(\left(x^3-x^2\right)-4x^2+8x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-x^2-4x^2+8x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-x^2-4x^2+4x+4x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^3-x^2\right)-\left(4x^2+4x\right)+\left(4x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)-4x\left(x-1\right)+4\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-4x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\x-2=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=2\end{cases}}}\)

a,\(6x^2+x-5=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac=1^2-4.6.\left(-5\right)=1+120=121\)
Vì \(\Delta>0\)nên pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
\(x_1=\frac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\frac{-1-\sqrt{121}}{2.6}=\frac{-1-11}{12}=\frac{-12}{12}=-1\)
\(x_2=\frac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\frac{-1+\sqrt{121}}{2.6}=\frac{-1+11}{12}=\frac{10}{12}=\frac{5}{6}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{-1;\frac{5}{6}\right\}\)
b, \(3x^2+4x+2=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac=4^2-4.3.2=16-24=-8\)
Vì \(\Delta< 0\)nên pt vô nghiệm
c, \(x^2-8x+16=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac=\left(-8\right)^2-4.1.16=64-64=0\)
Vì \(\Delta=0\)nên pt có nghiệm kép
\(x_1=x_2=\frac{-b}{2a}=\frac{-b'}{a}=\frac{8}{4}=\frac{4}{2}=2\)
a) \(6x^2+x-5=0\)
Ta có : \(\Delta=1+4.6.5=121>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{\Delta}=11\)
Phương trình có hai nghiệm :
\(x_1=\frac{-1+11}{2.6}=\frac{5}{6}\)
\(x_2=\frac{-1-11}{2.6}=-1\)
b) \(3x^2+4x+2=0\)
Ta có : \(\Delta=4^2-4.3.2=-8< 0\)
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm
c) \(x^2-8x+16=0\)
Ta có : \(\Delta=\left(-8\right)^2-4.1.16=0\)
Phương trình có nghiệm kép :
\(x_1=x_2=\frac{8}{2}=-4\)

\(a,x+\frac{4}{5}-x+4=\frac{x}{3}-x-1\)
\(x+\frac{24}{5}-x=\frac{x}{3}-x-1\)
\(x+\frac{24}{5}-x-\frac{x}{3}+x+1=0\)
\(x+\frac{29}{5}-\frac{x}{3}=0\)
\(x-\frac{1}{3}x=-\frac{29}{5}\)
\(\frac{2}{3}x=-\frac{29}{5}\)
\(x=-\frac{87}{10}\)


\(2x^3+7x^2+7x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^3+4x^2\right)+\left(3x^2+6x\right)+\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2\left(x+2\right)+3x\left(x+2\right)+\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(2x^2+3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left[2x\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+1\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
.......................................................................................
\(x^3-8x^2-8x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)-8x\left(x+1\right)=0\)
......................................................................................

a: Ta có: \(x^2+3x+4=0\)
\(\text{Δ}=3^2-4\cdot1\cdot4=9-16=-7< 0\)
Do đó: Phương trình vô nghiệm

a) \(2{x^2} + 3x + 1 \ge 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = 2{x^2} + 3x + 1\) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(x = - 1,x = \frac{{ - 1}}{2}\)
hệ số \(a = 2 > 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu f(x) như sau:
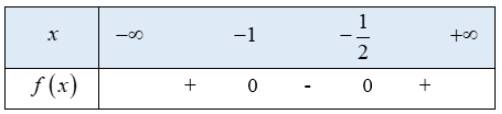
Từ bảng xét dấu ta thấy \(f\left( x \right) \ge 0 \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l}x \le - 1\\x \ge - \frac{1}{2}\end{array} \right.\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(\left( { - \infty ; - 1} \right] \cup \left[ { - \frac{1}{2}; + \infty } \right)\)
b) \( - 3{x^2} + x + 1 > 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = - 3{x^2} + x + 1\) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(x = \frac{{1 - \sqrt {13} }}{6},x = \frac{{1 + \sqrt {13} }}{6}\)
Hệ số \(a = - 3 < 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu f(x) như sau:

Từ bảng xét dấu ta thấy \(f\left( x \right) > 0\)\( \Leftrightarrow \frac{{1 - \sqrt {13} }}{6} < x < \frac{{1 + \sqrt {13} }}{6}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(\left( {\frac{{1 - \sqrt {13} }}{6};\frac{{1 + \sqrt {13} }}{6}} \right)\)
c) \(4{x^2} + 4x + 1 \ge 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = 4{x^2} + 4x + 1\) có nghiệm duy nhất \(x = \frac{{ - 1}}{2}\)
hệ số \(a = 4 > 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu f(x) như sau:

Từ bảng xét dấu ta thấy \(f\left( x \right) \ge 0 \Leftrightarrow x \in \mathbb{R}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(\mathbb{R}\)
d) \( - 16{x^2} + 8x - 1 < 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = - 16{x^2} + 8x - 1\) có nghiệm duy nhất \(x = \frac{1}{4}\)
hệ số \(a = - 16 < 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu f(x) như sau:
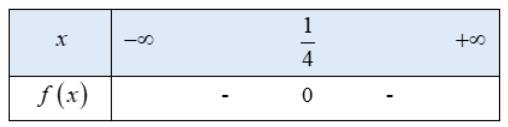
Từ bảng xét dấu ta thấy \(f\left( x \right) < 0 \Leftrightarrow x \ne \frac{1}{4}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(\mathbb{R}\backslash \left\{ {\frac{1}{4}} \right\}\)
e) \(2{x^2} + x + 3 < 0\)
Ta có \(\Delta = {1^2} - 4.2.3 = - 23 < 0\) và có \(a = 2 > 0\)
Sử dụng định lí về dấu của tam thức bậc hai, ta thấy tập hợp những giá trị của x sao cho \(2{x^2} + x + 3\) mang dấu “-” là \(\emptyset \)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình \(2{x^2} + x + 3 < 0\) là \(\emptyset \)
g) \( - 3{x^2} + 4x - 5 < 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = - 3{x^2} + 4x - 5\) có \(\Delta ' = {2^2} - \left( { - 3} \right).\left( { - 5} \right) = - 11 < 0\) và có \(a = - 3 < 0\)
Sử dụng định lí về dấu của tam thức bậc hai, ta thấy tập hợp những giá trị của x sao cho \( - 3{x^2} + 4x - 5\) mang dấu “-” là \(\mathbb{R}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình \( - 3{x^2} + 4x - 5 < 0\) là \(\mathbb{R}\)

1.
\(x^4-6x^2-12x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-2x^2+1-4x^2-12x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-1\right)^2=\left(2x+3\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-1=2x+3\\x^2-1=-2x-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-2x-4=0\\x^2+2x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\pm\sqrt{5}\)
3.
ĐK: \(x\ge-9\)
\(x^4-x^3-8x^2+9x-9+\left(x^2-x+1\right)\sqrt{x+9}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-x+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x+9}+x^2-9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x+9}+x^2-9=0\left(1\right)\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{x+9}=t\left(t\ge0\right)\Rightarrow9=t^2-x\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow t+x^2+x-t^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+t\right)\left(x-t+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-t\\x=t-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\sqrt{x+9}\\x=\sqrt{x+9}-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)

pt <=> x^4+8x-4x^3-5 = 0
<=> (x^4-x^3)-(3x^3-3x)+(5x-5) = 0
<=> x^3.(x-1)-3.x.(x-1).(x+1)+5.(x-1) = 0
<=> (x-1).(x^3-3x^2-3x+5) = 0
<=> (x-1).[(x^3-x^2)-(2x^2-2x)-(5x-5)] = 0
<=> (x-1)^2.(x^2-2x-5) = 0
<=> x-1=0 hoặc x^2-2x-5=0
<=> x=1 hoặc x = \(1+-\sqrt{6}\)
Vậy ...............
Tk mk nha

anh ơi, vậy là sai đề hả anh, chứ đề kêu chứng minh phương trình vô nghiệm mà em thấy anh ghi x=2
\(x^4-4x^3+8x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-x^3-3x^3+3x^2-3x^2+3x+5x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3\left(x-1\right)-3x^2\left(x-1\right)-3x\left(x-1\right)+5\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^3-3x^2-3x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^3-x^2-2x^2+2x-5x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left[x^2\left(x-1\right)-2x\left(x-1\right)-5\left(x-1\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x^2-2x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\x^2-2x-5=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x^2-2x+1=6\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\\left(x-1\right)^2=6\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x-1=\pm\sqrt{6}\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=\sqrt{6}\\x-1=-\sqrt{6}\end{cases}}\end{cases}}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=\pm\sqrt{6}+1\end{cases}}\)
Vậy...
x4 - 4x3 + 8x - 5 = 0
<=> x4 - x3 - 3x3 + 3x2 - 3x2 + 3x + 5x - 5 = 0
<=> x3( x - 1 ) - 3x2( x - 1 ) - 3x( x - 1 ) + 5( x - 1 ) = 0
<=> ( x - 1 )( x3 - 3x2 - 3x + 5 ) = 0
<=> ( x - 1 )( x3 - x2 - 2x2 + 2x - 5x + 5 ) = 0
<=> ( x - 1 )[ x2( x - 1 ) - 2x( x - 1 ) - 5( x - 1 ) ] = 0
<=> ( x - 1 )2( x2 - 2x - 5 ) = 0
<=> x - 1 = 0 hoặc x2 - 2x - 5 = 0
+) x - 1 = 0 <=> x = 1
+) x2 - 2x - 5 = 0
<=> ( x2 - 2x + 1 ) - 6 = 0
<=> ( x - 1 )2 - ( √6 )2 = 0
<=> ( x - 1 - √6 )( x - 1 + √6 ) = 0
<=> x = 1 + √6 hoặc x = 1 - √6
Vậy S = { 1 ; 1 ± √6 }