2x+1 – 2x = 32
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


cả 3 bài đều giống nhau nên mình làm 1 bài thôi nhé
\(\dfrac{2x}{32}=1\Rightarrow2x=32\)
x = 32 : 2
x = 16
\(\dfrac{2x}{32}=1\)
\(\Rightarrow2x.1=32.1\)
\(\Rightarrow2x=32\)
\(\Rightarrow x=16\)


\(\left(2x+1\right)y-2x-1=-32\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2xy-2x+y-1=-32\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(y-1\right)+\left(y-1\right)=-32\)
\(\left(2x+1\right)\left(y-1\right)=-32\)
Đề bài nên cho là x,y thuộc Z; chia trường hợp rồi làm :vv
(2x + 1) y − 2x − 1 = −32
⇔2xy − 2x + y − 1 = −32
⇔2x (y − 1) + (y − 1) = −32
(2x + 1) (y − 1) = −32
=> 2x+1 và y-1 thuộc Ư(-32)
| 2x+1 | 1 | -32 | -1 | 32 | 9 | -4 | -9 | -9 | ||||
| y-1 | -32 | 1 | 32 | -1 | -4 | 9 | 4 | -4 | ||||
| x | 0 | -33/2 | -1 | 31/2 | 4 | -5/2 | -5 | -5 | ||||
| y | -31 | 2 | 34 | 0 | -3 | 10 | 5 | -3 |
vậy.............................................................

Bài 2:
a: Ta có: \(2^{x+1}\cdot3^y=12^x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2^{x+1}\cdot3^y=2^{2x}\cdot3^x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1=2x\\x=y\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\dfrac{2x}{15}+\dfrac{2x}{35}+\dfrac{2x}{63}+...+\dfrac{2x}{195}=\dfrac{4}{5}\\ x\cdot\left(\dfrac{2}{15}+\dfrac{2}{35}+\dfrac{2}{63}+...+\dfrac{2}{195}\right)=\dfrac{4}{5}\\ x\cdot\left(\dfrac{2}{3\cdot5}+\dfrac{2}{5\cdot7}+\dfrac{2}{7\cdot9}+...+\dfrac{2}{13\cdot15}\right)=\dfrac{4}{5}\\ x\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{3}-\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{5}-\dfrac{1}{7}+\dfrac{1}{7}-\dfrac{1}{9}+...+\dfrac{1}{13}-\dfrac{1}{15}\right)=\dfrac{4}{5}\\ x\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{3}-\dfrac{1}{15}\right)=\dfrac{4}{5}\\ x\cdot\dfrac{4}{15}=\dfrac{4}{5}\\ x=\dfrac{4}{5}:\dfrac{4}{15}\\ x=3\)
Gọi \(D=\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{8}-\dfrac{1}{16}+\dfrac{1}{32}-\dfrac{1}{64}\)
\(2D=1-\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{1}{16}-\dfrac{1}{32}\\ 2D+D=\left(1-\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{1}{16}-\dfrac{1}{32}\right)+\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{8}-\dfrac{1}{16}+\dfrac{1}{32}-\dfrac{1}{64}\right)\\ 3D=1-\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dfrac{1}{16}-\dfrac{1}{32}+\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{8}-\dfrac{1}{16}+\dfrac{1}{32}-\dfrac{1}{64}\\ 3D=1-\dfrac{1}{64}< 1\\ \Rightarrow D=\dfrac{1-\dfrac{1}{64}}{3}< \dfrac{1}{3}\)
Vậy \(\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{8}-\dfrac{1}{16}+\dfrac{1}{32}-\dfrac{1}{64}< \dfrac{1}{3}\)

\(\left(2x+1\right)^3=125\\ \Rightarrow\left(2x+1\right)^3=5^3\\ \Rightarrow2x+1=5\\ \Rightarrow2x=4\\ \Rightarrow x=2.\\ b,\left(2x-1\right)^4=16\\ \Rightarrow\left(2x-1\right)^4=2^4\\ \Rightarrow2x-1=2\\ \Rightarrow2x=3\\ \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}.\\ c,6.3^x-2.3^x=36\\ \Rightarrow3^x.\left(6-2\right)=36\\ \Rightarrow3^x.4=36\\ \Rightarrow3^x=9\\ \Rightarrow3^x=3^2\\ \Rightarrow x=2.\\ d,2^{x+1}-2^x=32\\ \Rightarrow2^x.\left(2-1\right)=32\\ \Rightarrow2^x=2^5\\ \Rightarrow x=5.\)

a. (2x-1)4=81
=>(2x-1)4=34
=>2x-1=3
=>2x=3+1
=>2x=4
=>x=4:2
=>x=2
b.(x-1)5=-32
=>(x-1)5=(-2)5
=>x-1=-2
=>x=-2+1
=>x=-1
c.(2x-1)6=(2x-1)8
mà chỉ có: (-1)6=(-1)8; 06=08; 16=18
=> để (2x-1) \(\in\){-1;0;1} thì x \(\in\){0; 1/2; 1}

1: \(=6x^2+2x-15x-5-x^2+6x-9+4x^2+20x+25-27x^3-27x^2-9x-1\)
=-27x^3-18x^2+4x+10
2: =4x^2-1-6x^2-9x+4x+6-x^3+3x^2-3x+1+8x^3+36x^2+54x+27
=7x^3+37x^2+46x+33
5:
\(=25x^2-1-x^3-27-4x^2-16x-16-9x^2+24x-16+\left(2x-5\right)^3\)
\(=8x^3-60x^2+150-125+12x^2-x^3+8x-60\)
=7x^3-48x^2+8x-35
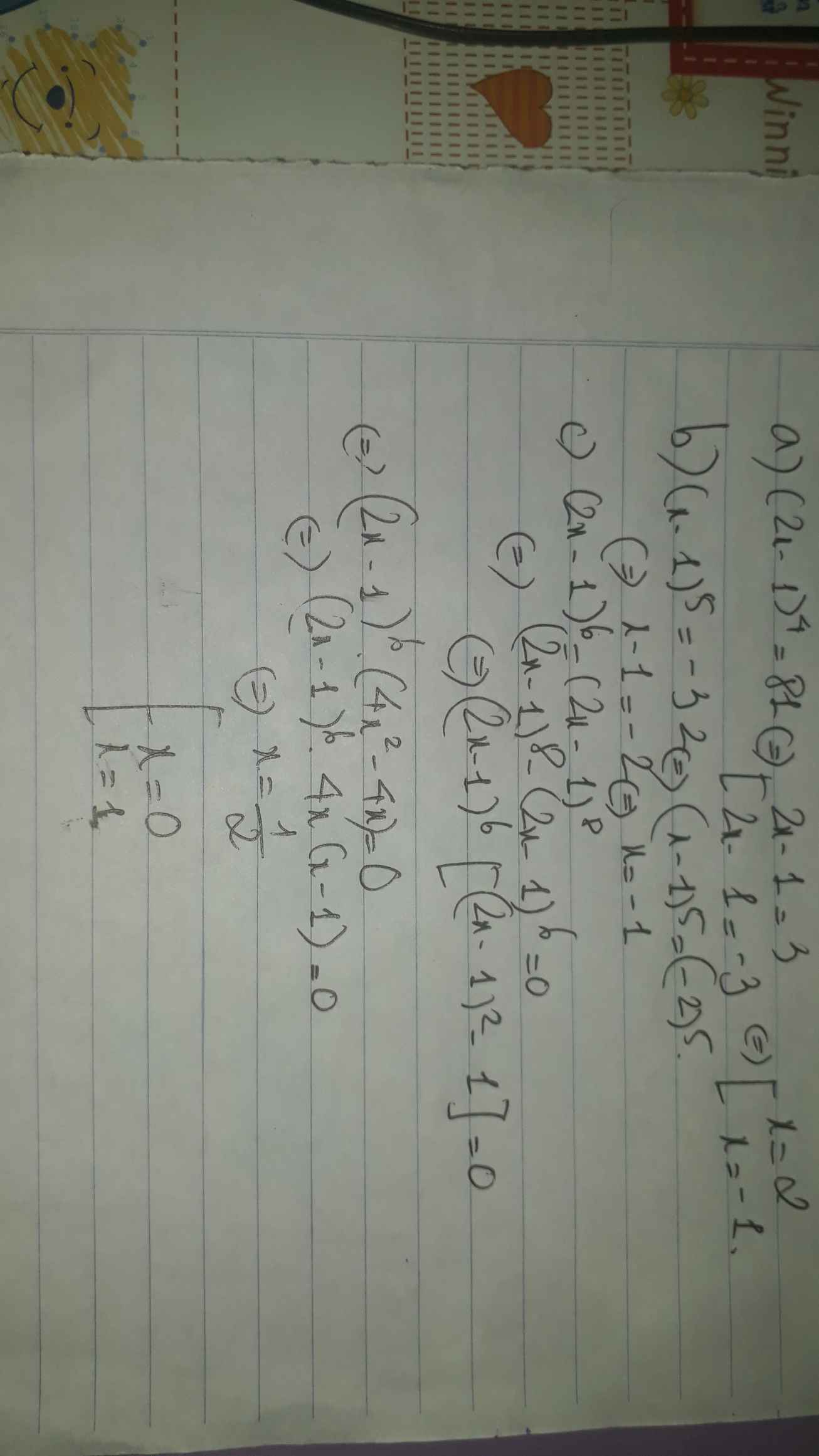
\(\Leftrightarrow2^x=32\)
hay x=5
X=5