Giải phương trình:
\(2\sin x=1\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(2sinx-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sinx=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi\\x=\dfrac{5\pi}{6}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\left(2cosx+\sqrt{3}\right)\left(cos2x+2sinx-\sqrt{3}\right)=1-4\left(1-cos^2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2cosx+\sqrt{3}\right)\left(cos2x+2sinx-\sqrt{3}\right)=4cos^2x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2cosx+\sqrt{3}\right)\left(cos2x+2sinx-\sqrt{3}\right)=\left(2cosx+\sqrt{3}\right)\left(2cosx-\sqrt{3}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cosx=-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\Rightarrow x=...\\cos2x+2sinx-\sqrt{3}=2cosx-\sqrt{3}\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow cos^2x-sin^2x-2\left(cosx-sinx\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(cosx-sinx\right)\left(cosx+sinx\right)-2\left(cosx-sinx\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(cosx-sinx\right)\left(cosx+sinx-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)

sin x + cos x = 1 + sin x.cos x
⇔ sin x.cos x – sin x – cos x + 1 = 0
⇔ (sinx. cosx –sinx)- (cosx -1 ) =0
⇔ sinx. (cosx – 1) – (cosx -1) = 0
⇔ (sin x – 1)(cos x – 1) = 0
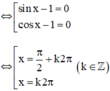
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 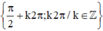

\(\Leftrightarrow cos6x-cos8x+2\left(1-cos4x\right)^2+\sqrt{3}sin6x=4-4cos4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos6x-cos8x+2\left(1+cos^24x-2cos4x\right)+\sqrt{3}sin6x=4-4cos4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos6x-cos8x+cos8x+3-4cos4x+\sqrt{3}sin6x=4-4cos4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos6x+\sqrt{3}sin6x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(6x-\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)

Với \(cosx=0\) ko phải nghiệm
Với \(cosx\ne0\) chia 2 vế cho \(cos^2x\)
\(\Rightarrow tan^2x-4\sqrt{3}tanx+1=-2\left(1+tan^2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3tan^2x-4\sqrt{3}tanx+3=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}tanx=\sqrt{3}\\tanx=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\\x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)


\(sin\left(2x+\dfrac{\Omega}{2}\right)=sin\left(x-\dfrac{\Omega}{3}\right)\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+\dfrac{\Omega}{2}=x-\dfrac{\Omega}{3}+k2\Omega\\2x+\dfrac{\Omega}{2}=\Omega-x+\dfrac{\Omega}{3}+k2\Omega\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{5}{6}\Omega+k2\Omega\\3x=\dfrac{4}{3}\Omega-\dfrac{1}{2}\Omega+k2\Omega\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{5}{6}\Omega+k2\Omega\\x=\dfrac{5}{18}\Omega+\dfrac{k2\Omega}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Lời giải:
$\sin (2x+\frac{\pi}{2})=\sin (x-\frac{\pi}{3})$
\(\Rightarrow \left[\begin{matrix}\ 2x+\frac{\pi}{2}=x-\frac{\pi}{3}+2k\pi\\ 2x+\frac{\pi}{2}=\pi -(x-\frac{\pi}{3})+2k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow \left[\begin{matrix}\ x=\pi (2k-\frac{5}{6})\\ x=\frac{1}{3}\pi (\frac{5}{6}+2k)\end{matrix}\right.\) với $k$ nguyên bất kỳ.
a thông cảm hộ nha, e học lớp 6 lên e o biết
2 sinx =1
<=> sin x=1/2
<=> x= 30 o
Em cũng chưa học cái này nên khong biết.Giải bừa thôi ạ .