Phân tích thành nhân tử (48x2+8x-1)(3x2+5x+2)-4
tks mn
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


* Chứng minh:
Phương trình a x 2 + b x + c = 0 có hai nghiệm x 1 ; x 2
⇒ Theo định lý Vi-et: 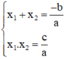
Khi đó : a.(x – x1).(x – x2)
= a.(x2 – x1.x – x2.x + x1.x2)
= a.x2 – a.x.(x1 + x2) + a.x1.x2
= 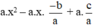
= a . x 2 + b x + c ( đ p c m ) .
* Áp dụng:
a) 2 x 2 – 5 x + 3 = 0
Có a = 2; b = -5; c = 3
⇒ a + b + c = 2 – 5 + 3 = 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm 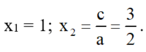
Vậy: 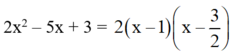
b) 3 x 2 + 8 x + 2 = 0
Có a = 3; b' = 4; c = 2
⇒ Δ ’ = 4 2 – 2 . 3 = 10 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt:
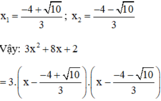

1)\(4x^2-4xy+y^2-8x+4y=\left(4x^2-4xy+y^2\right)-\left(8x-4y\right)=\left(2x-y\right)^2-4\left(2x-y\right)=\left(2x-y\right)\left(2x-y-4\right)\)
2) \(2x^3-3x^2+3x-1=x^2\left(2x-1\right)-x\left(2x-1\right)+\left(2x-1\right)=\left(2x-1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)\)

3x^2-8x+4
=3x^2-6x-2x+4
=3x(x-2)-2(x-2)
=(x-2)(3x-2)
l-kie cho mik nha bạn


Bài 1:
a: \(=6x^3-10x^2+6x\)
b: \(=-2x^3-10x^2-6x\)
Bài 4:
a: =>3x+10-2x=0
=>x=-10
c: =>3x2-3x2+6x=36
=>6x=36
hay x=6
Bài 1:
\(a,=6x^3-10x^2+6x\\ b,=-2x^3-10x^2-6x\)
Bài 4:
\(a,\Leftrightarrow3x+10-2x=0\Leftrightarrow x=-10\\ b,\Leftrightarrow x\left(2x^2+9x-5\right)-\left(2x^3+9x^2+x+4,5\right)=3,5\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^3+9x^2-5x-2x^3-9x^2-x-4,5=3,5\\ \Leftrightarrow-6x=8\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\\ c,\Leftrightarrow3x^2-3x^2+6x=36\Leftrightarrow x=6\)
Bài 1:
\(a,=7xy\left(2x-3y+4xy\right)\\ b,=x\left(x+y\right)-5\left(x+y\right)=\left(x-5\right)\left(x+y\right)\\ c,=\left(x-y\right)\left(10x+8\right)=2\left(5x+4\right)\left(x-y\right)\\ d,=\left(3x+1-x-1\right)\left(3x+1+x+1\right)\\ =2x\left(4x+2\right)=4x\left(2x+1\right)\\ e,=5\left[\left(x-y\right)^2-4z^2\right]=5\left(x-y-2z\right)\left(x-y+2z\right)\\ f,=x^2+8x-x-8=\left(x+8\right)\left(x-1\right)\\ g,\left(x+y\right)^3-\left(x+y\right)=\left(x+y\right)\left[\left(x+y\right)^2-1\right]\\ =\left(x+y\right)\left(x+y-1\right)\left(x+y+1\right)\\ h,=x^2+3x+x+3=\left(x+3\right)\left(x+1\right)\)

Cách 1: Nhóm hai hạng tử đầu tiên với nhau và hai hạng tử cuối với nhau:
3x2 – 3xy – 5x + 5y
= (3x2 – 3xy) – (5x – 5y)
(Nhóm thứ nhất có nhân tử chung là 3x ; nhóm thứ hai có nhân tử chung là 5)
= 3x(x – y) – 5(x – y)
(Xuất hiện nhân tử chung là (x – y))
= (x – y)(3x – 5)
Cách 2: Nhóm hạng tử thứ 1 với hạng tử thứ 3; hạng tử thứ 2 với hạng tử thứ 4:
3x2 – 3xy – 5x + 5y
= (3x2 – 5x) – (3xy – 5y)
(Nhóm thứ nhất có nhân tử chung là x, nhóm thứ hai có nhân tử chung là y)
= x.(3x – 5) – y.(3x – 5)
(Xuất hiện nhân tử chung 3x – 5)
= (x – y).(3x – 5).
Ta có: \(\left(48x^2+8x-1\right)\left(3x^2+5x+2\right)-4\)
\(=\left[\left(48x^2-4x\right)+\left(12x-1\right)\right]\left[\left(3x^2+3x\right)+\left(2x+2\right)\right]-4\)
\(=\left[4x.\left(12x-1\right)+\left(12x-1\right)\right]\left[3x.\left(x+1\right)+2.\left(x+1\right)\right]-4\)
\(=\left(4x+1\right).\left(12x-1\right)\left(3x+2\right).\left(x+1\right)-4\)
\(=\left[\left(4x+1\right)\left(3x+2\right)\right]\left[\left(12x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\right]-4\)
\(=\left(12x^2+11x+2\right)\left(12x^2+11x-1\right)-4\)
Gọi \(a=12x^2+11x-1\)\(\Rightarrow\)\(a+3=12x^2+11x+2\)
Ta lại có: \(\left(a+3\right).a-4=a^2+3a-4\)
\(=\left(a^2-a\right)+\left(4a-4\right)\)
\(=a.\left(a-1\right)+4.\left(a-1\right)\)
\(=\left(a+4\right).\left(a-1\right)\)
\(=\left(12a^2+11x-1+4\right).\left(12a^2+11-1-1\right)\)
\(=\left(12a^2+11x+3\right).\left(12a^2+11-2\right)\)