Tìm x biết x2 + x3 + x + 1 = 0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) x = -1. b) x = 4 hoặc x = 5.
c) x = ± 2 . d) x = 1 hoặc x = 2.

x 3 – x 2 – x + 1 = 0 ⇔ ( x 3 – x 2 ) – ( x – 1 ) = 0 ⇔ x 2 ( x – 1 ) – ( x – 1 ) = 0 ⇔ ( x 2 – 1 ) ( x – 1 ) = 0 ⇔ ( x – 1 ) ( x + 1 ) ( x – 1 ) = 0 ⇔ ( x – 1 ) 2 ( x + 1 ) = 0
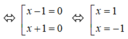
Vậy x = 1 hoặc x = -1
Đáp án cần chọn là: A

x 3 – x 2 – x + 1 = 0 ⇔ ( x 3 – x 2 ) – ( x – 1 ) = 0 ⇔ x 2 ( x – 1 ) – ( x – 1 ) = 0 ⇔ ( x 2 – 1 ) ( x – 1 ) = 0 ⇔ ( x – 1 ) ( x + 1 ) ( x – 1 ) = 0 ⇔ ( x – 1 ) 2 ( x + 1 ) = 0
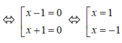
Vậy x = 1 hoặc x = -1
Đáp án cần chọn là: A

a: \(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=5\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)

1.
Đặt \(x^2-2x+m=t\), phương trình trở thành \(t^2-2t+m=x\)
Ta có hệ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-2x+m=t\\t^2-2t+m=x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-t\right)\left(x+t-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=t\\x=1-t\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=x^2-2x+m\\x=1-x^2+2x-m\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=-x^2+3x\\m=-x^2+x+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của \(y=-x^2+x+1\) và \(y=-x^2+3x\):
\(-x^2+x+1=-x^2+3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
Đồ thị hàm số \(y=-x^2+3x\) và \(y=-x^2+x+1\):
Dựa vào đồ thị, yêu cầu bài toán thỏa mãn khi \(m< \dfrac{5}{4}\)
Mà \(m\in\left[-10;10\right]\Rightarrow m\in[-10;\dfrac{5}{4})\)
Có cách nào lm bài này bằng cách lập bảng biến thiên k ạ

a) \(\Rightarrow x\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(\Rightarrow x\left(x^2-4\right)=0\Rightarrow x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=2\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(5x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
d) \(\Rightarrow2\left(x+5\right)-x\left(x+5\right)=0\Rightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(2-x\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-5\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
e) \(\Rightarrow2x^2-10x-3x-2x^2=26\)
\(\Rightarrow-13x=26\Rightarrow x=-2\)
f) \(\Rightarrow\left(x-2012\right)\left(5x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2012\\x=\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)

1. a) \(7x^2\left(2x^3+3x^5\right)=7x^2\cdot2x^3+7x^2\cdot3x^5=14x^5+21x^7\)
b) \(\left(x^3-x^2+x-1\right):\left(x-1\right)=\dfrac{x^3-x^2+x-1}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2\left(x-1\right)+\left(x-1\right)}{x-1}=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}{x-1}=x^2+1\)
2: \(x^2-8x+7=0\)
=>\(x^2-x-7x+7=0\)
=>\(x\left(x-1\right)-7\left(x-1\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x-1\right)\left(x-7\right)=0\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x-7=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
1:
a: \(7x^2\left(2x^3+3x^5\right)=7x^2\cdot2x^3+7x^2\cdot3x^5=21x^7+14x^5\)
b: \(\dfrac{x^3-x^2+x-1}{x-1}=\dfrac{x^2\left(x-1\right)+\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=x^2+1\)

a) x = 1; x = - 1 3 b) x = 2.
c) x = 3; x = -2. d) x = -3; x = 0; x = 2.

8 x 3 + 12 x 2 + 6x + 1 = 0
2 x 3 + 3. 2 x 2 .1 + 3.(2x). 1 2 + 1 3 = 0
2 x + 1 3 = 0
2x + 1 = 0
x = (-1)/2
x3+x2+x+1=0
<=> x2(x+1)+(x+1)=0
<=> (x2+1)(x+1)=0
<=> x+1=0 (vì x2+1>0 với mọi x)
<=> x=-1