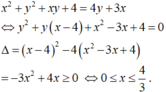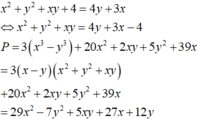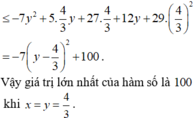Cho các số thực a,b thỏa mãn: 4x2+2xy+y2=3. Tìm GTNN, GTLN của P=x2+2xy-y2
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Ta có \(x^2+y^2=1\Leftrightarrow\left(x+y\right)^2=2xy+1\)
Từ đó \(P=\dfrac{\left(x+y\right)^2}{x+y+1}\). Đặt \(x+y=t\left(t\ge0\right)\). Vì \(x+y\le\sqrt{2\left(x^2+y^2\right)}=2\) nên \(t\le\sqrt{2}\). ĐTXR \(\Leftrightarrow x=y=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\). Ta cần tìm GTLN của \(P\left(t\right)=\dfrac{t^2}{t+1}\) với \(0\le t\le\sqrt{2}\).
Giả sử có \(0\le t_1\le t_2\le\sqrt{2}\). Ta có BDT luôn đúng \(\left(t_2-t_1\right)\left(t_2+t_1+t_2t_1\right)\ge0\) \(\Leftrightarrow t_2^2-t_1^2+t_2^2t_1-t_2t_1^2\ge0\) \(\Leftrightarrow t_1^2\left(t_2+1\right)\le t_2^2\left(t_1+1\right)\) \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{t_1^2}{t_1+1}\le\dfrac{t_2^2}{t_2+1}\) \(\Leftrightarrow P\left(t_1\right)\le P\left(t_2\right)\). Như vậy với \(0\le t_1\le t_2\le\sqrt{2}\) thì \(P\left(t_1\right)\le P\left(t_2\right)\). Do đó P là hàm đồng biến. Vậy GTLN của P đạt được khi \(t=\sqrt{2}\) hay \(x=y=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\), khi đó \(P=2\sqrt{2}-2\)
Lời giải:
$P=\frac{2xy+1}{x+y+1}=\frac{2xy+x^2+y^2}{x+y+1}=\frac{(x+y)^2}{x+y+1}$
$=\frac{a^2}{a+1}$ với $x+y=a$
Áp dụng BĐT AM-GM:
$1=x^2+y^2\geq \frac{(x+y)^2}{2}=\frac{a^2}{2}$
$\Rightarrow a^2\leq 2\Rightarrow a\leq \sqrt{2}$
$P=\frac{a^2}{a+1}=\frac{a}{1+\frac{1}{a}}$
Vì $a\leq \sqrt{2}\Rightarrow 1+\frac{1}{a}\geq 1+\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{2+\sqrt{2}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow P\leq \frac{\sqrt{2}}{\frac{2+\sqrt{2}}{2}}=-2+2\sqrt{2}$
Vậy $P_{\max}=-2+2\sqrt{2}$ khi $x=y=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$

A= -x2+2x+3
=>A= -(x2-2x+3)
=>A= -(x2-2.x.1+1+3-1)
=>A=-[(x-1)2+2]
=>A= -(x+1)2-2
Vì -(x+1)2 ≤0=> A≤-2
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi
-(x+1)2=0 => x=-1
Vây A lớn nhất= -2 khi x= -1
B=x2-2x+4y2-4y+8
=> B= (x2-2x+1)+(4y2-4y+1)+6
=> B=(x-1)2+(2y+1)2+6
=> B lớn nhất=6 khi x=1 và y=-1/2


a) (x + 3)(x2 – 3x + 9) – (54 + x3)
= ( x + 3)(x2 – 3.x + 32) – (54 + x3)
= x3 + 33 – (54 + x3)
= x3 + 27 – 54 – x3
= -27
b) (2x + y)(4x2 – 2xy + y2) – (2x – y)(4x2 + 2xy + y2)
= (2x + y)[(2x)2 – 2x.y + y2] – (2x – y)[(2x)2 + 2x.y + y2]
= [(2x)3 + y3] – [(2x)3 – y3]
= (2x)3 + y3 – (2x)3 + y3
= 2y3
a) (x + 3)(x2 – 3x + 9) – (54 + x3)
= ( x + 3)(x2 – 3.x + 32) – (54 + x3)
= x3 + 33 – (54 + x3) = x3 + 27 – 54 – x3
= -27
b) (2x + y)(4x2 – 2xy + y2) – (2x – y)(4x2 + 2xy + y2)
= (2x + y)[(2x)2 – 2x.y + y2] – (2x – y)[(2x)2 + 2x.y + y2]
= [(2x)3 + y3] – [(2x)3 – y3]
= (2x)3 + y3 – (2x)3 + y3
= 2y3

Đáp án C
G T ⇔ x 2 + y − 3 x + y 2 − 4 y + 4 = 0 y 2 + x − 4 y + x 2 − 3 x + 4 = 0
có nghiệm ⇔ Δ x ≥ 0 Δ y ≥ 0 ⇔ 0 ≤ x ≤ 4 3 1 ≤ y ≤ 7 3
Và:
x y = 3 x + 4 y − x 2 − y 2 − 4 ⇒ P = 3 x 3 + 18 x 2 + 45 x − 8 ⏟ f x + − 3 y 3 + 3 y 2 + 8 y ⏟ g y
Xét hàm số f x = 3 x 3 + 18 x 2 + 45 x − 8 trên 0 ; 4 3 ⇒ max 0 ; 4 3 f x = f 4 3 = 820 9
Xét hàm số g x = − 3 y 3 + 3 y 2 + 8 y trên 1 ; 7 3 ⇒ max 1 ; 7 3 g x = f 4 3 = 80 9
Vật P ≤ max 0 ; 4 3 f x + max 1 ; 7 3 g x = 100
Dấu “=” xảy ra khi x = y = 4 3