Giải dùm câu 21 vs 22a với
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


3.
Từ BBT ta thấy hàm đồng biến trên các khoảng \(\left(-\infty;-1\right)\) và \(\left(1;+\infty\right)\)
B đúng
4.
Từ BBT ta thấy hàm đồng biến trên các khoảng \(\left(-\infty;-1\right)\) và \(\left(0;1\right)\)
A đúng
1.
B sai (thiếu điều kiện \(f'\left(x\right)=0\) tại hữu hạn điểm)

11. \(I=\int\limits^2_1x\sqrt{x^2+1}dx\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{x^2+1}=t\Leftrightarrow x^2=t^2-1\Rightarrow xdx=tdt\) ; \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\Rightarrow t=\sqrt{2}\\x=2\Rightarrow t=\sqrt{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(I=\int\limits^{\sqrt{5}}_{\sqrt{2}}t.tdt=\int\limits^{\sqrt{5}}_{\sqrt{2}}t^2dt=\dfrac{1}{3}t^3|^{\sqrt{5}}_{\sqrt{2}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\left(5\sqrt{5}-2\sqrt{2}\right)\)
12. Đặt \(\sqrt[3]{8-4x}=t\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{8-t^3}{4}\Rightarrow dx=-\dfrac{3}{4}t^2dt\) ; \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\Rightarrow t=2\\x=2\Rightarrow t=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(I=\int\limits^0_2t.\left(-\dfrac{3}{4}t^2dt\right)=\dfrac{3}{4}\int\limits^2_0t^3dt=\dfrac{3}{16}t^4|^2_0=3\)
13. Đặt \(\sqrt{3-2x}=t\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{3-t^2}{2}\Rightarrow dx=-tdt\) ; \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\Rightarrow t=\sqrt{3}\\x=1\Rightarrow t=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(I=\int\limits^1_{\sqrt{3}}\dfrac{-tdt}{t}=\int\limits^{\sqrt{3}}_1dt=t|^{\sqrt{3}}_1=\sqrt{3}-1\)

1..so I tired
2..I tried my best
3.. the most beautiful place in the world
4..tease the dog
1The children are playing football at the moment
2I haven't met Lan for a long time
Ảnh 1:
1. I stayed up late, so I am tired
2. I did not pass my exam although I tried my best
3. My homeland is the best beautiful place in the world
4. Don't tease the dog

tìm n nguyên để gtri bth nguyên hả bạn ?
\(B=\dfrac{2n-6}{n-1}=\dfrac{2\left(n-1\right)-4}{n-1}=2-\dfrac{4}{n-1}\Rightarrow n-1\inƯ\left(4\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm2;\pm4\right\}\)
| n-1 | 1 | -1 | 2 | -2 | 4 | -4 |
| n | 2 | 0 | 3 | -1 | 5 | -3 |
Ta có 2n-6\(\in Z\)
n-1\(\in\)Z
n-1\(\ne0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) \(\dfrac{2n-6}{n-1}\)là phân số
Để B có giá trị nguyên thì 2n-6\(⋮\)n-1
2n-6\(⋮\)n-1
n-1\(⋮\)n-1\(\Rightarrow\)2(n-1)\(⋮\)n-1\(\Rightarrow\)2n-2\(⋮\)n-1
\(\Rightarrow\) (2n-2)\(-\left(2n-6\right)\)\(⋮\)n-1
\(\Rightarrow\)2n-2-2n+6\(⋮\)n-1
\(\Rightarrow\)(2n-2n)+(6-2) \(⋮\)n-1
\(\Rightarrow\) 4 \(⋮\)n-1
\(\Rightarrow n-1\) là ước của 4
\(\Rightarrow\)n-1\(\in\){1;-1;2;-2;4;-4}
\(\Rightarrow\)n\(\in\){2;0;3;-1;5;-3}


1.
\(y'=x^2-6x+5=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Dấu của y' trên trục số:
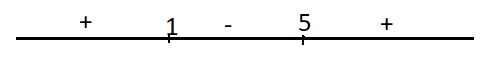
Hàm đồng biến trên các khoảng \(\left(-\infty;1\right)\) và \(\left(5;+\infty\right)\)
Hàm nghịch biến trên \(\left(1;5\right)\)
3.
TXĐ: \(D=R\backslash\left\{2\right\}\)
\(y'=\dfrac{-5}{\left(x-2\right)^2}< 0;\forall x\in D\)
Hàm nghịch biến trên các khoảng \(\left(-\infty;2\right)\) và \(\left(2;+\infty\right)\)
4.
\(y'=4x^3+4x=4x\left(x^2+1\right)=0\Rightarrow x=0\)
Dấu của y':
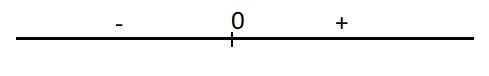
Hàm đồng biến trên \(\left(0;+\infty\right)\)
Hàm nghịch biến trên \(\left(-\infty;0\right)\)
6.
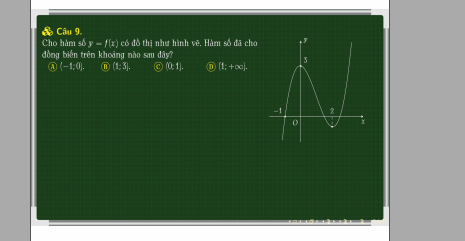
Từ đồ thị ta thấy hàm đồng biến trên các khoảng \(\left(-\infty;-1\right)\) và \(\left(1;+\infty\right)\)
Hàm nghịch biến trên \(\left(-1;1\right)\)

c: Xét ΔABH vuông tại H có HD là đường cao
nên \(AD\cdot AB=AH^2\left(1\right)\)
Xét ΔAHC vuông tại H có HE là đường cao
nên \(AE\cdot AC=AH^2\left(2\right)\)
Từ (1) và (2) suy ra \(AD\cdot AB=AE\cdot AC\)
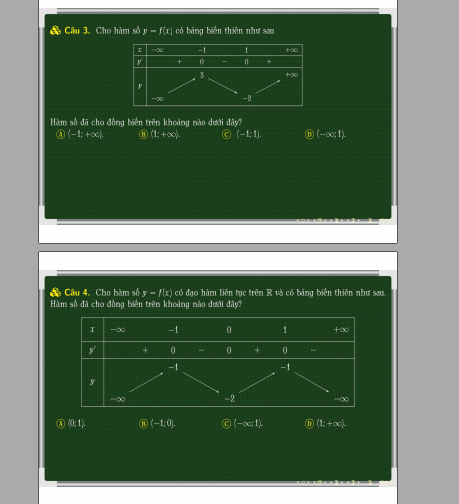

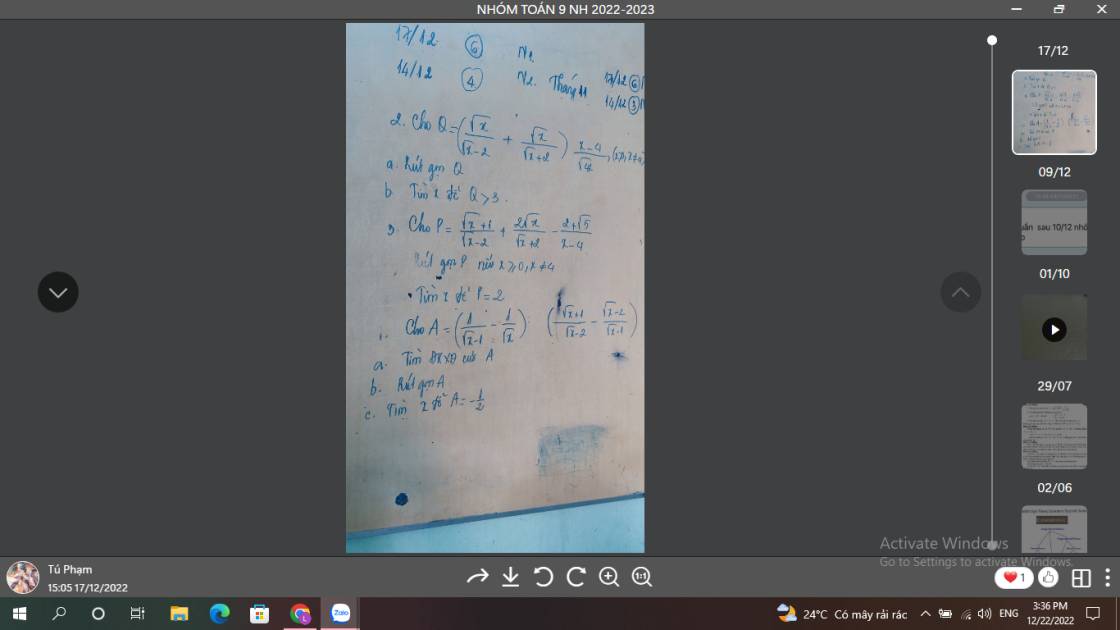 giải dùm câu 3 vs plss
giải dùm câu 3 vs plss










Bài 21:
\(C=x\left(x-4\right)\left(x^2-4x+8\right)=\left(x^2-4x\right)\left(x^2-4x+8\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-4x+4-4\right)\left(x^2-4x+4+4\right)=\left(x^2-4x+4\right)^2-4^2\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)^4-16\ge-16\)
Dấu \(=\)khi \(x-2=0\Leftrightarrow x=2\).
Bài 22:
a) Sai đề.