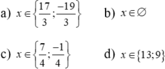Giải phương trình √(3x+1) = -4x^2 +13x - 5
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


đặt \(\sqrt{3x+1}=a\)
=> pt <=> 4x^2 +a +6=a^2 +12x
chuyển hết nt sang vế phải để vt =0 ptđttnt có ntc=a+2x-3
câu 2 đặt \(\sqrt[3]{3x-5}=2y-3\) rồi làm tt như bài trên lớp
sau khi chuyển cậu có pt a62-4x^2-a+12x-6=0
=> a^2+2ax-3a-2ax-4x^2+6x+2a+4x-6=0
<=> (a+2x-3)(a-2x+2)=0

a) \(x^2-3x^3+4x^2-3x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x^3+5x^2-3x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x^3+2x^2-x+3x^2-2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(-3x^2+2x-1\right)-1\left(-3x^2+2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(-3x^2+2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Vậy \(x=1\)
b) \(3x^4-13x^3+16x^2-13x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^4-4x^3+4x^2-x-9x^3+12x^2+12x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x^3-4x^2+4x-1\right)-3\left(3x^3-4x^2+4x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(3x^3-4x^2+4x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x-3\right)\left(x-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{3;\dfrac{1}{3}\right\}\)
a) Ta có: \(x^2-3x^3+4x^2-3x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x^3+5x^2-3x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x^3+3x^2+2x^2-2x-x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x^2\left(x-1\right)+2x\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(-3x^2+2x-1\right)=0\)
mà \(-3x^2+2x-1\ne0\forall x\)
nên x-1=0
hay x=1
Vậy: S={1}
b) Ta có: \(3x^4-13x^3+16x^2-13x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^4-9x^3-4x^3+12x^2+4x^2-12x-x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^3\left(x-3\right)-4x^2\left(x-3\right)+4x\left(x-3\right)-\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(3x^3-4x^2+4x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(3x^3-x^2-3x^2+x+3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left[x^2\left(3x-1\right)-x\left(3x-1\right)+\left(3x-1\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(3x-1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2-x+1\ne0\forall x\)
nên \(\left(x-3\right)\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\3x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\3x=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{1}{3};3\right\}\)

c.
ĐLXĐ: \(x\ge-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(-\left(3x+1\right)+\sqrt{3x+1}+4x^2-10x+6=0\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{3x+1}=t\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow-t^2+t+4x^2-10x+6=0\)
\(\Delta=1+4\left(4x^2-10x+6\right)=\left(4x-5\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=\dfrac{-1+4x-5}{-2}=3-2x\\t=\dfrac{-1-4x+5}{-2}=2x-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{3x+1}=3-2x\left(x\le\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\\\sqrt{3x-1}=2x-2\left(x\ge1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+1=4x^2-12x+9\left(x\le\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\\3x-1=4x^2-8x+4\left(x\ge1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)
a.
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge-\dfrac{5}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-12x-2-2\sqrt{4x+5}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x^2-8x+4\right)-\left(4x+5+2\sqrt{4x+5}+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-2\right)^2-\left(\sqrt{4x+5}+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-2-\sqrt{4x+5}-1\right)\left(2x-2+\sqrt{4x+5}+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3-\sqrt{4x+5}\right)\left(2x-1+\sqrt{4x+5}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{4x+5}=2x-3\left(x\ge\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\\\sqrt{4x+5}=1-2x\left(x\le\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x+5=4x^2-12x+9\left(x\ge\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\\4x+5=4x^2-4x+1\left(x\le\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)


1 3 x − 1 + 1 2 x + 4 = 1 9 x − 2 + 1 5 − 4 x Đ K : x ≠ 1 3 , x ≠ − 2 , x ≠ 2 9 , x ≠ 5 4
Ta có pt: 5 x + 3 ( 3 x − 1 ) ( 2 x + 4 ) = 5 x + 3 ( 9 x − 2 ) ( 5 − 4 x )
< = > x = − 3 5 ( 3 x − 1 ) ( 2 x + 4 ) = ( 9 x − 2 ) ( 5 − 4 x ) < = > x = − 3 5 6 x 2 + 12 x − 2 x − 4 = − 36 x 2 + 45 x + 8 x − 10 < = > x = − 3 5 ( T M ) x = 6 7 ( T M ) x = 1 6 ( T M )
Vậy phương trình đã có có 3 nghiệm phân biệt như trên.

Để giải các phương trình này, chúng ta sẽ làm từng bước như sau: 1. 13x(7-x) = 26: Mở ngoặc và rút gọn: 91x - 13x^2 = 26 Chuyển về dạng bậc hai: 13x^2 - 91x + 26 = 0 Giải phương trình bậc hai này để tìm giá trị của x. 2. (4x-18)/3 = 2: Nhân cả hai vế của phương trình với 3 để loại bỏ mẫu số: 4x - 18 = 6 Cộng thêm 18 vào cả hai vế: 4x = 24 Chia cả hai vế cho 4: x = 6 3. 2xx + 98x2022 = 98x2023: Rút gọn các thành phần: 2x^2 + 98x^2022 = 98x^2023 Chia cả hai vế cho 2x^2022: x + 49 = 49x Chuyển các thành phần chứa x về cùng một vế: 49x - x = 49 Rút gọn: 48x = 49 Chia cả hai vế cho 48: x = 49/48 4. (x+1) + (x+3) + (x+5) + ... + (x+101): Đây là một dãy số hình học có công sai d = 2 (do mỗi số tiếp theo cách nhau 2 đơn vị). Số phần tử trong dãy là n = 101/2 + 1 = 51. Áp dụng công thức tổng của dãy số hình học: S = (n/2)(a + l), trong đó a là số đầu tiên, l là số cuối cùng. S = (51/2)(x + (x + 2(51-1))) = (51/2)(x + (x + 100)) = (51/2)(2x + 100) = 51(x + 50) Vậy, kết quả của các phương trình là: 1. x = giá trị tìm được từ phương trình bậc hai. 2. x = 6 3. x = 49/48 4. S = 51(x + 50)

\(\left(3x-2\right)\left(4x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x-2=0\\4x+5=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{2}{3}\\x=-\frac{5}{4}\end{cases}}\)
ĐKXĐ: x khác -4;-5;-6;-7
\(\frac{1}{x^2+9x+20}+\frac{1}{x^2+11x+30}+\frac{1}{x^2+13x+42}=\frac{1}{18}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{1}{\left(x+4\right).\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{1}{\left(x+5\right).\left(x+6\right)}+\frac{1}{\left(x+6\right).\left(x+7\right)}=\frac{1}{18}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{1}{x+4}-\frac{1}{x+5}+\frac{1}{x+5}-\frac{1}{x+6}+\frac{1}{x+6}-\frac{1}{x+7}=\frac{1}{18}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{1}{x+4}-\frac{1}{x+7}=\frac{1}{18}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{x+7-x-4}{\left(x+4\right).\left(x+7\right)}=\frac{1}{18}\Rightarrow3.18=x^2+11x+28\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+11x-26=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right).\left(x+13\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=-13\end{cases}\left(tm\right)}\)
Vậy...