Để có dd có pH = 12 người ta phải thêm Vml H2O vào 2 ml dung dịch Ba(OH)2 0,1M. Giá trị đúng của V là: A. 28 ml B. 8ml C.18ml D. 38ml
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Đáp án : D
nOH = nKOH + 2nBa(OH)2 = 0,005 mol
nH+ = nHCl = 0,16V.10-3 mol
=> [H+] = 10-pH
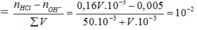
=> V = 36,67 ml

\(n_{H^+}=0.3\cdot0.1\cdot2+0.3\cdot0.15=0.105\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{OH^-}=0.001V\cdot0.3+0.001V\cdot2\cdot0.1=0.0032V\left(mol\right)\)
\(H^++OH^-\rightarrow H_2O\)
\(0.105.......0.105\)
\(n_{OH^-\left(dư\right)}=0.0032V-0.105\left(mol\right)\)
\(\left[OH^-\right]=\dfrac{0.0032V-0.105}{0.3+0.001V}\left(M\right)\)
\(pH=14+log\left[OH^-\right]=12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log\left[OH^-\right]=-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log\left[\dfrac{0.0032V-0.105}{0.3+0.001V}\right]=-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow V=33.85\left(ml\right)\)
nH+=0,3.0,1.2+0,3.0,15=0,105 mol
nOH- ban đầu =0,3V + 0,1.2V=0,5V mol
Sau phản ứng thu được dung dịch có pH=12
⇒OH- dư ⇒ pOH=2
⇒ [OH- ] dư = 0,01 M
nOH- dư = 0,01(0,3+V)=0,003+0,01V (mol)
nOH- phản ứng=nOH- ban đầu - nOH- dư
= 0,5V - 0,003 - 0,01V
= 0,49V - 0,003 (mol )
H+ + OH- → H2O
0,105 → 0,105
nOH- phản ứng = nH+
⇒0,49V - 0,003 =0,105
⇒ V≃0,22 lít=200ml

Đáp án B
nH+ ban đầu = 0,1.2.0,1 + 0,2.0,1 + 0,3.0,1 = 0,07
dung dịch C có pH=1 ⇒ nH+/C = 0,1.(0,3 + V)
⇒ nH+ ban đầu = nH+/C + nOH- ⇒ 0,07 = 0,1.(0,3 + V) + 0,2V +0,1.2V
⇒ V =0,08l
\(pH=12\Rightarrow pOH=2\\ \Rightarrow\left[OH^-\right]_{sau}=10^{-2}\left(M\right)\)
Ta có : \(n_{OH^-\left(củaBa\left(OH\right)_2\right)}=0,002.2.0,1=4.10^{-4}\left(mol\right)\)
=> \(V_{sau}=\dfrac{4.10^{-4}}{10^{-2}}=0,04\left(lít\right)=40\left(ml\right)\)
Mà ta có : \(V_{sau}=V_{dd}+V_{H_2O}=2+V_{H_2O}=40\left(ml\right)\\ \Rightarrow V_{H_2O}=38\left(ml\right)\)