
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 6:
a: \(\sqrt{\dfrac{2}{3-\sqrt{5}}}=\dfrac{\sqrt[4]{2}\cdot\left(\sqrt[2]{5}+1\right)}{2}\)
b: \(\sqrt{\dfrac{a-4}{2\left(\sqrt{a}-2\right)}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}\left(\sqrt{a}+2\right)}{2}\)

Bài 7:
a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{\dfrac{1}{2};-5\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x+5}{2x-1}-\dfrac{1-2x}{x+5}-2=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+5}{2x-1}+\dfrac{2x-1}{x+5}-2=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{\left(x+5\right)^2+\left(2x-1\right)^2}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(x+5\right)}=2\)
=>\(\left(x+5\right)^2+\left(2x-1\right)^2=2\left(2x-1\right)\left(x+5\right)\)
=>\(x^2+10x+25+4x^2-4x+1=2\left(2x^2+10x-x-5\right)\)
=>\(5x^2+6x+26-4x^2-18x+10=0\)
=>\(x^2-12x+36=0\)
=>\(\left(x-6\right)^2=0\)
=>x-6=0
=>x=6(nhận)
b: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{3;-2;4\right\}\)
\(1-\dfrac{8}{x-4}=\dfrac{5}{3-x}-\dfrac{8-x}{x+2}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x-4-8}{x-4}=\dfrac{-5}{x-3}+\dfrac{x-8}{x+2}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x-12}{x-4}=\dfrac{-5\left(x+2\right)+\left(x-8\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x-12}{x-4}=\dfrac{-5x-10+x^2-11x+24}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
=>\(\left(x-12\right)\left(x^2-x-6\right)=\left(x-4\right)\left(x^2-16x+14\right)\)
=>\(x^3-x^2-6x-12x^2+12x+72=x^3-16x^2+14x-4x^2+64x-56\)
=>\(-13x^2+6x+72=-20x^2+78x-56\)
=>\(7x^2-72x+128=0\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=8\left(nhận\right)\\x=\dfrac{16}{7}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{2;-2\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x-1}{x+2}+\dfrac{2}{x-2}=\dfrac{12}{x^2-4}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x-1}{x+2}+\dfrac{2}{x-2}=\dfrac{12}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)+2\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{12}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
=>\(x^2-3x+2+2x+4=12\)
=>\(x^2-x-6=0\)
=>(x-3)(x+2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\left(nhận\right)\\x=-2\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)


Xét phương trình \(x^2-2mx+2m-2=0\)
\(\Delta'=m^2-2m+2>0,\forall m\) nên phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt \(x_1,x_2\).
Áp dụng hệ thức Viet ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2m\\x_1x_2=2m-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để \(x_1+3x_2=6\) thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+3x_2=6\\x_1+x_2=2m\\x_1x_2=2m-1\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x_2=6-2m\\x_1=2m-x_2\\x_1x_2=2m-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_2=3-m\\x_1=3m-3\\x_1x_2=2m-1\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Rightarrow\left(3-m\right)\left(3m-3\right)=2m-1\)
\(\Rightarrow-3m^2+10m-8=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=2\\m=\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Bài 7:
\(\widehat{AOB}+\widehat{A}+\widehat{B}=360^0\)
nên Ax//By



7. a) Hợp chất X của A với C: ACx
Ta có: \(\dfrac{A}{A+12x}.100=62,5\)
Lập bảng:
| x | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| A | 20 | 40 | 60 |
| Kết luận | Loại | Chọn (Ca) | Loại |
Vậy nguyên tố A là Ca
CTPT của hợp chất X : CaC2
CTCT:
b)Gọi số oxh của C trong chất là x. Ta có số oxh của Ca là +2
Trong CaC2: 2 + 2. x = 0 → x = -1
Số oxh của C trong CaC2 là -1





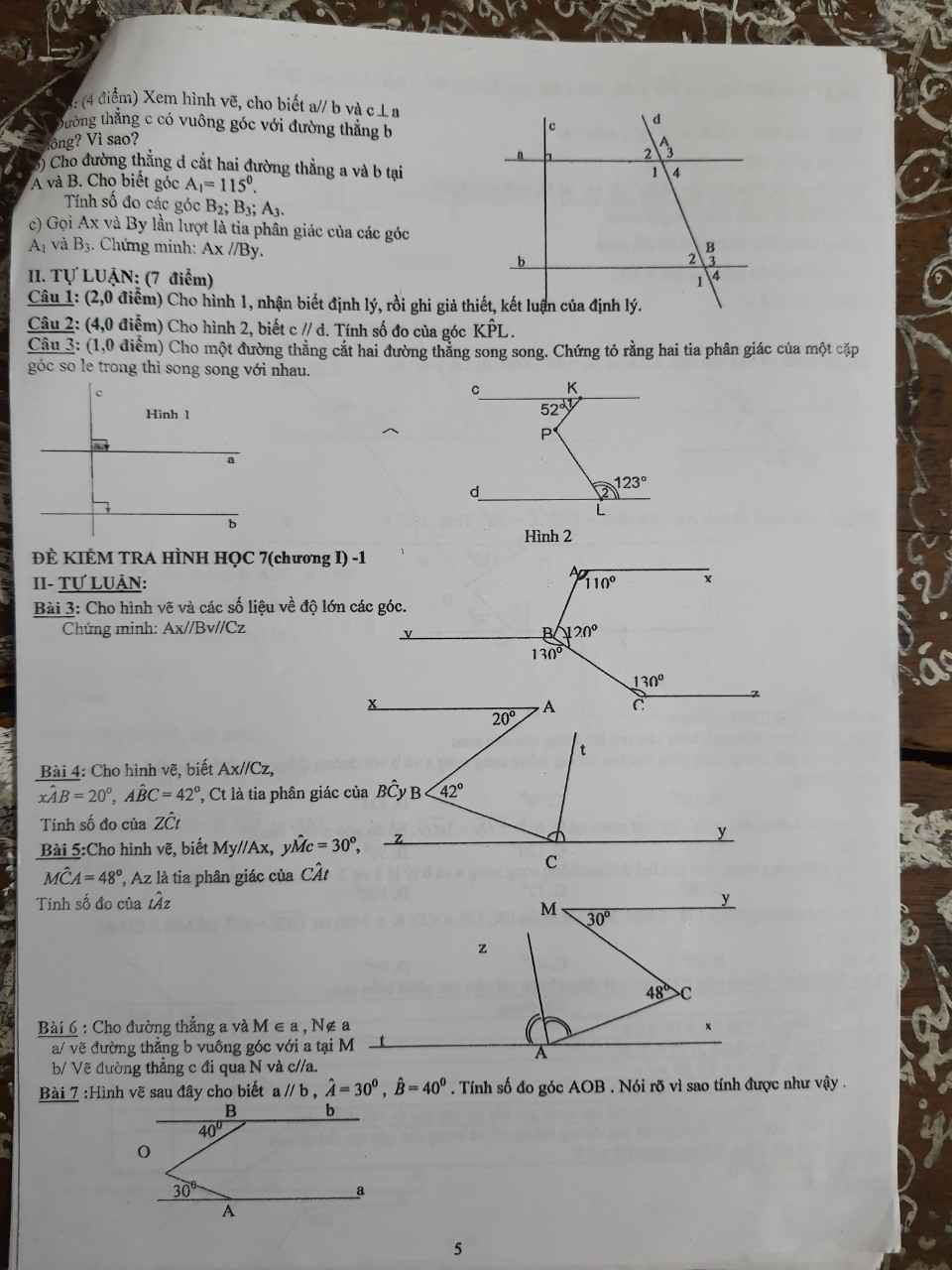
 giúp mình bài 7, bài 8 với ạ, cảm ơn nhiều
giúp mình bài 7, bài 8 với ạ, cảm ơn nhiều