Giải hộ mình Bài 3.11 với ạ
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



a) Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(x^2=\left(m+2\right)x-2m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-\left(m+2\right)x+2m=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(m+2\right)^2-8m=m^2+4m+4-8m=m^2-4m+4=\left(m-2\right)^2\)
Để (d) và (P) cắt nhau tại hai điểm phân biệt thì \(\Delta>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m-2\right)^2>0\)
mà \(\left(m-2\right)^2\ge0\)
nên \(m-2\ne0\)
hay \(m\ne2\)
Vậy: Để (d) và (P) cắt nhau tại hai điểm phân biệt thì \(m\ne2\)

1) Vì x=25 thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ nên Thay x=25 vào biểu thức \(A=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{x+1}\), ta được:
\(A=\dfrac{\sqrt{25}-2}{25+1}=\dfrac{5-2}{25+1}=\dfrac{3}{26}\)
Vậy: Khi x=25 thì \(A=\dfrac{3}{26}\)
2) Ta có: \(B=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-3}{\sqrt{x}+1}+\dfrac{2x+8\sqrt{x}-6}{x-\sqrt{x}-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}+\dfrac{2x+8\sqrt{x}-6}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-5\sqrt{x}+6+2x+8\sqrt{x}-6}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x+3\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)

Bài 5 hình 1: (tự vẽ hình nhé bạn)
a) Xét ΔABD và ΔACB ta có:
\(\widehat{BAD}\)= \(\widehat{BAC}\) (góc chung)
\(\widehat{ABD}\)= \(\widehat{ACB}\) (gt)
=> ΔABD ~ ΔACB (g-g)
=> \(\dfrac{AB}{AC}\) = \(\dfrac{BD}{CB}\) = \(\dfrac{AD}{AB}\) (tsđd)
b) Ta có: \(\dfrac{AB}{AC}\) = \(\dfrac{AD}{AB}\) (cm a)
=> \(AB^2\) = AD.AC
=> \(2^2\) = AD.4
=> AD = 1 (cm)
Ta có: AC = AD + DC (D thuộc AC)
=> 4 = 1 + DC
=> DC = 3 (cm)
c) Xét ΔABH và ΔADE ta có:
\(\widehat{AHB}\) = \(\widehat{AED}\) (=\(90^0\))
\(\widehat{ADB}\) = \(\widehat{ABH}\) (ΔABD ~ ΔACB)
=> ΔABH ~ ΔADE
=> \(\dfrac{AB}{AD}\) = \(\dfrac{AH}{AE}\) = \(\dfrac{BH}{DE}\) (tsdd)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{S_{ABH}}{S_{ADE}}\) = \(\left(\dfrac{AB}{AD}\right)^2\)= \(\left(\dfrac{2}{1}\right)^2\)= 4
=> đpcm
Tiếp bài 5 hình 2 (tự vẽ hình)
a) Xét ΔABC vuông tại A ta có:
\(BC^2\) = \(AB^2\) + \(AC^2\)
\(BC^2\) = \(21^2\) + \(28^2\)
BC = 35 (cm)
b) Xét ΔABC và ΔHBA ta có:
\(\widehat{BAC}\) = \(\widehat{AHB}\) ( =\(90^0\))
\(\widehat{ABC}\) = \(\widehat{ABH}\) (góc chung)
=> ΔABC ~ ΔHBA (g-g)
=> \(\dfrac{AB}{BH}\) = \(\dfrac{BC}{AB}\) (tsdd)
=> \(AB^2\) = BH.BC
=> \(21^2\) = 35.BH
=> BH = 12,6 (cm)
c) Xét ΔABC ta có:
BD là đường p/g (gt)
=> \(\dfrac{AD}{DC}\) = \(\dfrac{AB}{BC}\) (t/c đường p/g)
Xét ΔABH ta có:
BE là đường p/g (gt)
=> \(\dfrac{HE}{AE}\) = \(\dfrac{BH}{AB}\) (t/c đường p/g)
Mà: \(\dfrac{AB}{BC}\) = \(\dfrac{BH}{AB}\) (cm b)
=> đpcm
d) Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\widehat{HBE}+\widehat{BEH}=90^0\\\widehat{ABD}+\widehat{ADB=90^0}\\\widehat{HBE}=\widehat{ABD}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=> \(\widehat{BEH}=\widehat{ADB}\)
Mà \(\widehat{BEH}=\widehat{AED}\) (2 góc dd)
Nên \(\widehat{ADB}=\widehat{AED}\)
=> đpcm


Sửa đề là : 4.6 (g)
\(n_{H_2}=\dfrac{2.24}{22.4}=0.1\left(mol\right)\)
\(A+H_2O\rightarrow AOH+\dfrac{1}{2}H_2\)
\(0.2...............................0.1\)
\(M_A=\dfrac{4.6}{0.2}=23\left(\dfrac{g}{mol}\right)\)
\(A:Na\)
Đề này C1 em sửa thành 4,6 gam kim loại như bạn dưới, C2 em sửa thành 22,4 lít H2

Bài 5:
a: Ta có: \(x^2-8x+17\)
\(=x^2-8x+16+1\)
\(=\left(x-4\right)^2+1>0\forall x\)
b: Ta có: \(4x^2-12x+13\)
\(=4x^2-12x+9+4\)
\(=\left(2x-3\right)^2+4>0\forall x\)
c: Ta có: \(x^2-x+1\)
\(=x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}>0\forall x\)




 giải hộ mình mấy bài này vs ạ !
giải hộ mình mấy bài này vs ạ !

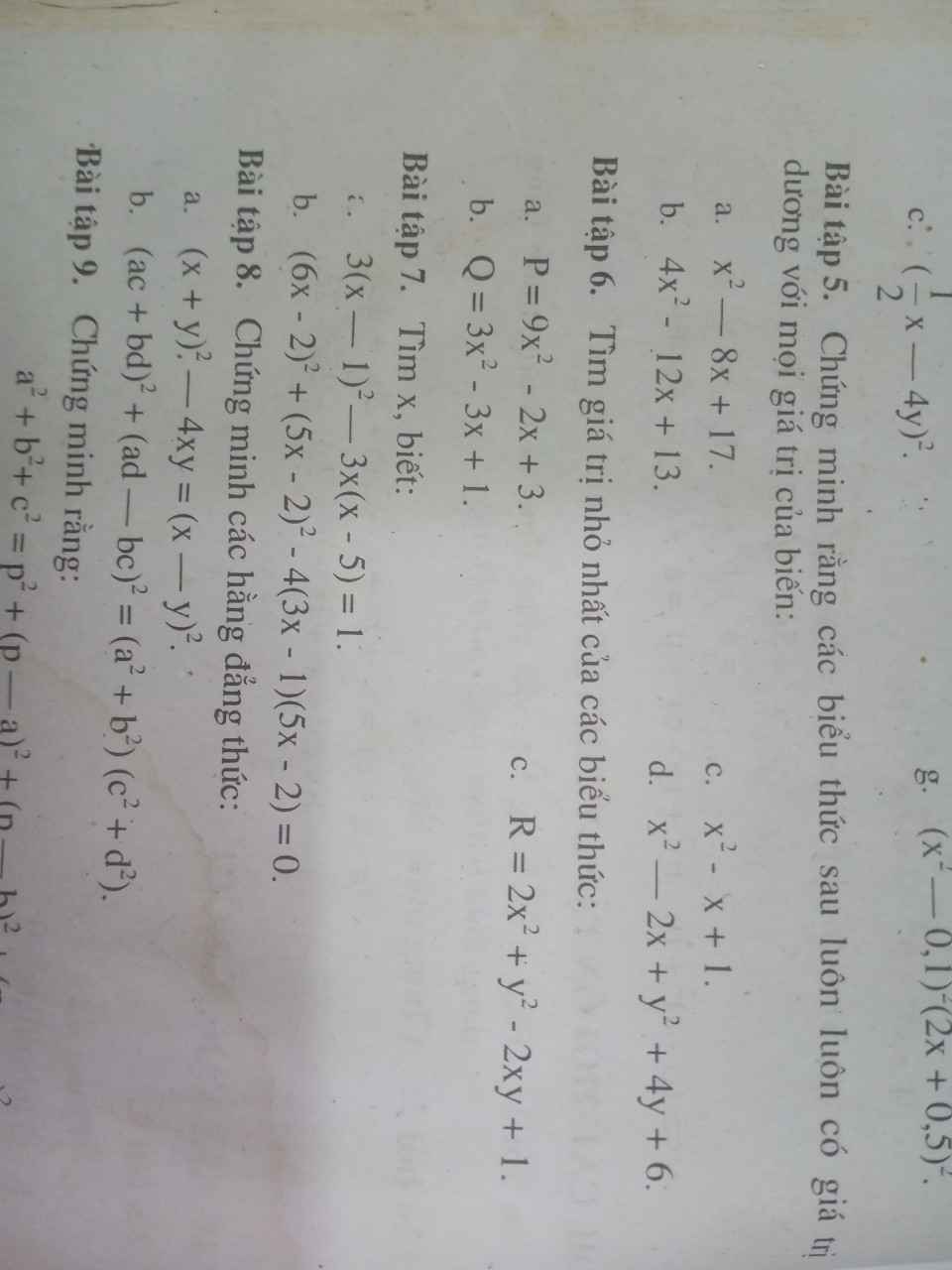
Lời giải:
a) Đặt \(\left\{\begin{matrix} u=x\\ dv=\cos 2xdx\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} du=dx\\ v=\frac{\sin 2x}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow \int x\cos 2xdx=\frac{x\sin 2x}{2}-\int \frac{\sin 2x}{2}dx=\frac{x\sin 2x}{2}+\frac{\cos 2x}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow \int ^{\frac{\pi}{2}}_{0}x\cos 2xdx=\left.\begin{matrix} \frac{\pi}{2}\\ 0\end{matrix}\right|\left ( \frac{x\sin 2x}{2}+\frac{\cos 2x}{4} \right )=\frac{-1}{2}\)
b) Đặt \(\left\{\begin{matrix} u=x\\ dv=e^{-2x}dx\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} du=dx\\ v=\frac{-e^{-2x}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow \int xe^{-2x}dx=\frac{-xe^{-2x}}{2}+\int \frac{e^{-2x}}{2}dx=\frac{-xe^{-2x}}{2}-\frac{e^{-2x}}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow \int ^{\ln 2}_{0}xe^{-2x}dx=\left.\begin{matrix} \ln 2\\ 0\end{matrix}\right|\left ( \frac{-xe^{-2x}}{2}-\frac{e^{2x}}{4} \right )=\frac{3}{16}-\frac{\ln 2}{8}\)
c)
\(\int ^{1}_{0}\ln (2x+1)dx=\frac{1}{2}\int ^{1}_{0}\ln (2x+1)d(2x+1)=\frac{1}{2}\int ^{3}_{1}\ln tdt\)
Đặt \(\left\{\begin{matrix} u=\ln t\\ dv=dt\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} du=\frac{dt}{t}\\ v=t\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow \int \ln tdt=t\ln t-\int dt=t\ln t-t\)
Do đó \(\frac{1}{2}\int ^{3}_{1}\ln tdt=\left.\begin{matrix} 3\\ 1\end{matrix}\right|\left(\frac{t\ln t-t}{2}\right)=\frac{3\ln 3}{2}-1\)
d)
Ta có \(\int ^{3}_{2}(\ln (x-1)-\ln (x+1))dx=\int ^{3}_{2}\ln (x-1)d(x-1)-\int ^{3}_{2}\ln (x+1)d(x+1)\)
\(=\int ^{2}_{1}\ln tdt-\int ^{4}_{3}\ln tdt\)
Theo phần c, ta đã chỉ ra được \(\int \ln tdt=t\ln t-t\), do đó:
\(\int ^{2}_{1}\ln tdt-\int ^{4}_{3}\ln tdt=\left.\begin{matrix} 2\\ 1\end{matrix}\right|(t\ln t-t)-\left.\begin{matrix} 4\\ 3\end{matrix}\right|(t\ln t-t)=\ln \left(\frac{27}{64}\right)\)
e)
Xét \(\int (x+1-\frac{1}{x})e^{x+\frac{1}{x}}dx=\int e^{x+\frac{1}{x}}dx+\int \left (x-\frac{1}{x}\right)e^{x+\frac{1}{x}}dx\)
Đặt \(\left\{\begin{matrix} u=e^{x+\frac{1}{x}}\\ dv=dx\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} du=\left(1-\frac{1}{x^2}\right)e^{x+\frac{1}{x}}dx\\ v=x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow \int e^{x+\frac{1}{x}}dx=xe^{x+\frac{1}{x}}-\int \left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)e^{x+\frac{1}{x}}dx\)
Do đó \(\int \left(x+1-\frac{1}{x}\right)e^{x+\frac{1}{x}}dx=xe^{x+\frac{1}{x}}\)
\(\int ^{2}_{\frac{1}{2}}\left(x+1-\frac{x}{x}\right)e^{x+\frac{1}{x}}dx=\left.\begin{matrix} 2\\ \frac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right|xe^{x+\frac{1}{x}}=\frac{3e^{\frac{5}{2}}}{2}\)