Tìm số thực x sao cho 2x - 1 và 2x^3 - 1 là 2 số chính phương
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


- Đặc điểm mạng lưới:
+ Có 78 phụ lưu chiều dài trên 10 km.
+ Các sông, suối trong hệ thống sông thường ngắn và dốc, phân thành nhiều lưu vực nhỏ độc lập.
+ Mạng lưới sông có dạng nan quạt.
- Chế độ nước sông: chia làm hai mùa rõ rệt (mùa lũ và mùa cạn)
+ Mùa lũ diễn ra từ tháng 10 đến tháng 12 phù hợp với mùa mưa thu đông và mùa bão, lượng nước mùa lũ chiếm khoảng 65% tổng lượng nước cả năm. Lũ tại hệ thống sông Thu Bồn lên rất nhanh và đột ngột, nhất là khi gặp bão và mưa lớn.
+ Mùa cạn kéo dài từ tháng 1 đến tháng 9, chiếm khoảng 35% tổng lượng nước cả năm.
+ Có 78 phụ lưu chiều dài trên 10 km.
+ Các sông, suối trong hệ thống sông thường ngắn và dốc, phân thành nhiều lưu vực nhỏ độc lập.
+ Mạng lưới sông có dạng nan quạt.
+ Mùa lũ diễn ra từ tháng 10 đến tháng 12 phù hợp với mùa mưa thu đông và mùa bão, lượng nước mùa lũ chiếm khoảng 65% tổng lượng nước cả năm.

\(\dfrac{5}{2x^2\left(6x+y\right)}+\dfrac{3}{5xy\left(6x+y\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{5\cdot5y}{2x^2\left(6x+y\right)\cdot5y}+\dfrac{3\cdot2x}{5xy\left(6x+y\right)\cdot2x}\)
\(=\dfrac{25y}{10x^2y\left(6x+y\right)}+\dfrac{6x}{10x^2y\left(6x+y\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{25y+6x}{10x^2y\left(6x+y\right)}\)

Khí hậu nhiệt đới ẩm gió mùa, có sự phân hóa theo mùa và theo đai cao ở nước ta đã tác động trực tiếp đến sự hình thành các điểm du lịch, loại hình du lịch, mùa vụ du lịch,...
- Phân hóa khí hậu theo độ cao ở khu vực đồi núi => Phát triển các loại hình du lịch nghỉ dưỡng, tham quan, khám phá,...
- Phân hóa khí hậu giữa 2 miền Bắc - Nam ảnh hưởng đến mùa vụ du lịch:
+ Miền Bắc: do nằm ở vĩ độ cao hơn nên có mùa đông lạnh, mùa hạ mát mẻ, nắng nhiều => Các hoạt động du lịch biển thưởng chỉ diễn ra vào mùa hè.
+ Miền Nam: biên độ nhiệt năm thấp, nắng nhiều, nhiệt độ trung bình thường trên 25 độ C => hoạt động du lịch biển có thể diễn ra quanh năm.

Lời giải:
$\frac{m}{n}=(1+\frac{1}{1992})+(\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{1991})+(\frac{1}{3}+\frac{1}{1990})+....+(\frac{1}{996}+\frac{1}{997})$
$=\frac{1993}{1.1992}+\frac{1993}{2.1991}+\frac{1993}{3.1990}+...+\frac{1993}{996.997}$
$=1993(\frac{1}{1992}+\frac{1}{2.1991}+...+\frac{1}{996.997})$
$\Rightarrow m\vdots 1993$

Cx k khó lắm vẽ hình chứ bn tự làm đc nhỉ:)) mình làm câu a vs B th nha mấy câu kia vẽ rắc rối lắm lười vẽ=))
Bài Làm
a) Áp dụng quan hệ giữa cạnh và đường cao trong tam giác vuông vào tam giác AHC vuông tại H ( H vuông góc BC ) :
\(\Rightarrow\) AH2= AE.AC ( đpcm ) (1)
Áp dụng quan hệ giữa cạnh và đường cao trong tam giác vuông vào tam giác AHB vuông tại H ( H vuông góc BC ) :
\(\Rightarrow\)AH2=AD.AB ( đpcm ) ( 2 )
b) Từ (1) và (2) ta có : AE.AC = AD.AB
\(\Rightarrow\)\(\dfrac{AE}{AD}\)=\(\dfrac{AC}{AB}\)
Xét tam giác ADE và tam giác ABC ta có :
góc A chung
\(\dfrac{AE}{AD}\)=\(\dfrac{AC}{AB}\) (cmt)
\(\Rightarrow\)tam giác ADE đồng dạng với tam giác ABC ( đpcm )

Đặt \(p^n+8=k^3\left(k\inℕ,k\ge3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow k^3-8=p^n\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(k-2\right)\left(k^2+2k+4\right)=p^n\)
\(\Leftrightarrow k-2=p^i\left(i\inℕ,i\le n\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow k=p^i+2\)
Ta có \(p^n+8=k^3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow p^n+8=\left(p^i+2\right)^3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow p^n=p^{3i}+6p^{2i}+12p^i\) (*)
Đặt \(p^j=\dfrac{p^n}{p^i}\left(j\inℕ,j\le n\right)\), khi đó (*) thành
\(p^j=p^{2i}+6p^{2i}+12\) (**)
Xét \(i=0\Leftrightarrow p^j=19\Leftrightarrow\left(p,j\right)=\left(19,1\right)\) \(\Rightarrow n=1\)
Ta tìm được một bộ \(\left(p,n\right)=\left(17,1\right)\)
Nếu \(j=0\) thì vô lí. Xét \(i,j\ge1\) . Khi đó ta có \(12⋮p\) \(\Rightarrow p\in\left\{2,3\right\}\)
Với \(p=2\), ta có \(2^n+8=k^3\) \(\Rightarrow k⋮2\Rightarrow k=2l\left(l\inℕ\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow2^n+8=8l^3\Leftrightarrow2^{n-3}+1=l^3\) \(\left(n\ge3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(l-1\right)\left(l^2+l+1\right)=2^{n-3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow l-1=2^m\left(m\le n-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow l=2^m+1\)
Do đó \(2^{n-3}+1=\left(2^m+1\right)^3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2^{n-3}=2^{3m}+3.2^{2m}+3.2^m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2^{n-3-m}=2^{2m}+3.2^m+3\)
\(\Rightarrow3⋮2^{n-3-m}\) \(\Leftrightarrow n-3-m=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow m=n-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow l^2+l+1=1\) \(\Leftrightarrow l=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow k=0\), vô lí.
Với \(p=3\), ta có \(3^n+8=k^3\) \(\Rightarrow k\) chia 3 dư 2 \(\Rightarrow k=3q+2\left(q\inℕ^∗\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow3^n+8=\left(3q+2\right)^3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3^n=27q^3+54q^2+36q\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3^{n-2}=q\left(3q^2+6q+4\right)\) \(\left(n\ge2\right)\)
Dễ thấy nếu \(n=2\) thì vô lí. Xét \(n\ge3\). Khi đó vì \(3q^2+6q+4⋮̸3\) nên \(3q^2+6q+4=1\), vô lí.
Vậy \(\left(p,n\right)=\left(19,1\right)\) là cặp số duy nhất thỏa mãn ycbt.

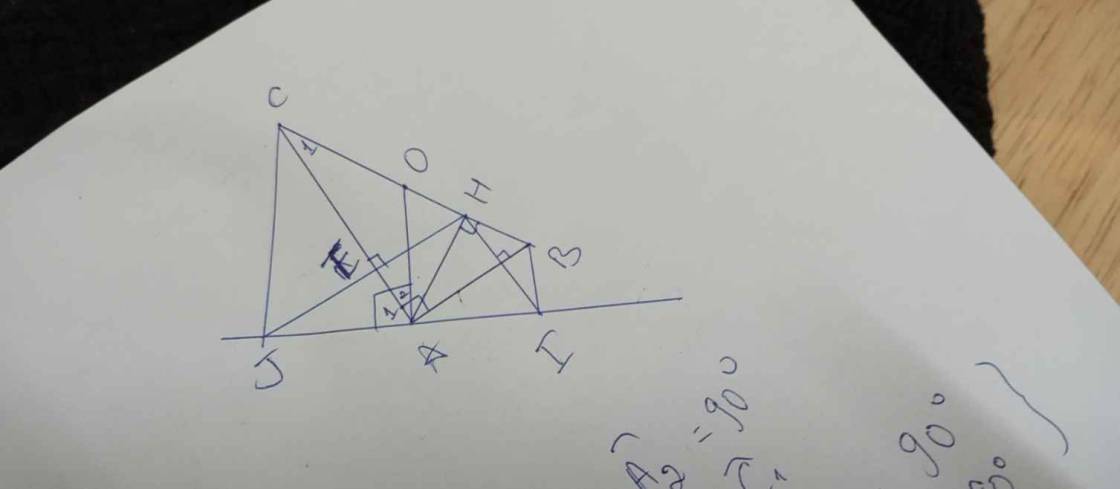
Câu e:
$\widehat {A_1}+\widehat{A_2}=90^{\circ}$
$\widehat{A_2}=\widehat{C_1}$
$\Rightarrow \widehat{A_1}+\widehat{C_1}=90^{\circ}$
Mặt khác $\widehat{C_1}+\widehat{CAH} = 90^{\circ}$
Suy ra $A_1=\widehat{CAH}$ (1)
Chứng minh được $\Delta JAE = \Delta HAE$ (cgv-gn)
$\Rightarrow AJ=AH$ (2)
Từ (1); (2) và chung cạnh $AC$ ta suy ra $\Delta AJC=\Delta AHC$ (c.g.c).
Suy ra $\widehat {J}=90^{\circ}$ hay $CJ\bot IJ$.
Chứng minh tương tự $BI \bot IJ$.
