
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1, Ta có: 3-x2+2x=-(x2-2x+1)+4=-(x-1)2+4
vì (x-1)2 luôn lớn hơn hoặc bằng không với mọi x-->-(x-1)2 nhỏ hơn hoặc bằng 0 với mọi x
vậy giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức 3-x2+2x là 4
các bài giá trị nhỏ nhất còn lại làm tương tự bạn nhé
chỉ cần đưa về nhân tử chung hoặc hằng đẳng thức là được

a) đk x khác 0;2
P = \(\dfrac{1}{x\left(x-2\right)}.\left(\dfrac{x^2+4}{x}-4\right)+1\)
= \(\dfrac{1}{x\left(x-2\right)}.\dfrac{x^2-4x+4}{x}+1\)
= \(\dfrac{1}{x\left(x-2\right)}.\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{x}+1\)
= \(\dfrac{x-2}{x^2}+1\)
= \(\dfrac{x^2+x-2}{x^2}\)
b) Để \(\left|2+x\right|=1\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2+x=1< =>x=-1\left(tm\right)\\2+x=-1< =>x=-3\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
TH1: x = -1
Thay x = -1 vào P, ta có:
\(P=\dfrac{\left(-1\right)^2-1-2}{\left(-1\right)^2}=-2\)
TH2: x = -3
Thay x = -3 vào P, ta có:
\(P=\dfrac{\left(-3\right)^2-3-2}{\left(-3\right)^2}=\dfrac{4}{9}\)
c) P = \(1+\dfrac{x-2}{x^2}\)
Xét \(\dfrac{x^2}{x-2}=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)^2+4\left(x-2\right)+4}{x-2}\)
= \(\left(x-2\right)+\dfrac{4}{x-2}+4\)
Áp dụng bdt co-si, ta có:
\(\left(x-2\right)+\dfrac{4}{x-2}\ge2\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)\dfrac{4}{x-2}}=4\)
<=> \(\dfrac{x^2}{x-2}\ge4+4=8\)
<=> \(\dfrac{x-2}{x^2}\le\dfrac{1}{8}\)
<=> A \(\le\dfrac{9}{8}\)
Dấu "=" <=> x = 4

Khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{4}\Leftrightarrow P=\dfrac{4.\dfrac{1}{4}-1}{\left(\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+3}=0\)
Khi \(x\ne\dfrac{1}{4}\Leftrightarrow P\ne\dfrac{4.\dfrac{1}{4}-1}{\left(\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+3}\Leftrightarrow P\ne0\)
\(P=\dfrac{4x-1}{x^2+3}\Leftrightarrow Px^2-4x+3P+1=0\) là pt bậc 2 do \(P\ne0\)
\(\Delta'=\left(-2\right)^2-P\left(3P+1\right)=-3P^2-P+4\)
Để pt có nghiệm thì \(\Delta'\ge0\Leftrightarrow-3P^2-P+4\ge0\Leftrightarrow-3\left(P+\dfrac{1}{6}\right)^2+\dfrac{49}{12}\ge0\Leftrightarrow P\le1\)
\(maxP=1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x-1}{x^2+3}=1\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+4=0\Leftrightarrow x=2\left(tm\right)\)
\(P=\dfrac{4x-1}{x^2+3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2P+3P-4x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow Px^2-4x+3P+1=0\left(1\right)\)
\(\left(1\right)\) có nghiệm khi:
\(\Delta'=4-P\left(3P+1\right)=-3P^2-P+4\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow P\in\left[-\dfrac{4}{3};1\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow P_{max}=1\Leftrightarrow x=2\)

A = x2 - 2x + 9 = ( x2 - 2x + 1 ) + 8 = ( x - 1 )2 + 8 ≥ 8 ∀ x
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x = 1
=> MinA = 8 <=> x = 1
B = x2 + 6x - 3 = ( x2 + 6x + 9 ) - 12 = ( x + 3 )2 - 12 ≥ -12 ∀ x
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x = -3
=> MinB = -12 <=> x = -3
C = ( x - 1 )( x - 3 ) + 9 = x2 - 4x + 3 + 9 = ( x2 - 4x + 4 ) + 8 = ( x - 2 )2 + 8 ≥ 8 ∀ x
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x = 2
=> MinC = 8 <=> x = 2
D = -x2 - 4x + 7 = -( x2 + 4x + 4 ) + 11 = -( x + 2 )2 + 11 ≤ 11 ∀ x
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x = -2
=> MaxD = 11 <=> x = -2

\(A=\left(x-1\right)^2+8\ge8\\ A_{min}=8\Leftrightarrow x=1\\ B=\left(x+3\right)^2-12\ge-12\\ B_{min}=-12\Leftrightarrow x=-3\\ C=x^2-4x+3+9=\left(x-2\right)^2+8\ge8\\ C_{min}=8\Leftrightarrow x=2\\ E=-\left(x+2\right)^2+11\le11\\ E_{max}=11\Leftrightarrow x=-2\\ F=9-4x^2\le9\\ F_{max}=9\Leftrightarrow x=0\)

a, \(A=x^4-2x^3+2x^2-2x+3\)
\(=\left(x^4+2x^2+1\right)-\left(2x^3+2x\right)+2\)
\(=\left(x^2+1\right)^2-2x\left(x^2+1\right)+2\)
\(=\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+2\)
\(=\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)^2+2\)
Vì \(\hept{\begin{cases}x^2\ge0\\\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x^2+1\ge1\\\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\end{cases}\Rightarrow}\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)^2+2\ge2\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x = 1
Vậy Amin = 2 khi x = 1
b, \(B=4x^2-2\left|2x-1\right|-4x+5=\left(4x^2-4x+1\right)-2\left|2x-1\right|+4=\left(2x-1\right)^2-2\left|2x-1\right|+4\)
đề sai ko
c, \(C=4-x^2+2x=-\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+5=-\left(x-1\right)^2+5\)
Vì \(-\left(x-1\right)^2\le0\Rightarrow C=-\left(x-1\right)^2+5\le5\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x=1
Vậy Cmin = 5 khi x = 1
2/
+) \(D=-x^2-y^2+x+y+3=-\left(x^2-x+\frac{1}{4}\right)-\left(y^2-y+\frac{1}{4}\right)+\frac{7}{2}=-\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-\left(y-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{7}{2}\)
Vì \(\hept{\begin{cases}-\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\le0\\-\left(y-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\le0\end{cases}\Rightarrow-\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-\left(y-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\le0}\Rightarrow D=-\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-\left(y-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{7}{2}\le\frac{7}{2}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x=y=1/2
Vậy Dmax=7/2 khi x=y=1/2
+) Đề sai
+)bài này là tìm min
\(G=x^2-3x+5=\left(x^2-3x+\frac{9}{4}\right)+\frac{11}{4}=\left(x-\frac{3}{2}\right)^2+\frac{11}{4}\ge\frac{11}{4}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x=3/2
Vậy Gmin=11/4 khi x=3//2
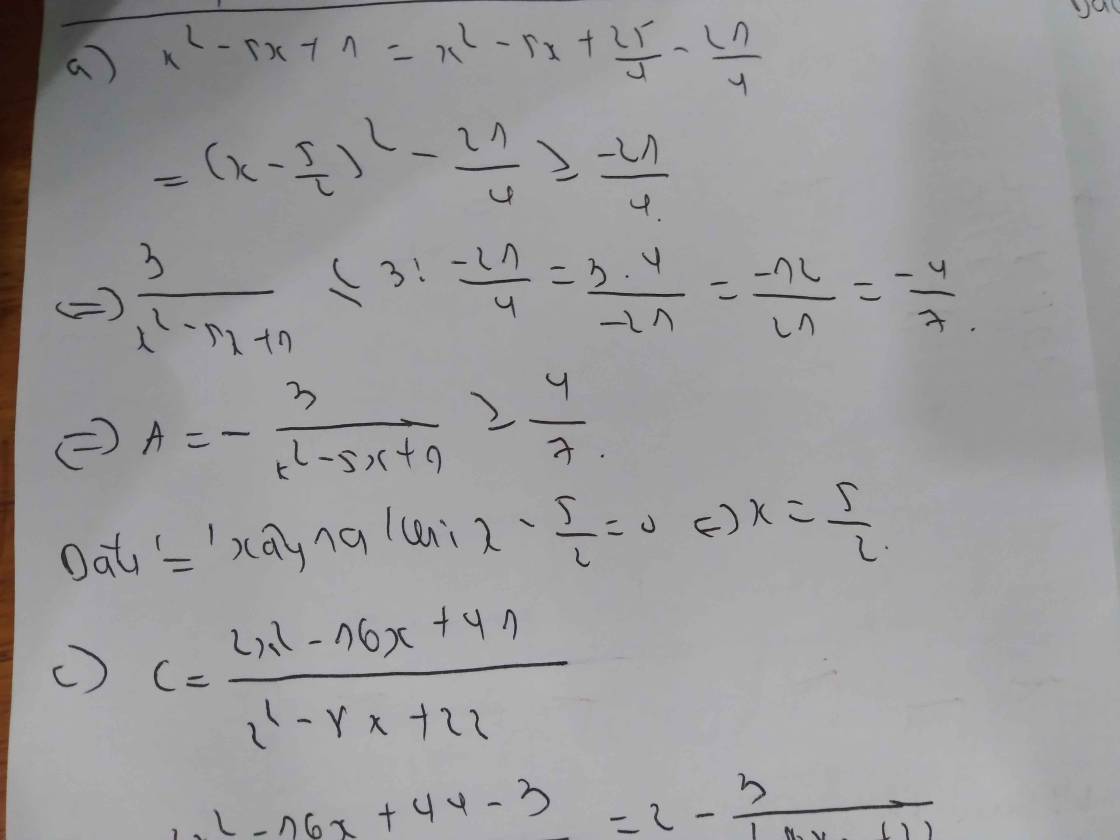
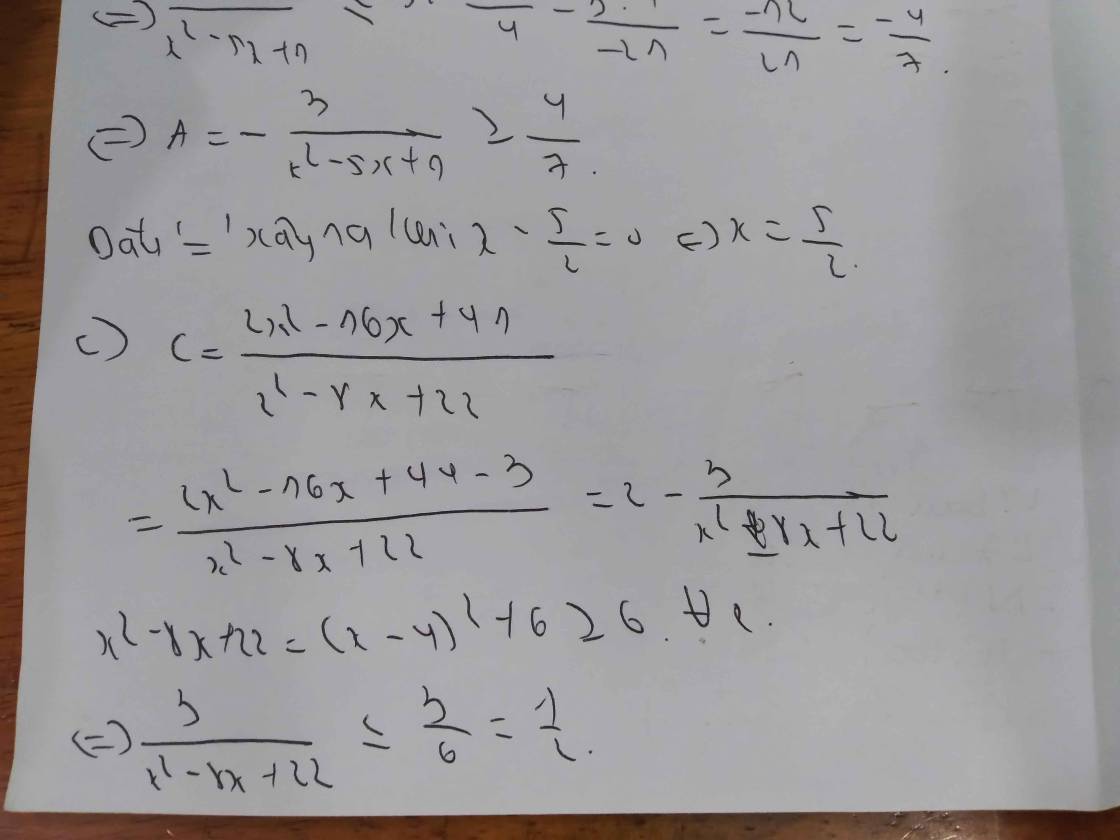
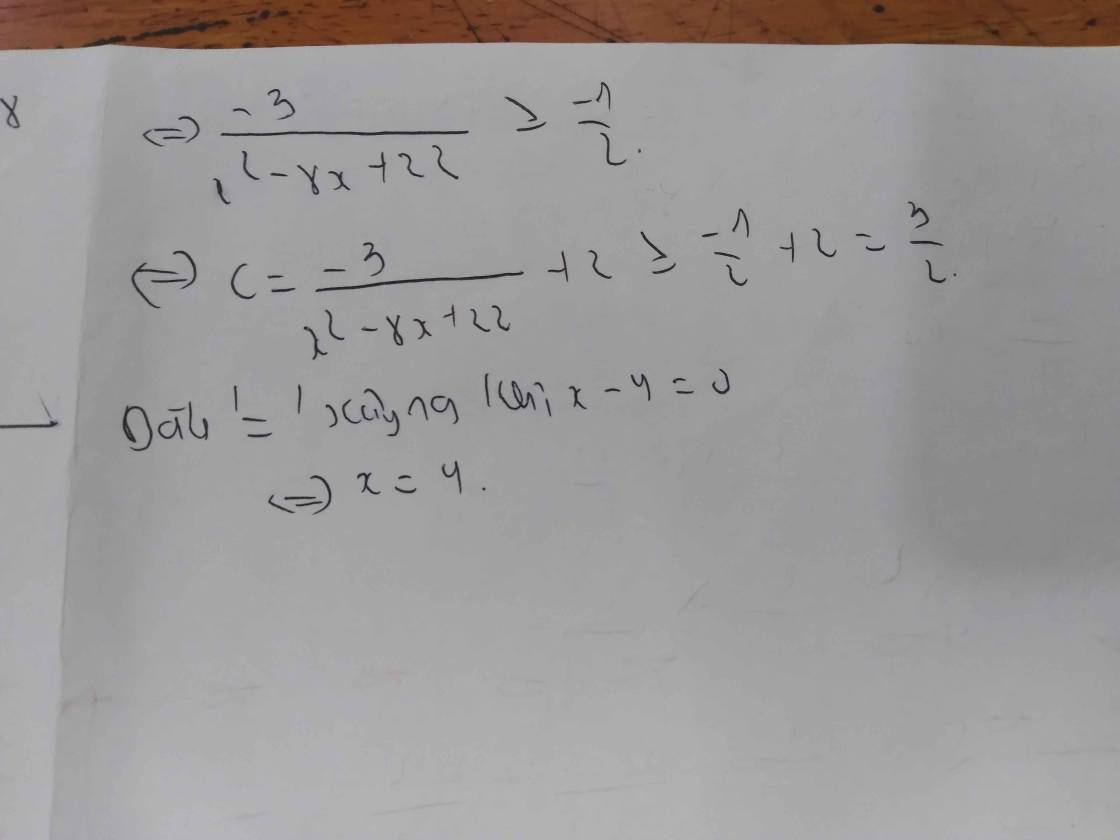
Ta có �2−4�+9=(�−2)2+5⩾5x2−4x+9=(x−2)2+5⩾5.
Suy ra �=1�2−4�+9=1(�−2)2+5⩽15B=x2−4x+91=(x−2)2+51⩽51.