Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

2) Xét pt hoành độ giao điểm chung của (d) và (P) có:
\(\frac{-1}{4}x^2=x-m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=-4x+4m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+4x-4m=0\)
\(\Delta^,=4+4m\)
Để (d) cắt (P) tại 2 điểm phân biệt \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta^,=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4+4m=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=-1\)
Vậy m=-1 thì (d) cắt (P) tại 2 điểm phân biệt

1) ĐK \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne y\\y\ge-1\end{cases}}\)
Đặt \(\hept{\begin{cases}\frac{1}{x-y}=a\left(a\ne0\right)\\\sqrt{y+1}=b\left(b\ge0\right)\end{cases}}\)hệ phương trình đã cho trở thành
\(\hept{\begin{cases}2a+b=4\\a-3b=-5\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2a+b=4\\2a-6b=-10\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}7b=14\\2a+b=4\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}a=1\\b=2\end{cases}\left(tm\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}\frac{1}{x-y}=1\\\sqrt{y+1}=2\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x-y=1\\y+1=4\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=4\\y=3\end{cases}}\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy ...

1) ĐK \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge0\\y\ne1\end{cases}}\)
Đặt \(\hept{\begin{cases}2\sqrt{x}=a\left(a\ge0\right)\\\frac{1}{y-1}=b\left(b\ne0\right)\end{cases}}\)hệ phương trình đã cho trở thành
\(\hept{\begin{cases}a+3b=5\\2a-b=3\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2a+6b=10\\2a-b=3\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}7b=7\\2a-b=3\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}a=2\\b=1\end{cases}\left(tm\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2\sqrt{x}=2\\\frac{1}{y-1}=1\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\y=2\end{cases}}\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy ...
1,\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\sqrt{x}+\dfrac{3}{y-1}=5\\4\sqrt{x}-\dfrac{1}{y-1}=3\end{matrix}\right.\) ĐKXĐ:x≥o,y≠1
⇔\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4\sqrt{x}+\dfrac{6}{y-1}=10\\4\sqrt{x}-\dfrac{1}{y-1}=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{7}{y-1}=7\\4\sqrt{x}-\dfrac{1}{y-1}=3\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y-1=1\\4\sqrt{x}-\dfrac{1}{y-1}=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y-1=1\\4\sqrt{x}-\dfrac{1}{1}=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=2\\4\sqrt{x}=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=2\\\sqrt{x}=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=2\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\left(TM\right)\)
vậy hpt đã cho có nghiệm duy nhất (x,y)=(1,2)
2,a, xét pthđgđ của (d) và (p) khi m=3:
x\(^2\)=3x-1⇔\(x^2-3x+1=0\)
Δ=(-3)\(^2\)-4.1.1=5>0
⇒pt có 2 nghiệm pb
\(x_1=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{5}}{2}\) ,\(x_2=\dfrac{3-\sqrt{5}}{2}\)
thay x=x\(_1\)=\(\dfrac{3+\sqrt{5}}{2}\) vào hs y=x\(^2\) ta được:
y=(\(\dfrac{3+\sqrt{5}}{2}\))\(^2\)=\(\dfrac{14+6\sqrt{5}}{4}\)⇒A(\(\dfrac{3+\sqrt{5}}{2},\dfrac{14+6\sqrt{5}}{4}\))
thay x=x\(_2\)=\(\dfrac{3-\sqrt{5}}{2}\) vào hs y=x\(^2\) ta được:
y=\(\left(\dfrac{3-\sqrt{5}}{2}\right)^2=\dfrac{14-6\sqrt{5}}{4}\)⇒B(\(\dfrac{3-\sqrt{5}}{2},\dfrac{14-6\sqrt{5}}{4}\))
vậy tọa độ gđ của (d) và (p) là A(\(\dfrac{3+\sqrt{5}}{2},\dfrac{14+6\sqrt{5}}{4}\)) và B (\(\dfrac{3-\sqrt{5}}{2},\dfrac{14-6\sqrt{5}}{4}\))
b,xét pthđgđ của (d) và (p) :
\(x^2=mx-1\)⇔\(x^2-mx+1=0\) (*)
Δ=(-m)\(^2\)-4.1.1=m\(^2\)-4
⇒pt có hai nghiệm pb⇔Δ>0
⇔m\(^2\)-4>0⇔m>16
với m>16 thì pt (*) luôn có hai nghiệm pb \(x_1,x_2\)
theo hệ thức Vi-ét ta có:
(I) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=m\\x_1.x_2=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1,x_2\) TM \(x_2\)(x\(_1\)\(^2\)+1)=3
⇒\(x_2.x_1^2\)+\(x_2\)=3⇔\(x_2.x_1.x_1+x_2=3\)⇔(\(x_2.x_1\))(\(x_1+x_2\))=3 (**)
thay (I) vào (**) ta được:
1.m=3⇔m=3 (TM m≠0)
vậy m=3 thì (d) cắt (p) tại hai điểm pb có hoanh độ \(x_1.x_2\) TM \(x_2\)(\(x_1^2+1\))=3

1/
\(\hept{\begin{cases}3x+4y=6\left(1\right)\\2x-y=-7\left(2\right)\end{cases}}\)
\(\left(2\right)\Leftrightarrow8x-4y=-28\left(3\right)\)
Cộng 2 vế của (1) với (3) \(\Rightarrow11x=-22\Rightarrow x=-2\) Thay vào (2) \(\Rightarrow2.\left(-2\right)-y=-7\Rightarrow y=3\)
2/
a/ d cắt p tại 2 điểm phân biệt khi \(x^2=5x+m\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x-m=0\) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
Điều kiện \(\Delta=25+4m>0\Leftrightarrow m>-\frac{25}{4}\)
b/ Khi m=-4
\(x^2-5x+4=0\Rightarrow x_1=1;x_2=4\)
Khi m=-4 d cắt p tại 2 điểm phân biệt A(1;0) và B(4;0)

a)\(x^2-\left(m+2\right)x+m=0\)
(a=1;b=-(m+2);c=m)
Ta có:\(\Delta=\left[-\left(m+2\right)\right]^2-4.1.m\)
\(=\left(m+2\right)^2-4m\)
\(=m^2+2m.2+2^2-4m\)
\(=m^2+4m+4-4m\)
\(=m^2+4\)
Vì\(m^2\ge0\forall m\Rightarrow m^2+4m\ge0\left(1\right)\)
Vậy pt luôn có nghiện với mọi m
b,Xét hệ thức vi-ét,ta có:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x_1+x_2=m+2\\x_1.x_2=m\end{cases}}\)
Theo đề bài ,ta có:
\(x_1+x_2-3x_1x_2=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m+2-3m=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2m+2=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2m=2-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=0\)[t/m(1)]
Vậy với m=0 thì pt thảo mãn điều kiện đề bài cho
a, Ta có : \(\Delta=\left(m+2\right)^2-4m=m^2+4m+4-4m=m^2+4>0\forall m\)
b, Theo Vi et ta có : \(\hept{\begin{cases}x_1+x_2=-\frac{b}{a}=m+2\\x_1x_2=\frac{c}{a}=m\end{cases}}\)
Lại có : \(x_1+x_2-3x_1x_2=2\Rightarrow m+2-3m=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2m=0\Leftrightarrow m=0\)

a:
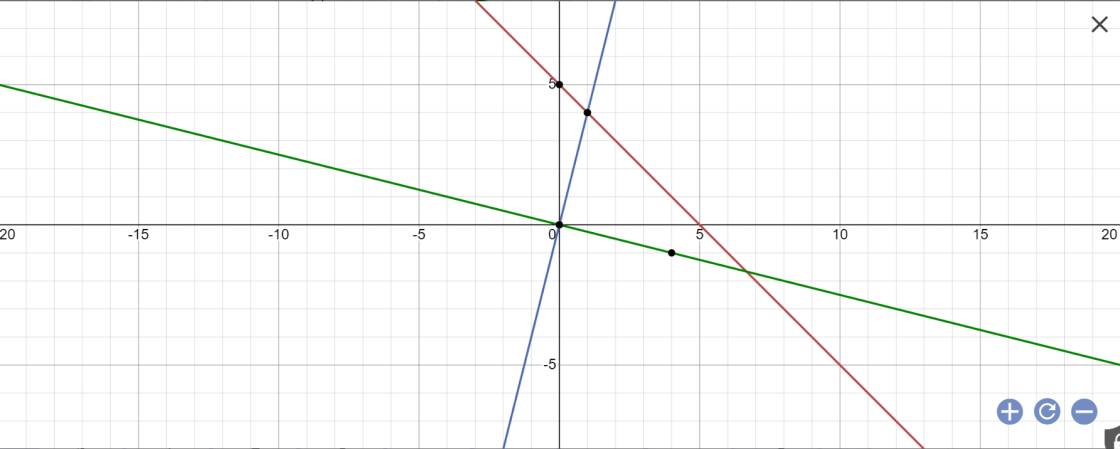
b: tọa độ A là;
-x+5=4x và y=4x
=>x=1 và y=4
Tọa độ B là;
-x+5=-1/4x và y=-1/4x
=>-3/4x=-5 và y=-1/4x
=>x=5:3/4=5*4/3=20/3 và y=-1/4*20/3=-5/3
=>B(20/3;-5/3)
c: O(0;0); A(1;4); B(20/3;-5/3)
\(OA=\sqrt{1^2+4^2}=\sqrt{17}\)
\(OB=\sqrt{\left(\dfrac{20}{3}\right)^2+\left(-\dfrac{5}{3}\right)^2}=\dfrac{5\sqrt{17}}{3}\)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(\dfrac{20}{3}-1\right)^2+\left(-\dfrac{5}{3}-4\right)^2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{818}}{3}\)
\(cosAOB=\dfrac{OA^2+OB^2-AB^2}{2\cdot OA\cdot OB}=\dfrac{-8}{17}\)
=>góc AOB tù
=>ΔOAB tù

c: Gọi (d): y=ax+b(a<>0) là phương trình đường thẳng cần tìm
Vì (d)//(d1) nên \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\dfrac{1}{2}\\b\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: (d): \(y=\dfrac{1}{2}x\)+b
Thay x=4 và y=5 vào (d), ta được:
\(b+\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot4=5\)
=>b+2=5
=>b=3
Vậy: (d): \(y=\dfrac{1}{2}x+3\)