
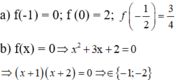
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

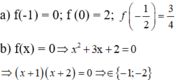

\(\text{1)}\)
\(\text{Thay }x=-2,\text{ ta có: }f\left(-2\right)-5f\left(-2\right)=\left(-2\right)^2\Rightarrow f\left(-2\right)=-1\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=x^2+5f\left(-2\right)=x^2-5\)
\(f\left(3\right)=3^2-5\)
\(\text{2)}\)
\(\text{Thay }x=1,\text{ ta có: }f\left(1\right)+f\left(1\right)+f\left(1\right)=6\Rightarrow f\left(1\right)=2\)
\(\text{Thay }x=-1,\text{ ta có: }f\left(-1\right)+f\left(-1\right)+2=6\Rightarrow f\left(-1\right)=2\)
\(\text{3)}\)
\(\text{Thay }x=2,\text{ ta có: }f\left(2\right)+3f\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)=2^2\text{ (1)}\)
\(\text{Thay }x=\frac{1}{2},\text{ ta có: }f\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)+3f\left(2\right)=\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\text{ (2)}\)
\(\text{(1) - 3}\times\text{(2) }\Rightarrow f\left(2\right)+3f\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)-3f\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)-9f\left(2\right)=4-\frac{1}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow-8f\left(2\right)=\frac{15}{4}\Rightarrow f\left(2\right)=-\frac{15}{32}\)

a) Thay f(0);f(\(-\frac{1}{2}\)) vào f(x)=2-x2 ta được:
\(f\left(0\right)=2-0^2=2\)
\(f\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right)=2-\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2=\frac{7}{4}\)
b) y = f(x) = 2-x2
Ta có f(x-1) = 2- (x-1)2
f(1-x) = 2 - (1-x)2 = 2 - (x-1)2
nên f(x-1) = f(1-x)


\(f\left(2\right)=2^2-2=2\)
\(f\left(1\right)=1^2-2=-1\)
\(f\left(0\right)=0^2-2=-2\)
\(f\left(-1\right)=\left(-1\right)^2-2=-1\)
\(f\left(7\right)=7^2-2=47\)
Ta có : y=f(x) =x\(^2\) - 2

a) * f(-2)
=-2.(-2)+1
=2
* f(3)
=-2.3+1
=-5
b) hàm số y=-2x+1
với x=-1 thì y=3 không bằng 1
Vậy M(-1,1)ko thuộc đồ thị hàm số f(x)
c) ta có 1>0
=> -2x+1=1
-2x=1-1
-2x=0
x=0/(-2)
x=0
=> x=0
vậy x=0 thì f(x)>0
nhớ k giùm mình nha
a)\(F\left(-2\right)=-2.\left(-2\right)+1=5\)
\(F\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)=-2.\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)+1=0\)
\(F\left(3\right)=-2.3+1=-5\)
\(F\left(1\right)=-2.1+1=-1\)

a)f(−1)=−1−2=−3f(0)=0−2=−2f(−1)=−1−2=−3f(0)=0−2=−2
b) Ta có phương trình:
x−2=0⇔x=2

a: Theo đề, ta có hệ phương trình:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{2}a\cdot\left(-4\right)+b=-3\\\dfrac{1}{2}a\cdot0+b=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-2a+b=-3\\b=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b=-3\\a=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: f(x)=-3
b: f(1)=f(2)=f(-2)=f(-1)=-3
c: Đặt y=4
=>f(x)=4
=>-3=4(vô lý)