Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a)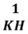
Gọi x là hóa trị của K
Theo quy tắc hóa trị ta có
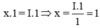
Vậy hóa trị của K là I.
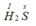
Gọi x là hóa trị của S
Theo quy tắc hóa trị ta có
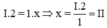
Vậy hóa trị của S là II
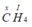
Gọi x là hóa trị của C
Theo quy tắc hóa trị ta có
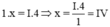
Vậy hóa trị của C là IV
b) 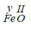
Gọi y là hóa trị của Fe
Theo quy tắc hóa trị ta có
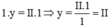
Vậy hóa trị của Fe là II
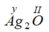
Gọi y là hóa trị của Ag
Theo quy tắc hóa trị ta có
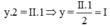
Vậy hóa trị của Ag là I
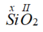
Gọi hóa trị của Si là y
Theo quy tắc hóa trị ta có
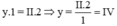
Vậy hóa trị của Si là IV

Câu 11:
\(a,Na_2O,MgO,SO_2,Al_2O_3,P_2O_5,CuO,CaO\\ b,KCl,BaCl_2,FeCl_3,ZnCl_2\\ c,Na_2SO_4,Al_2\left(SO_4\right)_3,CuSO_4,FeSO_4,ZnSO_4\)
Câu 7:
\(a,\) Gọi hóa trị Fe,Cu,SO4 trong các HC lần lượt là x,y,z(x,y,z>0)
\(Fe_1^xCl_3^I\Rightarrow x=I\cdot3=3\Rightarrow Fe\left(III\right)\\ Fe_1^xO_1^{II}\Rightarrow x=II\cdot1=2\Rightarrow Fe\left(II\right)\\ Cu_2^yO_1^{II}\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{II\cdot1}{2}=1\Rightarrow Cu\left(I\right)\\ Cu_1^y\left(NO_3\right)_2^I\Rightarrow y=I\cdot2=2\Rightarrow Cu\left(II\right)\\ Na_2^I\left(SO_4\right)_1^z\Rightarrow z=I\cdot2=2\Rightarrow SO_4\left(II\right)\)
\(b,\) Gọi hóa trị S,N trong các HC lần lượt là a,b(a,b>0)
\(S_1^aO_3^{II}\Rightarrow a=II\cdot3=6\Rightarrow S\left(VI\right)\\ H_2^IS_1^a\Rightarrow a=I\cdot2=2\Rightarrow S\left(II\right)\\ N_2^bO_1^{II}\Rightarrow b=\dfrac{II\cdot1}{2}=1\Rightarrow N\left(I\right)\\ N_1^bO_1^{II}\Rightarrow b=II\cdot1=2\Rightarrow N\left(II\right)\\ N_1^bO_2^{II}\Rightarrow b=II\cdot2=4\Rightarrow N\left(IV\right)\\ N_2^bO_5^{II}\Rightarrow b=\dfrac{II\cdot5}{2}=5\Rightarrow N\left(V\right)\)

Bài 11:
\(a,Na_2O;MgO;SO_2;Al_2O_3;P_2O_5;CuO;CaO\\ b,KCl;BaCl_2;FeCl_3;ZnCl_2\\ c,Na_2SO_4;Al_2\left(SO_4\right)_3;FeSO_4;ZnSO_4\)
Câu C mình nghĩ nên đổi \(C\rightarrow Cu\) thì sẽ đc \(CuSO_4\)

phần khái niệm thì bạn có thể tham khảo trong SGK nhé!
3. gọi hóa trị của các nguyên tố cần tìm là \(x\)
\(\rightarrow Cu_1^x\left(OH\right)_2^I\rightarrow x.1=I.2\rightarrow x=II\)
vậy \(Cu\) hóa trị \(II\)
\(\rightarrow P_1^xCl^I_5\rightarrow x.1=I.5\rightarrow x=V\)
vậy \(P\) hóa trị \(V\)
\(\rightarrow Si^x_1O_2^{II}\rightarrow x.1=II.2\rightarrow x=IV\)
vậy \(Si\) hóa trị \(IV\)
\(\rightarrow Fe_1^x\left(NO_3\right)_2^I\rightarrow x.1=I.2\rightarrow x=II\)
vậy \(Fe\) hóa trị \(II\)
4.
a. \(SiO_2\)
b. \(PH_3\)
c. \(CaSO_4\)
5. gọi hóa trị của \(X\) và \(Y\) là \(x\)
\(\rightarrow Y_1^x\left(PO_4\right)_1^{III}\rightarrow x.1=III.1\rightarrow x=III\)
vậy \(Y\) hóa trị \(III\)
\(\rightarrow X_1^x\left(OH\right)_2^I\rightarrow x.1=I.2\rightarrow x=II\)
vậy \(X\) hóa trị \(II\)
ta có CTHH: \(X^{II}_xY^{III}_y\)
\(\rightarrow II.x=III.y\rightarrow\dfrac{x}{y}=\dfrac{III}{II}=\dfrac{3}{2}\rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\rightarrow CTHH:X_3Y_2\)

Gọi hóa trị của các chất cần tính là a. Ta có:
- Cu(OH)2 1.a = I x 2 ⇒ a = II
Hay Cu có hóa trị II.
- PCl5 1.a = I x 5 ⇒ a = V
Hay P có hóa trị V.
- SiO2 1.a = II x 2 ⇒ a = IV
Hay Si có hóa trị IV.
- Fe(NO3)3 1.a = I x 3 ⇒ a = III
Hay Fe có hóa trị III.

K2O:Kali oxit
KOH:Kali hiđroxit
KNO3:Kali Nitrat
Cu(NO3)2:Đồng(II) nitrat
H2CO3:Axit cacbonic
H2S:Hydro sulfua
FeCl2:Sắt (II) clorua
Ba(OH)2:Bari hydroxit
AL2O3:Nhôm ôxít
Al(OH)3:Nhôm hydroxit
CaSO3:Canxi sunfit
ZnO:Kẽm ôxít
AgNO3:Bạc nitrat
Fe(OH)3 :Sắt(III) hidroxit
Pb(NO3)2:Chì(II) nitrat Ag2O:Bạc oxit BaSO4:Bari sunfat SiO2:Silic điôxít MnCl2:Mangan(II) clorua MgSO4:Magie sulfatK2O: Kali oxit
KOH :kali hidro xit
KNO3: kalinitrat
H2CO3: axit cacbonat
H2S: hiddro sunfua
FeCl2: Sắt (II) clo rua
BaO : bari oxit
Ba(OH)2: bari hidroxit
Al2O3: nhôm oxit
Al(OH)3: nhôm hidroxit
CaSO3 : Canxi sunfua
ZnO: kẽm oxit
AgNO3 :bạc nitrat
Fe(OH)3: Sắt (III) hidroxit
Pb(NO3)2 : chì nitrat
Ag2O: Bạc oxit
BaSO4 : bari sunfat
SiO2: Silic oxxit
MnCl2 : Mangan clorua
MgSO4 : magie sunfat
a) Ag2O: Ag (I); O(II)
SiO2: Si(IV) O(II)
b) CH4: C(IV), H(I)
H2S: H(I), S(II)
c) Cu(OH)2: Cu(II) OH(I)
Fe(NO)3: Fe(III), NO3(I)