Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Câu 2:
a) Ta có: \(x^4\ge0\forall x\)
\(3x^2\ge0\)
Do đó: \(x^4+3x^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow x^4+3x^2+2\ge2\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi
\(x^4+3x^2=0\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2+3\right)=0\)
Vì \(x^2\ge0\forall x\)
nên \(x^2+3\ge3>0\forall x\)
Do đó: \(x^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
Vậy: GTNN của biểu thức \(A=x^4+3x^2+2\) là 2 khi x=0
b)\(B=\left(x^4+5\right)^2\)
Ta có: \(x^4\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow x^4+5\ge5\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x^4+5\right)^2\ge25\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi
\(x^4+5=5\Leftrightarrow x^4=0\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
Vậy: GTNN của biểu thức \(B=\left(x^4+5\right)^2\) là 25 khi x=0
c) \(C=\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(y+2\right)^2-2\)
Ta có: \(\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\left(y+2\right)^2\ge0\forall y\)
Do đó: \(\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(y+2\right)^2\ge0\forall x,y\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(y+2\right)^2-2\ge-2\forall x,y\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-1\right)^2=0\\\left(y+2\right)^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\y+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: GTNN của biểu thức \(C=\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(y+2\right)^2-2\) là -2 khi x=1 và y=-2
Câu 3:
a) \(A=5-3\left(2x-1\right)^2\)
Ta có: \(A=5-3\left(2x-1\right)^2=-3\left(2x-1\right)^2+5\)
Ta có: \(\left(2x-1\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow-3\left(2x-1\right)^2\le0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow-3\left(2x-1\right)^2+5\le5\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi
\(\left(2x-1\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow2x-1=0\Leftrightarrow2x=1\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{1}{2}\)
Vậy: GTLN của biểu thức \(A=5-3\left(2x-1\right)^2\) là 5 khi \(x=\frac{1}{2}\)
b) \(B=\frac{1}{2\left(x-1\right)^2+3}\)
Ta có: \(\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow2\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow2\left(x-1\right)^2+3\ge3\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{1}{2\left(x-1\right)^2+3}\le\frac{1}{3}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi
\(\left(x-1\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x-1=0\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Vậy: GTLN của biểu thức \(B=\frac{1}{2\left(x-1\right)^2+3}\) là \(\frac{1}{3}\) khi x=1
c) \(C=\frac{x^2+8}{x^2+2}\)
Ta có: \(C=\frac{x^2+8}{x^2+2}=\frac{x^2+2+6}{x^2+2}=1+\frac{6}{x^2+2}\)
Ta có: \(x^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+2\ge2\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{6}{x^2+2}\le3\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow1+\frac{6}{x^2+2}\le4\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi
\(x^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
Vậy: Giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức \(C=\frac{x^2+8}{x^2+2}\) là 4 khi x=0

Làm tiếp nè :
2) / 2x + 4/ = 2x - 5
Do : / 2x + 4 / ≥ 0 ∀x
⇒ 2x - 5 ≥ 0
⇔ x ≥ \(\dfrac{5}{2}\)
Bình phương hai vế của phương trình , ta có :
( 2x + 4)2 = ( 2x - 5)2
⇔ ( 2x + 4)2 - ( 2x - 5)2 = 0
⇔ ( 2x + 4 - 2x + 5)( 2x + 4 + 2x - 5) = 0
⇔ 9( 4x - 1) = 0
⇔ x = \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) ( KTM)
Vậy , phương trình vô nghiệm .
3) / x + 3/ = 3x - 1
Do : / x + 3 / ≥ 0 ∀x
⇒ 3x - 1 ≥ 0
⇔ x ≥ \(\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Bình phương hai vế của phương trình , ta có :
( x + 3)2 = ( 3x - 1)2
⇔ ( x + 3)2 - ( 3x - 1)2 = 0
⇔ ( x + 3 - 3x + 1)( x + 3 + 3x - 1) = 0
⇔ ( 4 - 2x)( 4x + 2) = 0
⇔ x = 2 (TM) hoặc x = \(\dfrac{-1}{2}\) ( KTM)
KL......
4) / x - 4/ + 3x = 5
⇔ / x - 4/ = 5 - 3x
Do : / x - 4/ ≥ 0 ∀x
⇒ 5 - 3x ≥ 0
⇔ x ≤ \(\dfrac{-5}{3}\)
Bình phương cả hai vế của phương trình , ta có :
( x - 4)2 = ( 5 - 3x)2
⇔ ( x - 4)2 - ( 5 - 3x)2 = 0
⇔ ( x - 4 - 5 + 3x)( x - 4 + 5 - 3x) = 0
⇔ ( 4x - 9)( 1 - 2x) = 0
⇔ x = \(\dfrac{9}{4}\) ( KTM) hoặc x = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) ( KTM)
KL......
Làm tương tự với các phần khác nha
1)\(\left|4x\right|=3x+12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4.\left|x\right|=3x+12\\ \Leftrightarrow4.\left|x\right|-3x=12\)
\(TH1:4x-3x=12\left(x\ge0\right)\\\Leftrightarrow x=12\left(TM\right) \)
\(TH2:4.\left(-x\right)-3x=12\left(x< 0\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow-7x=12\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{12}{7}\left(TM\right)\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của PT: \(S=\left\{12;-\dfrac{12}{7}\right\}\)

Bài 3:
a: \(\Leftrightarrow M=6x^2+9xy-y^2-5x^2+2xy=x^2+11xy-y^2\)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow N=3xy-4y^2-x^2+7xy-8y^2=-x^2+10xy-12y^2\)
Bài 2:
\(A+B=4x^4-5xy+5y^2+3x^2+2xy-y=4x^4+3x^2-3xy+5y^2-y\)
\(A-B=4x^4-5xy+5y^2-3x^2-2xy+y=4x^4-3x^2+5y^2-7xy+y\)
\(B-A=-\left(A-B\right)=-4x^4+3x^2-5y^2+7xy-y\)

a/ Ta có \(x^2\ge0\)với mọi giá trị của x
=> \(x^2+5x\ge0\)với mọi giá trị của x
=> \(x^2+5x-17\ge0-17=-17\)với mọi giá trị của x.
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(x^2+5x=0\)
=> \(x\left(x+5\right)=0\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x+5=0\end{cases}}\)=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=-5\end{cases}}\)
Vậy f (x) có GTNN là -17 khi \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=-5\end{cases}}\).

f(x) + g(x) - h(x) = (x5 - 4x3 + x2 - 2x + 1) + (x5 - 2x4 + x2 - 5x + 3) - (x4 - 3x2 + 2x - 5)
= x5 - 4x3 + x2 - 2x + 1 + x5 - 2x4 + x2 - 5x + 3 - x4 + 3x2 - 2x + 5
= (x5 + x5) - (2x4 + x4) - 4x3 + ( x2 + x2 + 3x2) - (2x + 5x + 2x) + (1 + 3 + 5)
= 2x5 - 3x4 - 4x3 + 5x2 - 9x + 9
f(x)=
f(x) + g(x) - h(x) = (x5 - 4x3 + x2 - 2x + 1) + (x5 - 2x4 + x2 - 5x + 3) - (x4 - 3x2 + 2x - 5)
= x5 - 4x3 + x2 - 2x + 1 + x5 - 2x4 + x2 - 5x + 3 - x4 + 3x2 - 2x + 5
= (x5 + x5) - (2x4 + x4) - 4x3 + ( x2 + x2 + 3x2) - (2x + 5x + 2x) + (1 + 3 + 5)
= 2x5 - 3x4 - 4x3 + 5x2 - 9x + 9

2: Ta có: |x-1|+|x-2|=5(1)
Trường hợp 1: x<1
(1) trở thành 1-x+2-x=5
=>-2x+3=5
=>-2x=2
hay x=-1(nhận)
Trường hợp 2: 1<=x<2
(1) trở thành x-1+2-x=5
=>1=5(vô lý)
Trường hợp 3: x>=2
(1) trở thành x-1+x-2=5
=>2x-3=5
hay x=4(nhận)
3: |x-3|+|x+1|=10(2)
Trường hợp 1: x<-1
(2) trở thành -x-1+3-x=10
=>-2x+2=10
=>-2x=8
hay x=-4(nhận)
Trường hợp 2: -1<=x<3
(2) trở thành x+1+3-x=10
=>4=10(vô lý)
Trường hợp 3: x>=3
(2) trở thành x-3+x+1=10
=>2x-2=10
hay x=6(nhận)

Ta có:
P(x) = 2x4 –x - 2x3 + 1
Q(x) = 5x2 – x3 + 4x
H(x) = -2x4 + x2 + 5.
Sắp xếp các đa thức theo lũy thừa giảm dần rồi xếp các số hạng đồng dạng theo cùng cột dọc ta được:
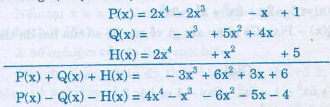
ta có:
P(x) = 2x4 –x – 2x3 + 1
Q(x) = 5x2 – x3 + 4x
H(x) = -2x4 + x2 + 5.
Sắp xếp các đa thức theo lũy thừa giảm dần rồi xếp các số hạng đồng dạng theo cùng cột dọc ta được:

1)
\(A=-5x^2-4x+1\)
\(A=-5\left(x^2+\dfrac{4}{5}x-\dfrac{1}{5}\right)\)
\(A=-5\left(x^2+\dfrac{4}{5}x+\dfrac{4}{25}-\dfrac{9}{25}\right)\)
\(A=-5\left[\left(x+\dfrac{2}{5}\right)^2-\dfrac{9}{25}\right]\)
\(A=-\left(x+\dfrac{2}{5}\right)^2+\dfrac{9}{25}\le\dfrac{9}{25}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi:
\(x=-\dfrac{2}{5}\)
2)
\(A=\left(x-1\right)\left(x-4\right)\left(x-5\right)\left(x-8\right)\)
\(A=\left[\left(x-1\right)\left(x-8\right)\right]\left[\left(x-4\right)\left(x-5\right)\right]\)
\(A=\left[x\left(x-8\right)-1\left(x-8\right)\right]\left[x\left(x-5\right)-4\left(x-5\right)\right]\)
\(A=\left(x^2-8x-x+8\right)\left(x^2-5x-4x+20\right)\)
\(A=\left(x^2-9x+8\right)\left(x^2-9x+20\right)\)
\(A=\left(x^2-9x+14-6\right)\left(x^2-9x+14+6\right)\)
\(A=\left(x^2-9x+14\right)^2-36\ge-36\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi:
\(x^2-9x+14=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-7x+14=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)-7\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-7\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=7\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy...
\(A=−5x^2−4x+1 \)
=\(-5\left(x^2+\dfrac{4}{5}x-\dfrac{1}{5}\right)\)=\(-5\left(x^2+\dfrac{4}{5}+\dfrac{4}{25}-\dfrac{9}{25}\right)\)
=\(-5\left(x+\dfrac{2}{5}\right)^2+\dfrac{9}{5}\)
Với mọi giá trị của x thì \(-5\left(x+\dfrac{2}{5}\right)^2\)nhỏ hơn hoặc bằng 0
=>\(\dfrac{9}{5}-5\left(x+\dfrac{2}{5}\right)^2\)nhỏ hơn hoặc bằng \(\dfrac{9}{5}\)
Hay Anhỏ hơn hoặc bằng \(\dfrac{9}{5}\)
Để A\(=\dfrac{9}{5}\)thì \(\left(x+\dfrac{2}{5}\right)^2=0\)
=>.\(x+\dfrac{2}{5}=0\)=>\(x=-\dfrac{2}{5}\)
Vậy ....
Theo mk câu 1 bác kia giải sai nhé