
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a)+1+1x=xx+1x=x+1x1+1x=xx+1x=x+1x
Áp dụng câu a) ta có :
1+11+1x=1+1x+1x=1+xx+1=x+1+x1+x=2x+1x+11+11+1x=1+1x+1x=1+xx+1=x+1+x1+x=2x+1x+1
Dùng kết quả câu b) ta có :
1+11+11+1x=1+12x+1x+1=1+x+12x+1=2x+1+x+12x+1=3x+22x+11+11+11+1x=1+12x+1x+1=1+x+12x+1=2x+1+x+12x+1=3x+22x+1
b)Đối với các biểu thức có dạng đã cho có thể dự đoán như sau :
Qua các kết quả của các bài ở câu a ta thấy kết quả tiếp theo sau là một phân thức mà tử bằng tổng của tử và mẫu, còn mẫu là tử của kết quả vế trước đó.
Như vậy có thể dự đoán rằng nếu biểu thức có 4 gạch phân số thì kết quả là 5x+33x+25x+33x+2, và trong trường hợp này có 5 gạch phân số, kết quả sẽ là 8x+55x+38x+55x+3 .
Thật vậy : 1+11+11+11+11+1x=1+13x+22x+1=1+2x+13x+2=3x+2+2x+13x+2=5x+33x+21+11+11+11+11+1x=1+13x+22x+1=1+2x+13x+2=3x+2+2x+13x+2=5x+33x+2
Do đó 1+11+11+11+11+1x=1+15x+33x+21+11+11+11+11+1x=1+15x+33x+2

a, Ta có : \(\dfrac{98x^2-2}{x-2}=0\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}98x^2-2=0\\x-2\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
hay \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2=\dfrac{1}{49}\\x\ne2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\dfrac{1}{7}\)
Vậy giá trị của phân thức này bằng 0 khi \(x=\pm\dfrac{1}{7}\)
b, Ta có : \(\dfrac{3x-2}{x^2+2x+1}=0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x-2}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=0\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-2=0\\\left(x+1\right)^2\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
hay \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\x\ne-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy giá trị của phân thức này bằng 0 khi \(x=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
a)
98x^2 -2 =0 =>x^2 =1/49 => x= -+1/7 nhận
b)
3x-2=0=>x=2/3 nhận

Bài 7:(Sbt/25) Dùng tính chất cơ bản của phân thức hoặc quy tắc đổi dấu để biến mỗi cặp phân thức sau thành một cặp phân thức bằng nó và có cùng mẫu thức :
a. \(\dfrac{3x}{x-5}\) và \(\dfrac{7x+2}{5-x}\)
Ta có:
\(\dfrac{3x}{x-5}=\dfrac{-\left(3x\right)}{-\left(x-5\right)}=\dfrac{-3x}{5-x}\)
\(\dfrac{7x+2}{5-x}\)
Vậy .....
b.\(\dfrac{4x}{x+1}\) và \(\dfrac{3x}{x-1}\)
Ta có:
\(\dfrac{4x}{x+1}=\dfrac{4x\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{4x^2-4x}{x^2-1}\)
\(\dfrac{3x}{x-1}=\dfrac{3x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{3x^2+3x}{x^2-1}\)
Vậy ..........
c. \(\dfrac{2}{x^2+8x+16}\) và \(\dfrac{x-4}{2x+8}\)
Ta có:
\(\dfrac{2}{x^2+8x+16}=\dfrac{4}{2\left(x+4\right)^2}\)
\(\dfrac{x-4}{2x+8}=\dfrac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)}{2\left(x+4\right)\left(x+4\right)}=\dfrac{x^2-16}{2\left(x+4\right)^2}\)
Vậy .........
d. \(\dfrac{2x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\) và \(\dfrac{x+3}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
Ta có:
\(\dfrac{2x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{2x\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{2x^2-4x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{x+3}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{x^2-9}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
Vậy .........

a/ \(1-\dfrac{1}{1-\dfrac{1}{x}}=1-\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{x-1}{x}}=1-\dfrac{x}{x-1}=\dfrac{x-1-x}{x-1}=\dfrac{-1}{x-1}\)
b/ \(\dfrac{\dfrac{x}{x+1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x}}{\dfrac{x}{x-1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{x^2-\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x.\left(x+1\right)}}{\dfrac{x^2-\left(x-1\right)^2}{x.\left(x-1\right)}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{x^2-x^2+1}{x.\left(x+1\right)}}{\dfrac{x^2-x^2+2x-1}{x.\left(x-1\right)}}\)
\(=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{x.\left(x+1\right)}}{\dfrac{2x-1}{x.\left(x-1\right)}}=\dfrac{1}{x.\left(x+1\right)}:\dfrac{2x-1}{x.\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x.\left(x-1\right)}{x.\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-1}{2x^2-x+2x-1}=\dfrac{x-1}{2x^2+x-1}\)
a) \(1-\dfrac{1}{1-\dfrac{1}{x}}=1-\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{x-1}{x}}=\dfrac{x-1-x}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{-1}{x-1}\)
b) \(\dfrac{\dfrac{x}{x+1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x}}{\dfrac{x}{x-1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{x^2-\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}}{\dfrac{x^2-\left(x-1\right)^2}{x\left(x-1\right)}}\)
\(=\dfrac{\dfrac{x^2-\left(x^2-1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}}{\dfrac{x^2-\left(x-1\right)^2}{x\left(x-1\right)}}=\dfrac{x-1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x^2+2x-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-1}{2x^2+x-1}\)

Bài 6:(Sbt/25) Dùng tính chất cơ bản của phân thức để biến đổi mỗi cặp phân thức sau thành một cặp phân thức bằng nó và có cùng tử thức :
a) \(\dfrac{3}{x+2}\)và\(\dfrac{x-1}{5x}\)
Ta có:
\(\dfrac{3}{x+2}\) = \(\dfrac{3.\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{3x-3}{x^2+x-2}\)
\(\dfrac{x-1}{5x}\) = \(\dfrac{\left(x-1\right).3}{5x.3}\) =\(\dfrac{3x-3}{15x}\)
Vậy .....
b. \(\dfrac{x+5}{4x}\) và \(\dfrac{x^2-25}{2x+3}\)
Ta có:
\(\dfrac{x+5}{4x}\) = \(\dfrac{\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)}{4x.\left(x-5\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{x^2-25}{4x^2-20x}\)
\(\dfrac{x^2-25}{2x+3}\)
Vậy .....
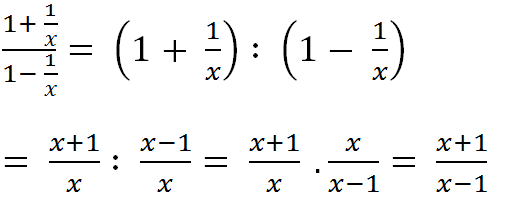
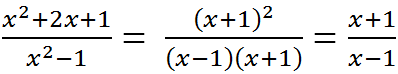

\(\dfrac{x}{0}\)