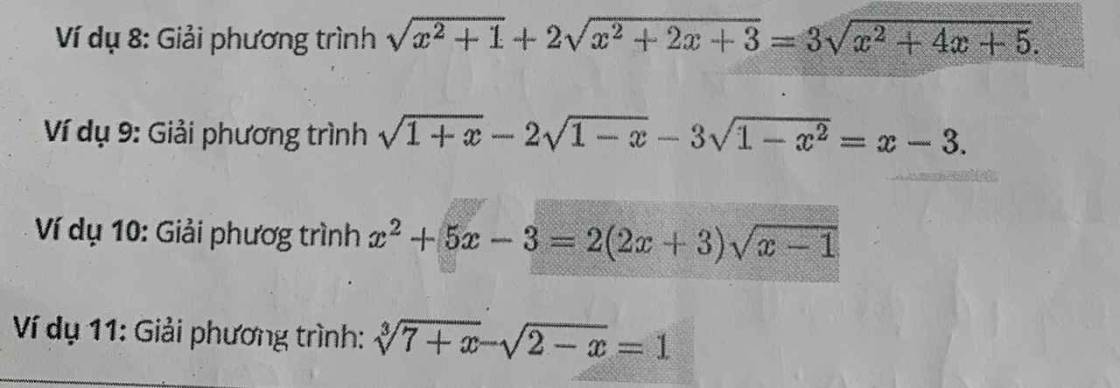Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



a: f(x)=0
=>(x-3)(x+3)=0
=>x=3 hoặc x=-3
b: f(x)=0
=>(-2x+4)(2x^2+1)=0
=>4-2x=0
=>x=2

a)\(\frac{a+b}{2}\ge\sqrt{ab}\Rightarrow a+b\ge2\sqrt{ab}\)
\(\Rightarrow a^2+2ab+b^2\ge4ab\)
\(\Rightarrow a^2-2ab+b^2\ge0\Rightarrow\left(a-b\right)^2\ge0\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(a=b\)
b)Áp dụng BĐT AM-GM ta có:
\(\left\{\begin{matrix}\frac{bc}{a}+\frac{ca}{b}\ge2\sqrt{\frac{bc}{a}\cdot\frac{ca}{b}}=2c\\\frac{bc}{a}+\frac{ab}{c}\ge2\sqrt{\frac{bc}{a}\cdot\frac{ab}{c}}=2b\\\frac{ca}{b}+\frac{ab}{c}\ge2\sqrt{\frac{ca}{b}\cdot\frac{ab}{c}}=2a\end{matrix}\right.\)
Cộng từng vế của 3 BĐT trên rồi thu gọn ta được điều cần chứng minh
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(a=b=c\)
c)Áp dụng BĐT AM-GM ta có:
\(\frac{3a+5b}{2}\ge\sqrt{3a\cdot5b}\Leftrightarrow\left(3a+5b\right)^2\ge4\cdot15P\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12^2\ge60P\Leftrightarrow P\le\frac{12}{5}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(\left\{\begin{matrix}a=2\\b=\frac{6}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) Bảng phân bố tần số (về tuổi thọ bóng đèn điện) có thể viết dưới dạng như sau:

Số trung bình về tuổi thọ của bóng đèn trong bảng phân bố trên là:
.(3x1150 + 6x1160 + 12x1170 + 6x1180 + 3x1190)
= 1170.
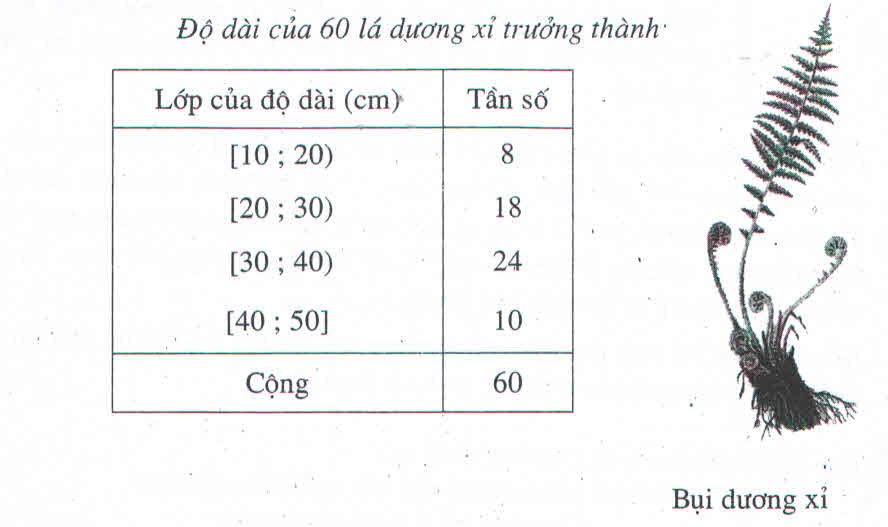
b) Số trung bình về chiều dài lá cây dương xỉ trong bài tập 2 trong là:
.(8x15 + 18x25 + 24x35 + 10x45) = 31 (cm).

Lời giải:
GTLN:
Áp dụng BĐT Cauchy-Schwarz:
\(B^2=(6\sqrt{x-1}+8\sqrt{3-x})^2\leq (6^2+8^2)(x-1+3-x)=200\)
\(\Rightarrow B_{\max}= 10\sqrt{2}\Leftrightarrow \frac{3}{\sqrt{x-1}}=\frac{4}{\sqrt{3-x}}\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{43}{25}\)
GTNN:
Ta biết một bổ đề sau: Với \(a,b\geq 0\Rightarrow \sqrt{a}+\sqrt{b}\geq \sqrt{a+b}\)
Cách CM rất đơn giản vì nó tương đương với \(\sqrt{ab}\geq 0\) (luôn đúng)
Áp dụng vào bài toán:
\(\Rightarrow B\geq \sqrt{36x-36+192-64x}=\sqrt{156-28x}\geq 6\sqrt{2}\) (do \(x\leq 3\))
Vậy \(B_{\min}=6\sqrt{2}\Leftrightarrow x=3\)


8.
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2+2x+3}=a>0\\\sqrt{x^2+4x+5}=b>0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow2a^2-b^2=x^2+1\)
Pt trở thành:
\(\sqrt{2a^2-b^2}+2a=3b\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2a^2-b^2}=3b-2a\)
\(\Rightarrow2a^2-b^2=4a^2-12ab+9b^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2a^2-12ab+10b^2=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=b\\a=5b\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2+2x+3}=\sqrt{x^2+4x+5}\\\sqrt{x^2+2x+3}=5\sqrt{x^2+4x+5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2+2x+3=x^2+4x+5\\x^2+2x+3=25\left(x^2+4x+5\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\24x^2+98x+122=0\left(vn\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
9.
ĐKXĐ: \(-1\le x\le1\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{1+x}=a\ge0\\\sqrt{1-x}=b\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow a^2+2b^2=3-x=-\left(x-3\right)\)
Pt trở thành:
\(a-2b-3ab=-\left(a^2+2b^2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a-2b+a^2-3ab+2b^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a-2b+\left(a-b\right)\left(a-2b\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a-2b\right)\left(a-b+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=2b\\a+1=b\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{1+x}=2\sqrt{1-x}\\\sqrt{1+x}+1=\sqrt{1-x}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}1+x=4\left(1-x\right)\\x+2+2\sqrt{1+x}=1-x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5x=3\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{5}\\-1-2x=2\sqrt{1+x}\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Xét (1) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-1-2x\ge0\\\left(-1-2x\right)^2=4\left(1+x\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\le-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x^2=\dfrac{3}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
Vậy \(x=\left\{\dfrac{3}{5};-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right\}\)