Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(a,\left(2x^2+1\right)+4x>2x\left(x-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+1+4x>2x^2-4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+4x>-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8x>-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-\frac{1}{8}\)
\(b,\left(4x+3\right)\left(x-1\right)< 6x^2-x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x+3x-3< 6x^2-x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-x-3< 6x^2-x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-6x^2< 1+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x^2< 4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2>2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>\pm\sqrt{2}\)

Bàii làm
a) ( x - 2 )( x - 3 ) = x2 - 4
<=> x2 - 2x - 3x + 6 = x2 - 4
<=> x2 - x2 - 5x + 6 - 4 = 0
<=> -5x + 2 = 0
<=> -5x = -2
<=> x = 2/5
Vậy x = 2/5 là nghiệm phương trình.
b) \(\frac{x+2}{x-2}-\frac{1}{x}=\frac{x+6}{x\left(x-2\right)}\)
=> x( x + 2 ) - ( x - 2 ) = x + 6
<=> x2 + 2x - x + 2 - x - 6 = 0
<=> x2 - 4 = 0
<=> x2 = 4
<=> x = + 4
Vậy nghiệm S = { + 4 }
c) \(\frac{2x-1}{-3}>1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x-1}{-3}.\left(-3\right)< 1\left(-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-1< -3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x< -2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< -1\)
Vậy nghiệm bất phương trình S = { x / x < -1 }
d) ( x - 1 )2 < 5 - 2x
<=> x2 - 2x + 1 < 5 - 2x
<=> x2 - 2x + 1 - 5 + 2x < 0
<=> x2 - 4 < 0
<=> x2 < 4
<=> x < + 2
Vậy tập nghiệm S = { x / x < +2 }

Lập bảng xét dấu :
| x | -2 | \(\frac{1}{2}\) | |||
| x+2 | - | 0 | + | \(|\) | + |
| 2x-1 | - | \(|\) | - | 0 | + |
+) Nếu \(x\le-2\) thì \(|x+2|=-x-2\)
\(|2x-1|=1-2x\)
\(pt\Leftrightarrow\left(1-2x\right)-\left(-x-2\right)=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-2x+x+2=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x+3=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2\left(tm\right)\)
Nếu \(-2< x< \frac{1}{2}\) thì \(|2x-1|=1-2x\)
\(|x+2|=x+2\)
\(pt\Leftrightarrow\left(1-2x\right)-\left(x+2\right)=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-2x-x-2=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x-1=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2\) ( loại )
+) Nếu \(x\ge\frac{1}{2}\) thì \(|2x-1|=2x-1\)
\(|x+2|=x+2\)
\(pt\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)-\left(x+2\right)=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-1-x-2=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-3=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=8\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy ...
Trường hợp 1: Nếu x+2>/ thì x>/-2 nên ta có phương trình :
Suy ra : 2x+1-x+2=5
Suy ra : 2x-x=5-1-2
Suy ra : x=2(nhận)
Trường hợp 2: Nếu x+2<0 thì x<-2 nên ta có phương trình :
Suy ra : 2x-1-x-2=5
Suy ra : 2x-x=5+1+2
Suy ra : x= 8(loại)
S=(2)

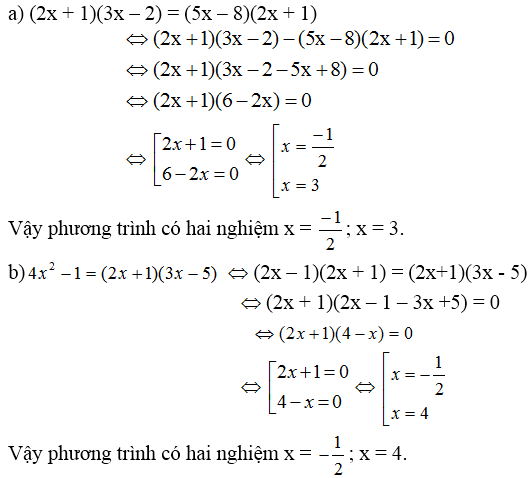
a)(2x+1)(3x-2)=(5x-8)(2x+1)
⇔(2x+1)(3x-2)-(5x-8)(2x+1)=0
⇔(2x+1)(3x-2-5x+8)=0
⇔(2x+1)(-2x+6)=0
⇔2x+1=0 hoặc -2x+6=0
1.2x+1=0⇔2x=-1⇔x=-1/2
2.-2x+6=0⇔-2x=-6⇔x=3
phương trình có 2 nghiệm x=-1/2 và x=3

\(\left(x^3-27\right)\left(x^3-1\right)\left(2x+3-x^2\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+3x+9\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left[4-\left(x-1\right)^2\right]\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left[\left(x+\frac{3}{2}\right)^2+\frac{27}{4}\right]\left(x-1\right)\left[\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}\right]\left(4-x+1\right)\left(4+x-1\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(5-x\right)\left(x+3\right)\left[...\right]\left[...\right]\ge0\)(1)
Do [...] và [...] > 0
nên \(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(5-x\right)\left(x+3\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)\le0\)
Có: \(x-5< x-3< x-1< x+3\)
Nên xảy ra các trường hợp sau :
TH1:\(\hept{\begin{cases}x-5\le0\\x-3\ge0\end{cases}}\)(Tự giải)
TH2:\(\hept{\begin{cases}x-1\le0\\x+3\ge0\end{cases}}\)(Tự giải)
Cuối cùng gộp khoảng (Nếu được)
Kết luận......

a) \(8x+3\left(x+1\right)>5x-\left(2x-6\right)\)
⇒ \(8x + 3x + 3 > 5x - 2x + 6\)
⇒ \(11x+3>3x+6\)
⇒ \(11x - 3x > 6 -3\)
⇒ \(8x > 3\)
⇒ \(8x.\dfrac{1}{8}>3.\dfrac{1}{8}\)
⇒ \(x>\dfrac{3}{8}\)
S = \(\left\{x\backslash x>\dfrac{3}{8}\right\}\)
b) \(2x(6x-1) > (3x -2)(4x+3)\)
⇒ \(12x^2 - 2x > 12x^2 +9x -8x -6\)
⇒ \(12x^2 - 2x > 12x^2 + x - 6\)
⇒ \(-2x-x>12x^2 -6-12x^2\)
⇒ \(- 3x > -6 \)
⇒ \(x > 2\)
S = {x / x > 2}

a)\(\frac{x+3}{6}\)+\(\frac{x-2}{10}\)>\(\frac{x+1}{5}\)
<=> \(\frac{5\left(x+3\right)}{30}\)+\(\frac{3\left(x-2\right)}{30}\)>\(\frac{6\left(x+1\right)}{30}\)
<=>5(x+3)+3(x-2)>6(x+1)
<=>5x+15+3x-6>6x+6
<=>8x-6x >6-15+6
<=>2x >-3
<=>x >-1,5
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là {x/x>-1,5}

\(2x-\left(2x^2+x\right)\le15-\left(2x^2+4x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=15-4x\Leftrightarrow5x=15\Leftrightarrow x=3\)Vậy phương trình có nghiệm là x=3
Ta có: \(2x-x\left(2x+1\right)\le15-2x\left(x+2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-2x^2-x\le15-2x^2-4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2x^2+2x^2+4x\le15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x\le15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\le3\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\forall x\inℝ/x\le3\right\}\)