Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a)|3x| = x + 8 ⇔[3x=x+8;x≥0−3x=x+8;x<0[3x=x+8;x≥0−3x=x+8;x<0
⇔[2x=8−4x=8[2x=8−4x=8
⇔[x=4;x=−2;[x=4;x=−2;
x = 4 thỏa mãn ĐK x ≥ 0 và x = -2 thỏa mãn ĐK x < 0
Vậy tập hợp nghiệm S = {4;-2}
b)|-2x| = 4x + 18 vì |-2x| = |2x| ⇔ |2x| = 4x +18
⇔ [2x=4x+18;x≥0−2x=4x+18;x<0⇔[−2x=18−6x=18[2x=4x+18;x≥0−2x=4x+18;x<0⇔[−2x=18−6x=18
⇔[x=−9;x=−3[x=−9;x=−3
x = -9 không thỏa mãn ĐK x ≥ 0
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-3}
c)|x – 5| = 3x ⇔[x−5=3x;x≥5−x+5=3x;x<5[x−5=3x;x≥5−x+5=3x;x<5
⇔[−5=2x5=4x[−5=2x5=4x
⇔[x=−52x=54[x=−52x=54
x=−52x=−52 không thỏa mãn ĐK x ≥ 5
Vậy tập hợp nghiệm của phương trình S={54}S={54}
d) |x + 2| = 2x – 10.
⇔[x+2=2x−10;x≥−2−x−2=2x−10;x<−2[x+2=2x−10;x≥−2−x−2=2x−10;x<−2
⇔[x=12x=83[x=12x=83
x=83x=83 không thỏa mãn điều kiện x < -2
Vậy tập hợp nghiệm của phương trình S ={12 }

\(a,2x\left(x-3\right)+5\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+5\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x+5=0\\x-3=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x=-5\\x=3\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{5}{2}\\x=3\end{cases}}\)
Vậy .........
\(b,\left(x^2-4\right)+\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x=0\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4-2x^2+7x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x^2+7x-10=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(x-5\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=5\\x=2\end{cases}}\)
Vậy ..................
\(c,x^3-3x^2+3x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
\(d,x\left(2x-7\right)-4x+14=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-7x-4x+14=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-11x+14=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-7\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{7}{2}\\x=2\end{cases}}\)
Vậy ............
\(e,\left(2x-5\right)^2-\left(x+2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-20x+25-x^2-4x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-24x+21=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x-7\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-7=0\\x-1=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=7\\x=1\end{cases}}\)
Vậy .....................
\(f,x^2-x-\left(3x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-3x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-3=0\\x-1=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=1\end{cases}}\)
Vậy ..............

a)(2x+1)(3x-2)=(5x-8)(2x+1)
⇔(2x+1)(3x-2)-(5x-8)(2x+1)=0
⇔(2x+1)(3x-2-5x+8)=0
⇔(2x+1)(-2x+6)=0
⇔2x+1=0 hoặc -2x+6=0
1.2x+1=0⇔2x=-1⇔x=-1/2
2.-2x+6=0⇔-2x=-6⇔x=3
phương trình có 2 nghiệm x=-1/2 và x=3

a) 0,75x(x + 5) = (x + 5)(3 - 1,25x)
<=> 0,75x(x + 5) - (x + 5)(3 - 1,25x) = (x + 5)(3 - 1,25x) - (x + 5)(3 - 1,25x)
<=> 0,75x(x + 5) - (x + 5)(3 - 1,25x) = 0
<=> (x + 5)(0,75 + 1,25x - 3) = 0
<=> (x + 5)(2x - 3) = 0
<=> x + 5 = 0 hoặc 2x - 3 = 0
<=> x = -5 hoặc x = 3/2
b) 4/5 - 3 = 1/5x(4x - 15)
<=> -11/5 = x(4x - 15)/5
<=> -11 = x(4x - 15)
<=> -11 = 4x2 - 15x
<=> 11 + 4x2 - 15x = 0
<=> 4x2 - 4x - 11x + 11 = 0
<=> 4x(x - 1) - 11(x - 1) = 0
<=> (4x - 11)(x - 1) = 0
<=> 4x - 11 = 0 hoặc x - 1 = 0
<=> x = 11/4 hoặc x = 1
c) \(\left(x-3\right)-\frac{\left(x-3\right)\left(2x-5\right)}{6}=\frac{\left(x-3\right)\left(3-x\right)}{4}\)
<=> 12x - 36 - 2(x - 3)(2x - 5) = 3(x - 3)(3 - x)
<=> 12x - 36 - 4x2 + 10x + 12x - 30 = 9x - 3x2 - 27 + 9x
<=> 34x - 66 - 4x2 = 18x - 3x2 - 27
<=> 34x - 66 - 4x2 - 18x + 3x2 + 27 = 0
<=> 16x - 39x - x2 = 0
<=> x2 - 16x + 39x = 0
<=> (x - 3)(x - 13) = 0
<=> x - 3 = 0 hoặc x - 13 = 0
<=> x = 3 hoặc x = 13
d) \(\frac{\left(3x+1\right)\left(3x-2\right)}{3}+5\left(3x+1\right)=\frac{2\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x+1\right)}{3}+2x\left(3x+1\right)\)
<=> (3x + 1)(3x - 2) + 15(3x + 1) = 2(2x + 1)(3x + 1) + 6x(3x + 1)
<=> 9x2 - 6x + 3x - 2 + 45x + 15 = 12x3 + 4x + 6x + 2 + 18x2 + 6x
<=> 9x2 + 42x + 13 = 30x2 + 16x + 2
<=> 9x2 + 42x + 13 - 30x2 - 16x - 2 = 0
<=> -21x2 + 26x + 11 = 0
<=> 21x2 - 26x - 11 = 0
<=> 21x2 + 7x - 33x - 11 = 0
<=> 7x(3x + 1) - 11(3x + 1) = 0
<=> (7x - 11)(3x + 1) = 0
<=> 7x - 11 = 0 hoặc 3x + 1 = 0
<=> x = 11/7 hoặc x = -1/3

a) <=> \(6x^2-5x+3-2x+3x\left(3-2x\right)=0\)
<=> \(6x^2-5x+3-2x+9x-6x^2=0\)
<=> \(2x+3=0\)
<=> \(x=\frac{-3}{2}\)
b) <=> \(10\left(x-4\right)-2\left(3+2x\right)=20x+4\left(1-x\right)\)
<=> \(10x-40-6-4x=20x+4-4x\)
<=> \(6x-46-16x-4=0\)
<=> \(-10x-50=0\)
<=> \(-10\left(x+5\right)=0\)
<=> \(x+5=0\)
<=> \(x=-5\)
c) <=> \(8x+3\left(3x-5\right)=18\left(2x-1\right)-14\)
<=> \(8x+9x-15=36x-18-14\)
<=> \(8x+9x-36x=+15-18-14\)
<=> \(-19x=-14\)
<=> \(x=\frac{14}{19}\)
d) <=>\(2\left(6x+5\right)-10x-3=8x+2\left(2x+1\right)\)
<=> \(12x+10-10x-3=8x+4x+2\)
<=> \(2x-7=12x+2\)
<=> \(2x-12x=7+2\)
<=> \(-10x=9\)
<=> \(x=\frac{-9}{10}\)
e) <=> \(x^2-16-6x+4=\left(x-4\right)^2\)
<=> \(x^2-6x-12-\left(x-4^2\right)=0\)
<=> \(x^2-6x-12-\left(x^2-8x+16\right)=0\)
<=> \(x^2-6x-12-x^2+8x-16=0\)
<=> \(2x-28=0\)
<=> \(2\left(x-14\right)=0\)
<=> x-14=0
<=> x=14
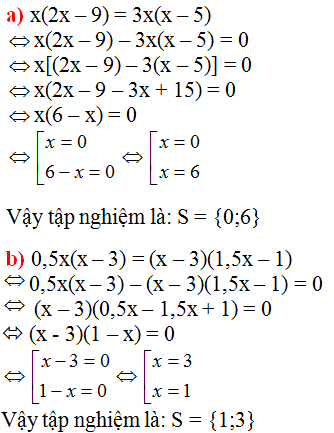
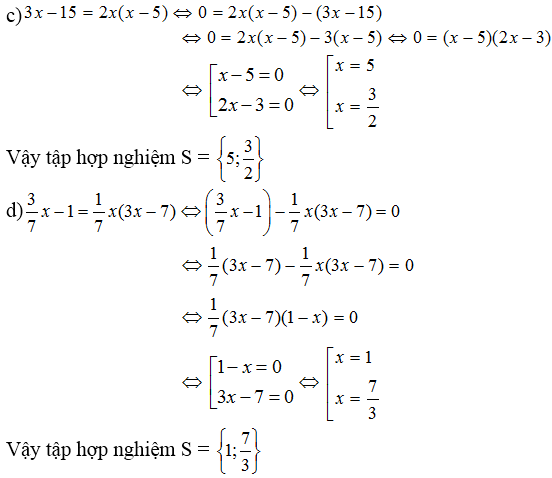

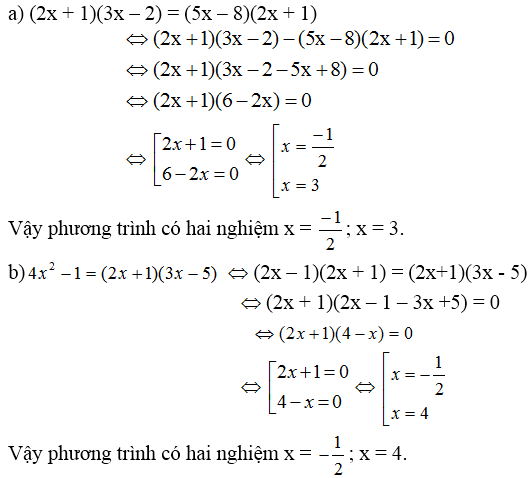
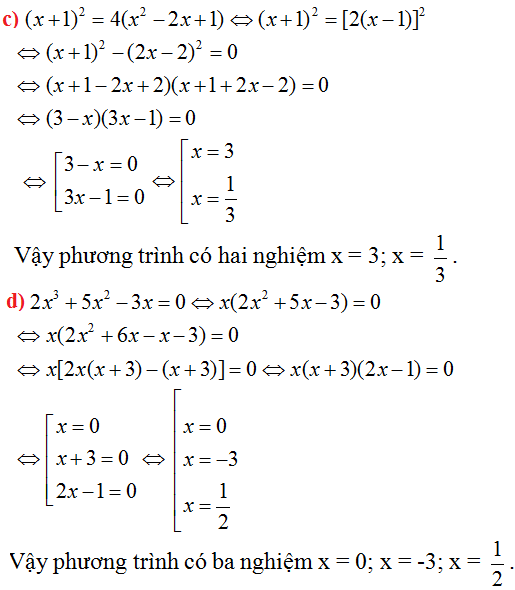

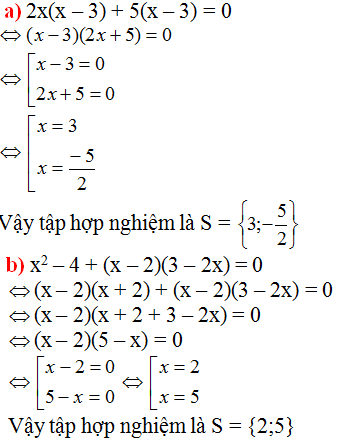
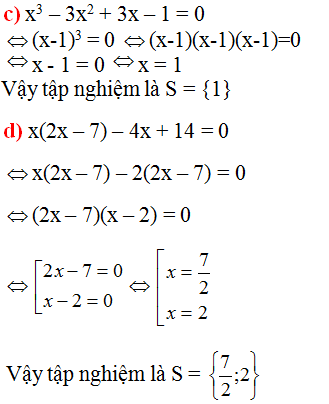
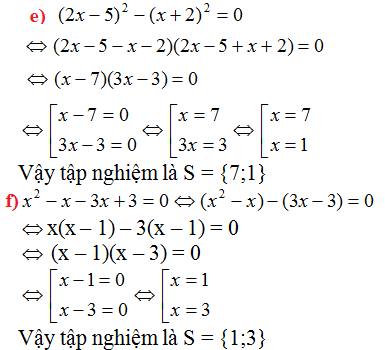
a) \(2x\left(3x+5\right)=3x\left(10+2x\right)+15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2+10x=30x+6x^2+15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2+10x-30x-6x^2=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-20x=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-0.75\)
b) \(3x\left(x+5\right)-x\left(3x-10\right)+7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2+15x-3x^2+10x+7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow25x+7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow25x=-7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-0.28\)