Trong mặt phẳng tọa độ $Oxy$, cho hàm số $y=\dfrac14x^2$ có đồ thị $(P)$ và đường thẳng $(d): \, y=-\dfrac12x+2.$
a) Vẽ đồ thị $(P)$ và $(d)$ trên cùng mặt phẳng tọa độ.
b) Tìm tọa độ giao điểm của $(P)$ và $(d)$.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Giải:
Cứ một giờ ca nô xuôi dòng được: 1 : 5 = \(\dfrac{1}{5}\) (quãng sông AB)
Cứ một giờ ca nô ngược dòng được: 1 : 7 = \(\dfrac{1}{7}\)(quãng sông AB)
3 km ứng với phân số là: (\(\dfrac{1}{5}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{7}\)) : 2 = \(\dfrac{1}{35}\) (quãng sông AB)
Quãng sông AB dài là: 3 : \(\dfrac{1}{35}\) = 105 (km)
Đáp số: 105 km

Gọi thời gian ô tô đi trên quãng đường AB là x(giờ)
(Điều kiện: x>0)
30p=0,5 giờ
Thời gian ô tô đi trên quãng đường BC là x+0,5(giờ)
Độ dài quãng đường AB là 50x(km)
Độ dài quãng đường BC là 45(x+0,5)(km)
Tổng độ dài là 165km nên ta có:
\(50x+45\left(x+0,5\right)=165\)
=>50x+45x+22,5=165
=>95x=165-22,5=142,5
=>x=1,5(nhận)
vậy: Thời gian ô tô đi trên quãng đường AB là 1,5 giờ
Thời gian ô tô đi trên quãng đường BC là 1,5+0,5=2 giờ

Giải:
a; \(\widehat{A}\) + \(\widehat{B}\) + \(\widehat{C}\) = 1800 (tổng ba góc trong một tam giác)
⇒ \(\widehat{C}\) = 1800 - \(\widehat{A}\) - \(\widehat{B}\) = 1800 - 900 - 600 = 300
Áp dụng công thức: cos\(\widehat{ABC}\) = \(\dfrac{AB}{BC}\) ⇒ AB = BC.cos\(\widehat{ABC}\)
⇒ AB = 6.cos 600 = 6. \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) = 3
Vậy AB = 3cm
Áp dụng công thức: sin \(\widehat{ABC}\) = \(\dfrac{AC}{BC}\) ⇒ AC = BC.sin \(\widehat{ABC}\)
⇒ AC = 3.sin 600 = 6.\(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) = 3\(\sqrt{3}\)
Diện tích tam giác ABC là: 3\(\sqrt{3}\) x 3 : 2 = \(\dfrac{9\sqrt{3}}{2}\) (cm2)
b; Độ dài đường cao AH là: \(\dfrac{9\sqrt{3}}{2}\) .2 : 6 = \(\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}\) (cm)
Xét tam giác vuông HAC vuông tại H
Theo pytago ta có: AH2 + HC2 = AC2
⇒ HC2 = AC2 - AH2 = (3\(\sqrt{3}\))2 - (\(\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}\))2 = \(\dfrac{81}{4}\)
HC = \(\sqrt{\dfrac{81}{4}}\) = \(\dfrac{9}{2}\) (cm)
Kết luận: a; góc C là 300; Độ dài AB; AC; AH; HC lần lượt là:
3cm ; 3\(\sqrt{3}\)cm; \(\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}\)cm; \(\dfrac{9}{2}\)cm

a: Xét (O) có
ΔBAC nội tiếp
BC là đường kính
Do đó: ΔBAC vuông tại A
=>BA\(\perp\)AC tại A
Xét (O') có
ΔBAD nội tiếp
BD là đường kính
Do đó: ΔBAD vuông tại A
=>BA\(\perp\)AD tại A
Ta có: BA\(\perp\)AD
BA\(\perp\)AC
mà AC,AD có điểm chung là A
nên C,A,D thẳng hàng
b: Gọi H là giao điểm của AB và O'O
Ta có: OA=OB
=>O nằm trên đường trung trực của AB(1)
Ta có: O'A=O'B
=>O' nằm trên đường trung trực của AB(2)
Từ (1),(2) suy ra O'O là đường trung trực của AB
=>O'O\(\perp\)AB tại H và H là trung điểm của AB
Xét ΔOBO' có \(BO^2+BO'^2=O'O^2\left(3^2+4^2=5^2\right)\)
nên ΔOBO' vuông tại B
Xét ΔOBO' vuông tại B có BH là đường cao
nên \(BH\cdot O'O=BO\cdot BO'\)
=>\(BH=3\cdot\dfrac{4}{5}=2,4\left(cm\right)\)
H là trung điểm của AB
=>\(AB=2\cdot2,4=4,8\left(cm\right)\)
O là trung điểm của BC
=>BC=2*BO=2*4=8(cm)
O' là trung điểm của BD
=>BD=2*BO'=2*3=6(cm)
ΔBCD vuông tại B
=>\(S_{BCD}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot BC\cdot BD=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot6\cdot8=24\left(cm^2\right)\)

a: Vì OO'=13cm<5cm+12cm
nên (O) cắt (O') tại hai điểm phân biệt
b: Xét ΔOAO' có \(OA^2+O'A^2=OO'^2\left(5^2+12^2=13^2\right)\)
nên ΔOAO' vuông tại A
=>AO\(\perp\)AO' tại A
Xét (O) có
AO là bán kính
AO\(\perp\)AO' tại A
Do đó: AO' là tiếp tuyến của (O) tại A
Xét (O') có
O'A là bán kính
AO\(\perp\)AO'
Do đó: AO là tiếp tuyến của (O') tại A

a: \(P=\left(\dfrac{2\sqrt{xy}}{x-y}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}}{2\sqrt{x}-2\sqrt{y}}\right)\cdot\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{y}}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{2\sqrt{xy}}{\left(\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}}{2\left(\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{y}\right)}\right)\cdot\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{y}}\)
\(=\dfrac{4\sqrt{xy}-\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)^2}{2\cdot\left(\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)}\cdot\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{y}\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-x+2\sqrt{xy}-y}{\left(\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{y}\right)^2}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}}=\dfrac{-\left(\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{y}\right)^2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{y}\right)^2}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}}\)
\(=-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}}\)
b: \(\dfrac{x}{y}=\dfrac{4}{9}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x}{4}=\dfrac{y}{9}=k\)
=>x=4k; y=9k
\(P=\dfrac{-\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}}=\dfrac{-\sqrt{4k}}{\sqrt{4k}+\sqrt{9k}}=\dfrac{-2\sqrt{k}}{2\sqrt{k}+3\sqrt{k}}=-\dfrac{2}{5}\)

ĐKXĐ: x>0; x<>9
a:\(P=\left(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}+3}+\dfrac{3}{x\sqrt{x}-9\sqrt{x}}\right):\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+3}-\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}-3}{x+3\sqrt{x}}\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}+3}+\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)}\right):\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+3}-\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}-3}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x-3\sqrt{x}+3}{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\cdot\sqrt{x}}:\dfrac{x-3\sqrt{x}+3}{\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\cdot\sqrt{x}}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-3\sqrt{x}+3}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)}{x-3\sqrt{x}+3}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}-3}\)
b: P>1
=>P-1>0
=>\(\dfrac{1-\sqrt{x}+3}{\sqrt{x}-3}>0\)
=>\(\dfrac{4-\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-3}>0\)
=>\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-4}{\sqrt{x}-3}< 0\)
=>\(3< \sqrt{x}< 4\)
=>9<x<16
a: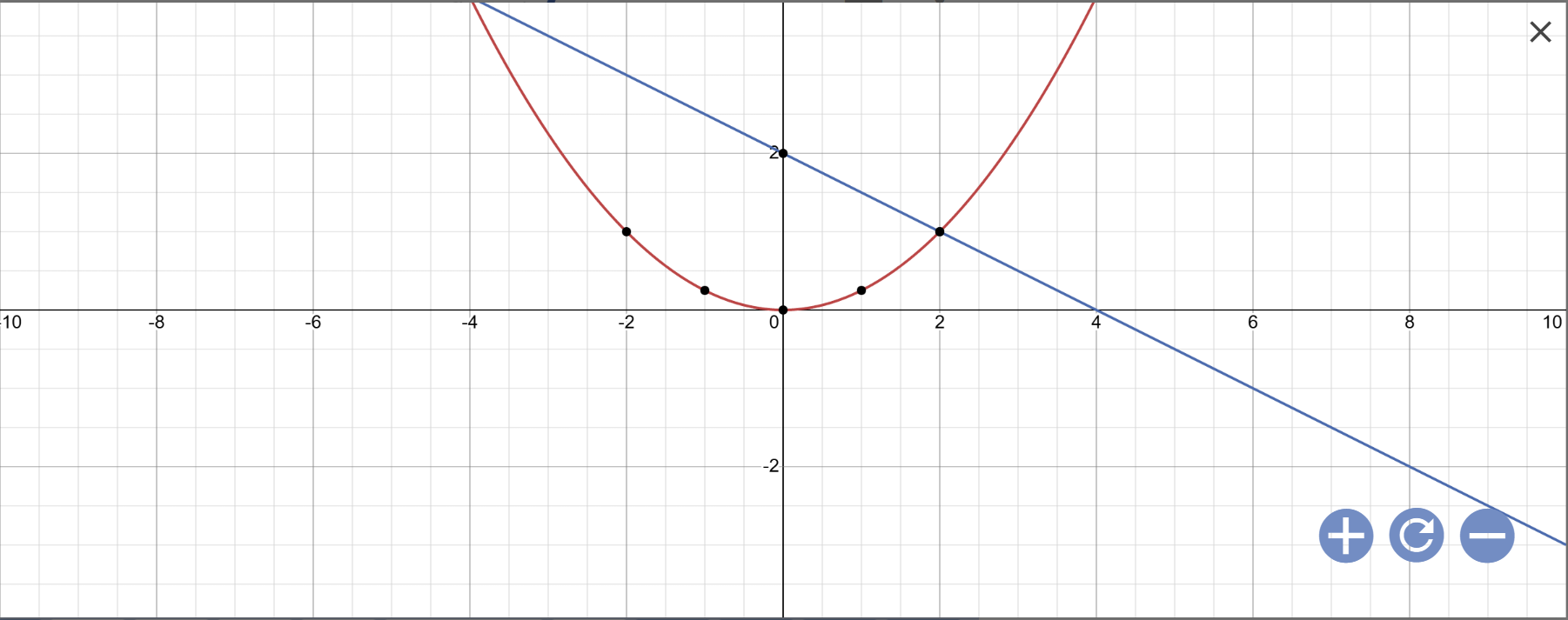
b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(\dfrac{1}{4}x^2=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+2\)
=>\(x^2=-2x+8\)
=>\(x^2+2x-8=0\)
=>(x+4)(x-2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+4=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi x=-4 thì \(y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\left(-4\right)+2=2+2=4\)
Khi x=2 thì \(y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot2+2=-1+2=1\)
Vậy: Tọa độ giao điểm của (P) và (d) là A(-4;4); B(2;1)