(2 điểm) Cho phương trình $x^2-mx+m-1=0$ (1), $m$ là tham số.
a) Giải phương trình (1) với $m=-2$.
b) Tìm $m$ để phương trình (1) có hai nghiệm $x_1$, $x_2$ và biểu thức $A=\dfrac{2x_1x_2+3}{x_{1}^{2}+x_{2}^{2}+2(x_1x_2+1)}$ đạt giá trị lớn nhất.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a; (\(\sqrt{45}\) - \(\sqrt{125}\) + \(\sqrt{20}\)) : \(\sqrt{5}\)
= (\(\sqrt{9.5}\) - \(\sqrt{25.5}\) + \(\sqrt{4.5}\)):\(\sqrt{5}\)
= (3\(\sqrt{5}\) - 5\(\sqrt{5}\) + 2\(\sqrt{5}\)): \(\sqrt{5}\)
= (- 2\(\sqrt{5}\) + 2\(\sqrt{5}\)) : \(\sqrt{5}\)
= 0 : \(\sqrt{5}\)
= 0

a: 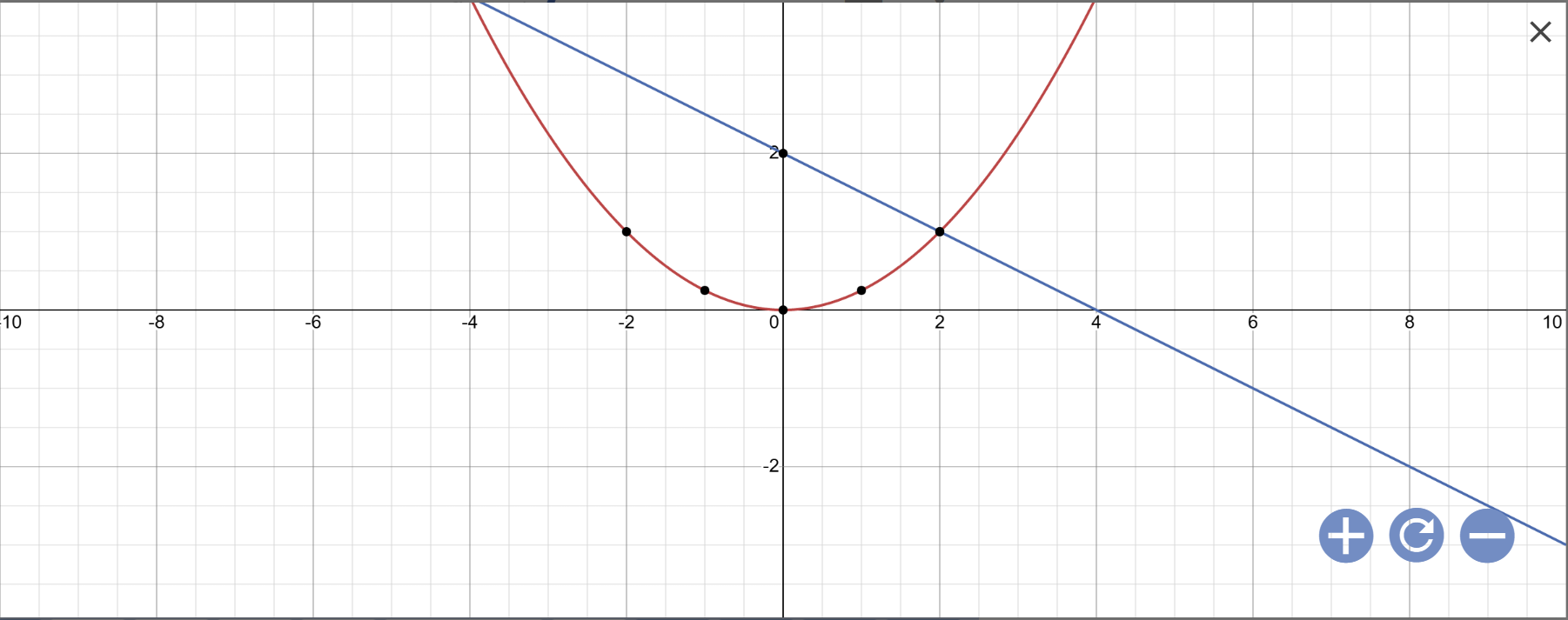
b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(\dfrac{1}{4}x^2=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+2\)
=>\(x^2=-2x+8\)
=>\(x^2+2x-8=0\)
=>(x+4)(x-2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+4=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi x=-4 thì \(y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\left(-4\right)+2=2+2=4\)
Khi x=2 thì \(y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot2+2=-1+2=1\)
Vậy: Tọa độ giao điểm của (P) và (d) là A(-4;4); B(2;1)

Bài 4:
a: Xét (O) có \(\widehat{AMB};\widehat{ANB}\) là các góc nội tiếp chắn cung AB
nên \(\widehat{AMB}=\widehat{ANB}=\dfrac{\widehat{AOB}}{2}=\dfrac{120^0}{2}=60^0\)
b: Diện tích hình quạt tròn OAB là:
\(S_{q\left(OAB\right)}=\dfrac{\Omega\cdot R^2\cdot n}{180}=\dfrac{\Omega\cdot6^2\cdot120}{180}=24\Omega\)
Diện tích tam giác OAB là:
\(S_{OAB}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot OA\cdot OB\cdot sinAOB=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot6\cdot6\cdot sin120\simeq9\sqrt{3}\)(cm2)
Diện tích hình viên phân giới hạn bởi dây AB và cung nhỏ AB là:
\(24\Omega-9\sqrt{3}\simeq59,8\left(cm^2\right)\)

Bài 4:
a: Xét (O) có \(\widehat{AMB};\widehat{ANB}\) là các góc nội tiếp chắn cung AB
nên \(\widehat{AMB}=\widehat{ANB}=\dfrac{\widehat{AOB}}{2}=\dfrac{120^0}{2}=60^0\)
b: Diện tích hình quạt tròn OAB là:
\(S_{q\left(OAB\right)}=\dfrac{\Omega\cdot R^2\cdot n}{180}=\dfrac{\Omega\cdot6^2\cdot120}{180}=24\Omega\)
Diện tích tam giác OAB là:
\(S_{OAB}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot OA\cdot OB\cdot sinAOB=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot6\cdot6\cdot sin120\simeq9\sqrt{3}\)(cm2)
Diện tích hình viên phân giới hạn bởi dây AB và cung nhỏ AB là:
\(24\Omega-9\sqrt{3}\simeq59,8\left(cm^2\right)\)
Bài 5:
a: Xét (O) có
ΔAMB nội tiếp
AB là đường kính
Do đó: ΔAMB vuông tại M
=>\(\widehat{AMB}=90^0\)
b: ΔAMB vuông tại M
=>AM\(\perp\)BC tại M
ΔCMA vuông tại M
mà MI là đường trung tuyến
nên IA=IM
Xét ΔIAO và ΔIMO có
IA=IM
OA=OM
IO chung
Do đó: ΔIAO=ΔIMO
=>\(\widehat{IAO}=\widehat{IMO}\)
=>\(\widehat{IMO}=90^0\)
=>IM là tiếp tuyến của (O)
c: Xét ΔMAB vuông tại M có \(cosMAB=\dfrac{MA}{AB}=\dfrac{R}{2R}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
nên \(\widehat{MAB}=60^0\)
Xét ΔMNA vuông tại N có \(sinMAN=\dfrac{MN}{MA}\)
=>\(\dfrac{MN}{R}=sin60=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
=>\(MN=\dfrac{R\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{MN}{AB}=\dfrac{R\sqrt{3}}{2}:2R=\dfrac{R\sqrt{3}}{2\cdot2R}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}\simeq0,43\)

a: Xét tứ giác OBDA có \(\widehat{OBD}+\widehat{OAD}=90^0+90^0=180^0\)
nên OBDA là tứ giác nội tiếp
=>O,B,D,A cùng thuộc một đường tròn
b: Xét (O) có
ΔBAC nội tiếp
BC là đường kính
Do đó: ΔBAC vuông tại A
=>BA\(\perp\)CE tại A
Xét ΔBEC vuông tại B có BA là đường cao
nên \(CA\cdot CE=CB^2=\left(2R\right)^2=4R^2\)
c:
i: Xét (O) có
DA,DB là các tiếp tuyến
Do đó: DA=DB
=>D nằm trên đường trung trực của AB(1)
Ta có: OA=OB
=>O nằm trên đường trung trực của AB(2)
Từ (1),(2) suy ra OD là đường trung trực của AB
=>OD\(\perp\)AB tại K và K là trung điểm của AB
Xét tứ giác AKOI có \(\widehat{AKO}=\widehat{AIO}=\widehat{KAI}=90^0\)
nên AKOI là hình chữ nhật
=>OA=IK
=>IK=R
ii: ΔAHB vuông tại H
mà HK là đường trung tuyến
nên HK=KA=KB
=>K là tâm đường tròn ngoại tiếp ΔAHB
Gọi M là giao điểm của AO và KI
AKOI là hình chữ nhật
=>AO cắt KI tại trung điểm của mỗi đường
=>M là trung điểm chung của AO và KI
ΔAHO vuông tại H
mà HM là đường trung tuyến
nên \(HM=\dfrac{AO}{2}=\dfrac{KI}{2}\)
Xét ΔHKI có
HM là đường trung tuyến
HM=KI/2
Do đó: ΔHKI vuông tại H
=>HK\(\perp\)HI
Xét (K) có
HK là bán kính
HI\(\perp\)HK tại H
Do đó: HI là tiếp tuyến của (K)
=>HI là tiếp tuyến của đường tròn ngoại tiếp ΔHAB
iii: Vì \(\widehat{AHO}=\widehat{AKO}=\widehat{AIO}=90^0\)
nên A,H,K,O,I cùng thuộc đường tròn đường kính AO
trung bình cộng của 50 số lẻ liên tiếp là 50 . Số lớn nhất là?


a: ΔABC vuông tại A
=>\(AB^2+AC^2=BC^2\)
=>\(BC=\sqrt{6^2+8^2}=10\left(cm\right)\)
Xét ΔABC vuông tại A có AH là đường cao
nên \(AH\cdot BC=AB\cdot AC\)
=>\(AH=\dfrac{6\cdot8}{10}=4,8\left(cm\right)\)
Xét ΔABC vuông tại A có \(sinB=\dfrac{AC}{BC}=\dfrac{8}{10}=\dfrac{4}{5}\)
nên \(\widehat{B}\simeq53^0\)
b: Xét ΔABC vuông tại A có \(cosB=\dfrac{BA}{BC};cosC=\dfrac{AC}{BC}\)
\(AB\cdot cosB+AC\cdot cosC\)
\(=AB\cdot\dfrac{AB}{BC}+AC\cdot\dfrac{AC}{BC}\)
\(=\dfrac{AB^2+AC^2}{BC}=\dfrac{BC^2}{BC}=BC\)
a; Thay m=-2 vào (1), ta được:
\(x^2-\left(-2\right)x+\left(-2\right)-1=0\)
=>\(x^2+2x-3=0\)
=>(x+3)(x-1)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\text{Δ}=\left(-m\right)^2-4\cdot1\cdot\left(m-1\right)=m^2-4m+4=\left(m-2\right)^2>=0\forall m\)
=>Phương trình (1) luôn có hai nghiệm
Theo Vi-et, ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=m\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=m-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(A=\dfrac{2x_1x_2+3}{x_1^2+x_2^2+2\left(x_1x_2+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(m-1\right)+3}{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2+2x_1x_2+2}=\dfrac{2m-2+3}{m^2+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2m+1}{m^2+2}\)
=>\(A-1=\dfrac{2m+1-m^2-2}{m^2+2}=\dfrac{-m^2+2m-1}{m^2+2}=-\dfrac{\left(m-1\right)^2}{m^2+2}< =0\forall m\)
=>\(A< =1\forall m\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi m-1=0
=>m=1