5/2-3/2x(x-2)=2
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


(x - 13 + y)2 + (x - 6 - y)2 ≥ 0 + 0 = 0
Vì dấu "=" xảy ra nên x - 13 + y = 0 và x - 6 - y = 0
x + y = 13 và x - y = 6
x = (13 - 6) : 2 = 3,5
y = 13 - 3,5 = 9,5
Vậy x = 3,5 và y = 9,5
(\(x\) - 13 + y)2 + (\(x\) - 6 - y)2 = 0
(\(x\) - 13 + y)2 ≥ 0 ∀ \(x;y\)
(\(x-6-y\))2 ≥ 0 ∀ \(x;y\)
⇒(\(x-13+y\))2 + (\(x\) - 6- y)2 = 0
⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-13+y=0\\x-6-y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇒ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-6-y=0\\x-13+y+x-6-y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇒ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=x-6\\2x=19\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇒ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{19}{2}\\y=\dfrac{19}{2}-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇒ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{19}{2}\\y=\dfrac{7}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

|5 - \(\dfrac{2}{3}\)\(x\)| + |\(\dfrac{2}{3}\)y - 4| =0
|5 - \(\dfrac{2}{3}\)\(x\)| ≥ 0 ∀ \(x\); |\(\dfrac{2}{3}\)y - 4| ≥ 0 ∀ y
⇒ |5 - \(\dfrac{2}{3}\)\(x\)| + |\(\dfrac{2}{3}\)y - 4| = 0 ⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5-\dfrac{2}{3}x=0\\\dfrac{2}{3}y-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇒ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{15}{2}\\y=6\end{matrix}\right.\)

-1\(\dfrac{1}{2}\) = - (1\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)) = - \(\dfrac{2+1}{2}\) = - \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Chọn b, - \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)

\(\dfrac{5}{6}\) - (\(\dfrac{3}{4}\) + \(\dfrac{7}{8}\) - \(x\)) = 10 - | \(\dfrac{1}{3}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)|
\(\dfrac{5}{6}\) - (\(\dfrac{13}{8}\)- \(x\)) = 10 - |-\(\dfrac{1}{6}\)|
\(\dfrac{5}{6}\) - \(\dfrac{13}{8}\) + \(x\) = 10 + \(\dfrac{1}{6}\)
- \(\dfrac{19}{24}\) + \(x\) = \(\dfrac{61}{6}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{61}{6}\) + \(\dfrac{19}{24}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{263}{24}\)


\(A=\left|x+1\right|-3\\ min_A=-3.khi.x+1=0\Leftrightarrow x=-1\\ B=-\left|x-\dfrac{3}{7}\right|-\dfrac{1}{4}\\ max_B=-\dfrac{1}{4}.khi.\left(x-\dfrac{3}{7}\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{7}\)
a)
A = |x + 1| - 3 ≥ 0 - 3 = -3
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x + 1 = 0 hay x = -1
Do đó A đạt GTNN là -3 khi x = -1
b)
\(B=-\left|x-\dfrac{3}{7}\right|-\dfrac{1}{4}\le-0-\dfrac{1}{4}=-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi khi \(x-\dfrac{3}{7}=0\) hay \(x=\dfrac{3}{7}\)
Do đó B đạt GTLN là \(-\dfrac{1}{4}\) khi \(x=\dfrac{3}{7}\)

tỉ số của a / b là (92 - 1/9 - 2/ 10 - 3/11 - ... - 92/100) trên 1/45 + 1/50 + ... + 1/500 :)) hay ngắn tắc hơn là A/B cho nhanh :)))))))))))))))
\(A=\left(1+1+...+1\right)-\left(\dfrac{1}{9}+\dfrac{2}{10}+...+\dfrac{92}{100}\right)\)𝓒𝓸́ 92 𝓼𝓸̂́ 1
\(A=\left(1-\dfrac{1}{9}\right)+\left(1-\dfrac{2}{10}\right)+...+\left(1-\dfrac{92}{100}\right)\)
\(A=\dfrac{8}{9}+\dfrac{8}{10}+...+\dfrac{8}{100}\)
\(A=8.\left(\dfrac{1}{9}+\dfrac{1}{10}+...+\dfrac{1}{100}\right)\)
\(B=\dfrac{1}{45}+\dfrac{1}{50}+...+\dfrac{1}{500}\)
\(B=\dfrac{1}{5}.\left(\dfrac{1}{9}+\dfrac{1}{10}+...+\dfrac{1}{100}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{A}{B}=\dfrac{8.\left(\dfrac{1}{9}+\dfrac{1}{10}+...+\dfrac{1}{100}\right)}{\dfrac{1}{5}.\left(\dfrac{1}{9}+\dfrac{1}{10}+...+\dfrac{1}{100}\right)}\\ \Rightarrow\dfrac{A}{B}=\dfrac{8}{\dfrac{1}{5}}=40\)
𝓥𝓪̣̂𝔂 𝓽𝓲̉ 𝓼𝓸̂́ 𝓬𝓾̉𝓪 𝓐 𝓿𝓪̀ 𝓑 𝓵𝓪̀ 40

0,4=2/5
3/11= 6/22
=> Biểu diễn 3 điểm trên trục số
Ta có:
0,4 = 2/5
3/11 = 6/22
Vậy 0,4; 2/5; 3/11; 4/5; 6/22 biểu diễn 3 số hữu tỉ trên trục số

2x + 624 = 5x
624 = 5x - 2x
Vì x ϵ N nên ta có thể lập bảng sau:
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ... |
| 5x - 2x | 0 | 3 | 21 | 117 | 609 | 3093 | ... |
Khi x > 5 thì 5x - 2x bằng 3093 hoặc lớn hơn nên giá trị trên không thể bằng 624. Còn khi 0 ≤ x < 5 thì không có giá trị nào của x ϵ N thì giá trị bằng 624.
Do đó không có giá trị x ϵ N thõa mãn đề bài.
2\(^x\) + 624 = 5\(y\)
Nếu \(x\) = 0 ta có: 20 + 624 = 5y
5y = 625
5y = 54
y = 4
Nếu \(x\) > 0 ⇒ 2\(x\) + 624 ⋮ 2 ∀ \(x\) \(\in\) N
2\(^x\) + 624 = 5y ⇒ 5y ⋮ 2 (vô lý)
vì 5y = 1 hoặc 5y = \(\overline{..5}\) không chia hết cho 2 ∀ y
Vậy \(x\) = 0 và y = 4 là nghiệm duy nhất thỏa mãn đề bài
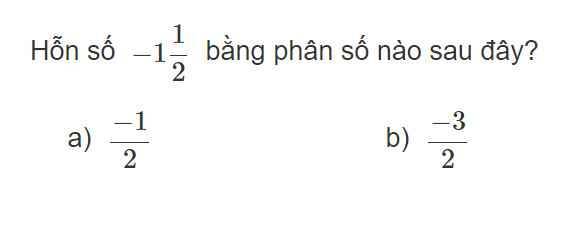
\(\dfrac{5}{2}\) - \(\dfrac{3}{2}\) \(\times\)(\(x\) - 2) = 2
\(\dfrac{3}{2}\) \(\times\)(\(x\) - 2) = \(\dfrac{5}{2}\) - 2
\(\dfrac{3}{2}\) \(\times\) (\(x\) - 2) = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(x\) - 2 = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) : \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(x\) - 2 = \(\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{1}{3}\) + 2
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{7}{3}\)
\(\dfrac{5}{2}-\dfrac{3}{2}\cdot\left(x-2\right)=2\\ \Rightarrow\dfrac{5}{2}-\dfrac{3}{2}x+\dfrac{6}{2}=2\\ \Rightarrow\dfrac{5}{2}-\dfrac{3}{2}x=2-3\\ \Rightarrow\dfrac{5}{2}-\dfrac{3}{2}x=-1\\ \Rightarrow\dfrac{3}{2}x=\dfrac{5}{2}-\left(-1\right)\\ \Rightarrow\dfrac{3}{2}x=\dfrac{7}{2}\\ \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{7}{2}:\dfrac{3}{2}\\ \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{7}{3}\)