Một hình chữ nhật có chu vi là 80 cm ,biết 5 lần chiều dài hơn 2 lần chiều rộng là 130cm . Tính diện tích hình chữ nhật
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


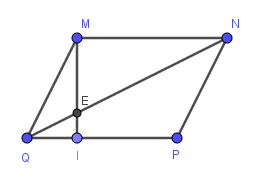
Do \(MNPQ\) là hình bình hành (gt)
\(\Rightarrow MN=PQ\)
Mà \(QI=\dfrac{1}{3}PQ\left(gt\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow QI=\dfrac{1}{3}MN\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{QI}{MN}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Do \(MNPQ\) là hình bình hành (gt)
\(\Rightarrow MN\) // \(PQ\)
\(\Rightarrow MN\) // \(QI\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{QI}{MN}=\dfrac{QE}{EN}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\dfrac{QE}{EN}=\dfrac{1}{3}\Rightarrow EN=3QE\)
Mà \(EN+QE=NQ=18\left(cm\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow3QE+QE=18\)
\(\Rightarrow4QE=18\)
\(\Rightarrow QE=\dfrac{18}{4}=4,5\left(cm\right)\)

Ta có: MNPQ là hình bình hành
=>MP cắt NQ tại trung điểm của mỗi đường
=>O là trung điểm chung của MP và NQ
Xét ΔMQN có
ND,MO là các đường trung tuyến
ND cắt MO tại H
do đó: H là trọng tâm của ΔMQN
=>\(NH=\frac23ND\)
Xét ΔNQP có
NE,PO là các đường trung tuyến
NE cắt PO tại K
Do đó: K là trọng tâm của ΔNQP
=>\(NK=\frac23NE\)
Xét ΔNDE có \(\frac{NH}{ND}=\frac{NK}{NE}\left(=\frac23\right)\)
nên HK//DE
=>\(\frac{HK}{DE}=\frac{NH}{ND}=\frac23\)
=>\(\frac{28}{DE}=\frac23=\frac{28}{42}\)
=>DE=42(cm)

a: Vẽ đồ thị:
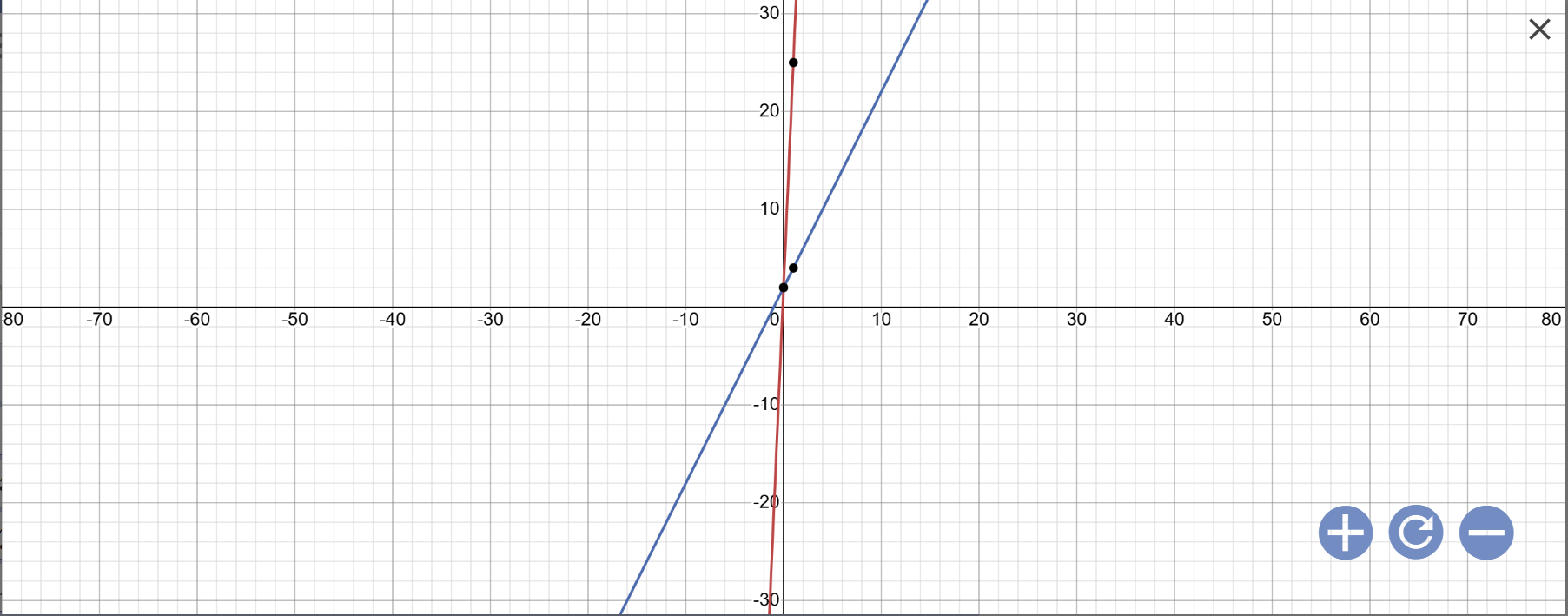
b: Tọa độ giao điểm của (d1) với trục Ox là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\23x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\23x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=-\dfrac{2}{23}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ giao điểm của (d1) với trục Oy là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=23x+2=23\cdot0+2=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
23x+2=2x+2
=>23x-2x=0
=>21x=0
=>x=0
Khi x=0 thì \(y=2x+2=2\cdot0+2=2\)
Vậy: (d1) cắt (d2) tại A(0;2)

`(-x^2 + x)/(-2x^2 + 3x - 1) ` `(đkxđ: x ne 1/2; x ne 1)`
`= (x^2 - x)/(2x^2 - 3x + 1) `
`= (x(x-1))/((x-1)(2x - 1))`
`= x/(2x -1)`
\(\dfrac{-x^2+x}{-2x^2+3x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-x}{2x^2-3x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x-1\right)}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x}{2x-1}\)

Chúng ta cần tìm giá trị lớn nhất và giá trị nhỏ nhất của hai hàm số đã chọn. ### **Câu a: \( F = \frac{2x + 3}{x^2 + 4} \)** #### **Bước 1: Tìm đạo hàm của \( F \)** Gọi: \[ F(x) = \frac{2x + 3}{x^2 + 4} \] Đạo hàm của \( F(x) \) theo quy tắc kinh tế: \[ F'(x) = \frac{(2)(x^2+4) - (2x+3)(2x)}{(x^2+4)^2} \] \[ = \frac{2x^2 + 8 - (4x^2 + 6x)}{(x^2+4)^2} \] \[ = \frac{-2x^2 - 6x + 8}{(x^2+4)^2} \] #### **Bước 2: Tìm các điểm cực trị** Phương pháp giải thích: \[ -2x^2 - 6x + 8 = 0 \] Chia hai vế cho -2: \[ x^2 + 3x - 4 = 0 \] \[ (x + 4)(x - 1) = 0 \] \[ x = -4, x = 1 \] #### **Bước 3: chắc hạn tại \( x \to \pm\infty \)** \[ \lim_{x \to \pm\infty} F(x) = 0 \] #### **Bước 4: Tính giá trị của \( F(x) \) tại các cực trị và một số điểm đặc biệt**### **Câu a: Tìm giá trị lớn nhất, nhỏ nhất của \( F = \frac{2x + 3}{x^2 + 4} \)** #### **Bước 1: Tìm đạo hàm của \( F(x) \)** Sử dụng quy tắc đạo hàm của một phân thức: \[ F(x) = \frac{2x + 3}{x^2 + 4} \] áp dụng công thức: \[ F'(x) = \frac{(2)(x^2 + 4) - (2x + 3)(2x)}{(x^2 + 4)^2} \] \[ = \frac{2x^2 + 8 - (4x^2 + 6x)}{(x^2 + 4)^2} \] \[ = \frac{-2x^2 - 6x + 8}{(x^2 + 4)^2} \] #### **Bước 2: Tìm các cực trị** Giải thích phương trình \( F'(x) = 0 \): \[ -2x^2 - 6x + 8 = 0 \] Chia hai vế cho -2: \[ x^2 + 3x - 4 = 0 \] Phân tích thành nhân tử: \[ (x + 4)(x - 1) = 0 \] \[ x = -4, x = 1 \] #### **Bước 3: dừng giới hạn tại \( x \to \pm\infty \)** \[ \lim_{x \to \pm\infty} F(x) = 0 \] Do đó đồ thị có đỉnh ngang là \( y = 0 \). #### **Bước 4: Tính giá trị của \( F(x) \) tại các cực trị** \[ F(-4) =

Olm chào em, em xem hướng dẫn chi tiết dưới đây em sẽ hiểu vì sao em nhé.
Giải:
\(x^2\) - 5\(x\) + 6
= (\(x^2\) - 3\(x\)) - (2\(x-6\))
= \(x\left(x-3\right)-2\left(x-3\right)\)
= (\(x-3\))(\(x-2\))

1: Để (d) cắt (d') tại một điểm trên trục tung thì
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a\ne a'\\b=b'\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ne m-2\\m-1=-2m\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow3m=1\)
=>\(m=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
2: Thay x=2 vào y=mx+m-1, ta được:
\(y=m\cdot2+m-1=3m-1\)
Thay x=2 và y=3m-1 vào (d'), ta được:
\(2\left(m-2\right)-2m=3m-1\)
=>3m-1=-4
=>3m=-3
=>m=-1
3: Thay x=-1 và y=2 vào (d), ta được:
\(m\cdot\left(-1\right)+m-1=2\)
=>-m+m-1=2
=>-1=2(vô lý)
vậy: \(m\in\varnothing\)

Giải:
Số trái cây sầu riêng cửa hàng đã bán được là:
400 x 20 : 100 = 80 (kg)
Kết luận số trái cây sầu riêng cửa hàng đã bán là 80 kg.

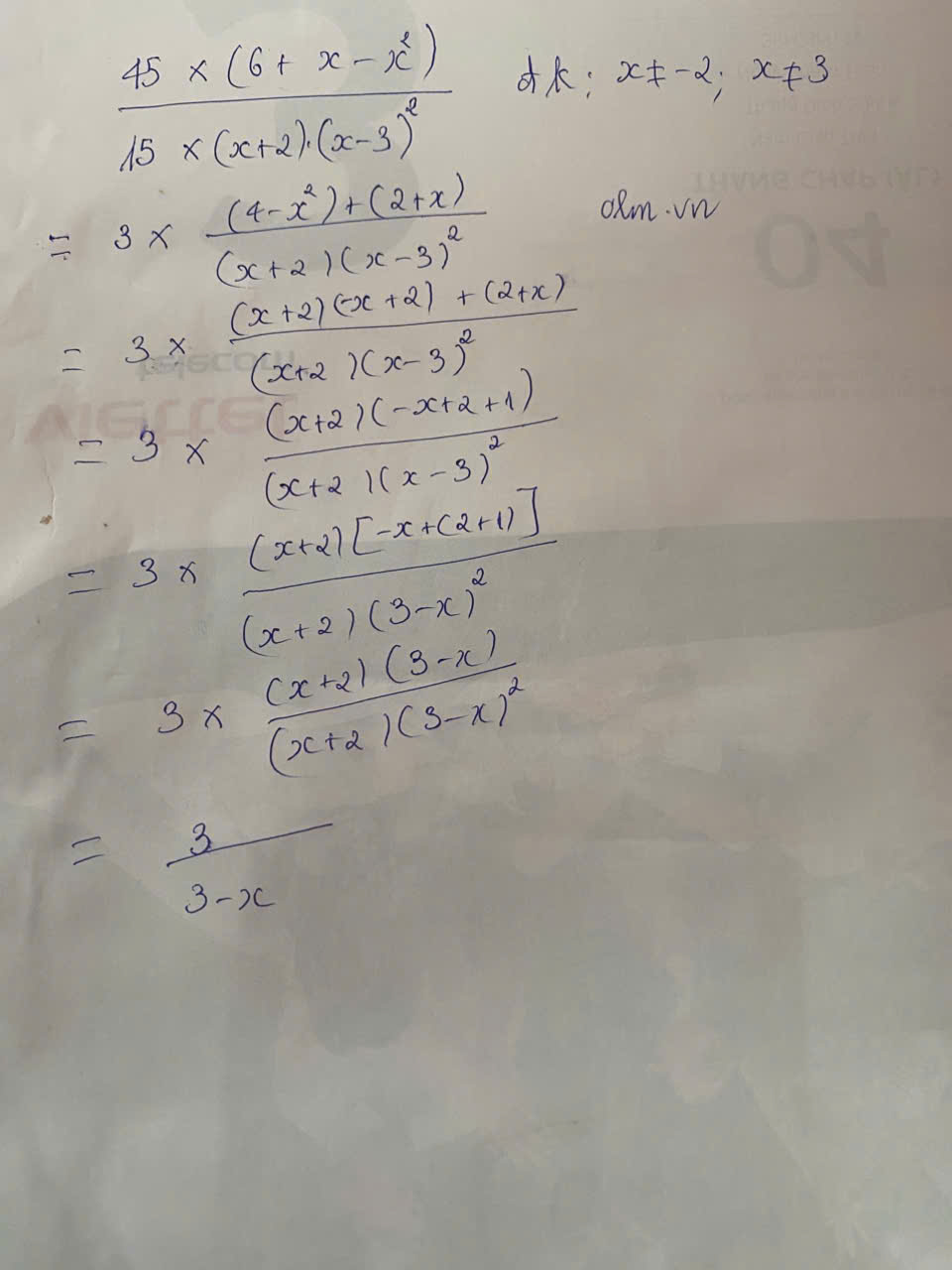
nửa chu vi HCN là: 80 : 2 = 40 (cm)
gọi x; y (cm) lần lượt là chiều dài và chiều rộng (đk: 0 < y < x < 40)
nửa chu vi HCN là 40cm nên: x + y = 40 (cm) ⇒ x = 40 - y (1)
mà 5 lần chiều dài hơn 2 lần chiều rộng là 130cm nên: 5x - 2y = 130 (2)
thay (1) vào (2) ta được: \(5\cdot\left(40-y\right)-2y=130\)
\(\Rightarrow200-5y-2y=130\\ \Rightarrow-7y=-70\\ \Rightarrow y=10\\ \Rightarrow x=40-10=30\)
diện tích hình chữ nhật: 30 x 10 = 300 (cm²)
Xin lỗi vì sự phức tạp, mình sẽ giải thích lại một cách đơn giản hơn nhé!
Bài toán:
Bước 1: Gọi chiều dài và chiều rộng
Bước 2: Sử dụng chu vi
Ta có công thức tính chu vi của hình chữ nhật là:
\(\text{Chu}\&\text{nbsp};\text{vi} = 2 \times \left(\right. l + w \left.\right)\)
Đề bài cho chu vi là 80 cm, vậy ta có:
\(2 \times \left(\right. l + w \left.\right) = 80\)
Chia cả hai vế cho 2:
\(l + w = 40\)
(Phương trình này nói rằng tổng chiều dài và chiều rộng là 40 cm)
Bước 3: Dùng mối quan hệ giữa chiều dài và chiều rộng
Đề bài còn cho biết: "5 lần chiều dài hơn 2 lần chiều rộng là 130 cm". Vậy ta có phương trình thứ hai:
\(5 l - 2 w = 130\)
(Mối quan hệ này nói rằng 5 lần chiều dài trừ đi 2 lần chiều rộng thì bằng 130 cm)
Bước 4: Giải hệ phương trình
Phương trình 1: \(l + w = 40\)
Phương trình 2: \(5 l - 2 w = 130\)
Bây giờ ta sẽ giải hệ phương trình này:
\(l = 40 - w\)
\(5 \left(\right. 40 - w \left.\right) - 2 w = 130\)
Giải phương trình này:
\(200 - 5 w - 2 w = 130\) \(200 - 7 w = 130\) \(- 7 w = 130 - 200\) \(- 7 w = - 70\) \(w = 10\)
Vậy chiều rộng là \(w = 10\) cm.
Bước 5: Tính chiều dài
Bây giờ ta thay \(w = 10\) vào phương trình \(l + w = 40\):
\(l + 10 = 40\) \(l = 40 - 10 = 30\)
Vậy chiều dài là \(l = 30\) cm.
Bước 6: Tính diện tích
Diện tích của hình chữ nhật là:
\(\text{Di}ệ\text{n}\&\text{nbsp};\text{t} \overset{ˊ}{\imath} \text{ch} = l \times w = 30 \times 10 = 300 \textrm{ } \text{cm}^{2}\)
Vậy diện tích hình chữ nhật là 300 cm².
😊