giải pt: \(2x^2+3x-2=\sqrt{1-x}\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



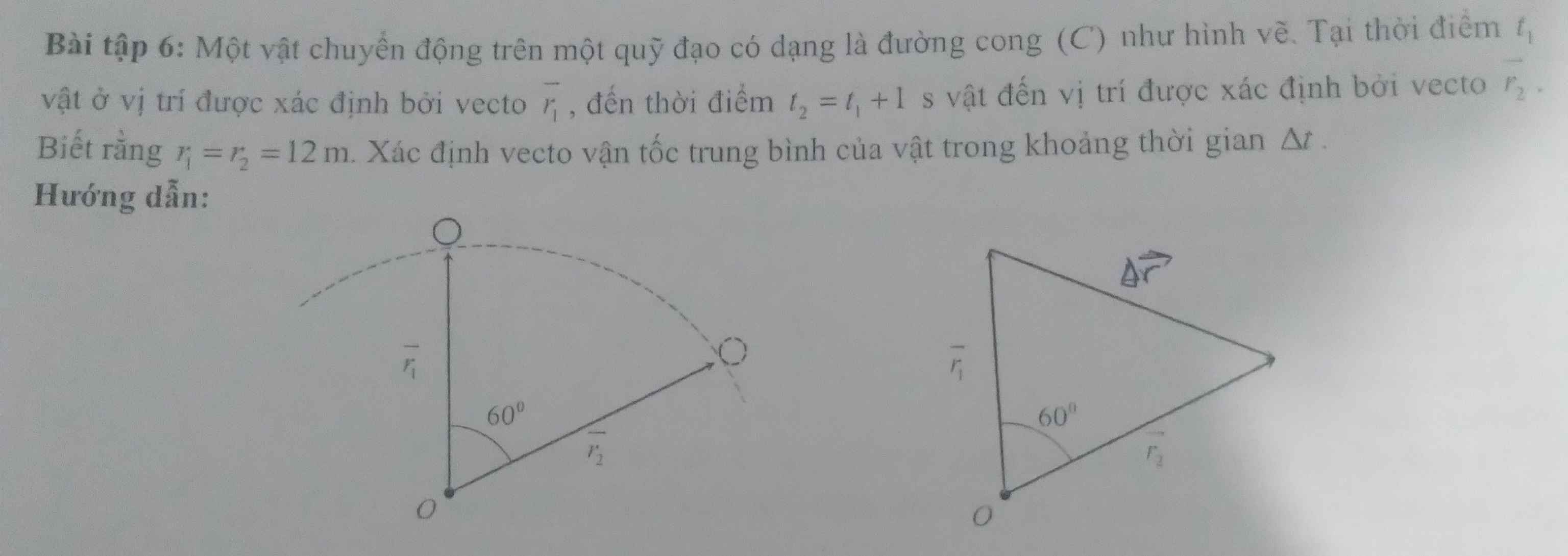
Vectơ vận tốc trung bình có phương và chiều trùng với vectơ độ dời
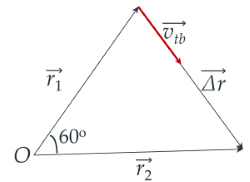
Độ lớn của vận tốc trung bình được tính như sau:
$|\overrightarrow{v_{tb}}|=\dfrac{|\overrightarrow{\Delta r}|}{\Delta t}=\dfrac{12}{1}=12$ (m/s)
(Do tam giác tạo bởi các vectơ $\overrightarrow{r_1},\,\overrightarrow{r_2},\,\overrightarrow{\Delta r}$ đều)

1: A(1;2); C(4;-2)
\(\overrightarrow{AC}=\left(3;-4\right)\)
Phương trình tham số đường thẳng AC là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1+3t\\y=2-4t\end{matrix}\right.\)
2: \(\overrightarrow{BC}=\left(7;-1\right)\)
=>Vecto pháp tuyến là (1;7)
Phương trình tổng quát của đường thẳng BC là:
1(x+3)+7(y+1)=0
=>x+3+7y+7=0
=>x+7y+10=0
3: M là trung điểm của AB
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_M=\dfrac{1-3}{2}=-1\\y_M=\dfrac{2-1}{2}=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: M(-1;0,5); C(4;-2)
\(\overrightarrow{MC}=\left(5;-2,5\right)=\left(2;-1\right)\)
Phương trình tham số đường thẳng MC là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=4+2t\\y=-2+\left(-1\right)\cdot t=-2-t\end{matrix}\right.\)

Mỗi kí tự có 10 cách chọn số, 26 cách chọn chữ in hoa và 26 cách chọn chữ in thường. Do đó mỗi kí tự có \(10+2.26=62\) cách chọn. Khi đó số mật khẩu có thể là \(62^{10}\)
Trong trường hợp xấu nhất, kẻ gian sẽ mất \(62^{10}\) giây, để cho gọn hơn thì là \(62^{10}:60:60:24:365:100=266140083\) thể kỷ
P/S: Đó là khi kẻ gian không chết trước khi phá được mật khẩu.

- Số 1 có 1 ước nguyên dương duy nhất là chính nó, mặt khác:
+, Số nguyên tố là số có 2 ước nguyên dương là 1 và chính nó nên 1 không là số nguyên tố
+, Hợp số là số có 2 ước nguyên dương trở lên
Do đó, mệnh đề "1 không là số nguyên tố cũng không là hợp số" là 1 mệnh đề đúng.
*Bạn xem lại đề nha.

a) Với `m=-1` ta có:
\(\dfrac{2x-1}{2-x}+\dfrac{2x+1}{2+x}=\dfrac{4}{4-x^2}\left(x\ne\pm2\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2+x\right)}{\left(2-x\right)\left(2+x\right)}+\dfrac{\left(2x+1\right)\left(2-x\right)}{\left(2-x\right)\left(2+x\right)}=\dfrac{4}{\left(2-x\right)\left(2+x\right)}\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)\left(2+x\right)+\left(2x+1\right)\left(2-x\right)=4\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(4x+2x^2-2-x\right)+\left(4x-2x^2+2-x\right)=4\\ \Leftrightarrow3x+2x^2-2+3x-2x^2+2=4\\ \Leftrightarrow6x=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{4}{6}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{2}{3}\left(tm\right)\)
b) Vì pt có nghiệm `x=1` nên thay `x=1` vào pt ta có:
\(\dfrac{2\cdot1+m}{2-1}+\dfrac{2\cdot1-m}{2+1}=\dfrac{4}{4-1^2}\\ \Leftrightarrow2+m+\dfrac{2-m}{3}=\dfrac{4}{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(2+m\right)+2-m}{3}=\dfrac{4}{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow3\left(2+m\right)+2-m=4\\ \Leftrightarrow6+3m+2-m=4\\ \Leftrightarrow8-2m=4\\ \Leftrightarrow2m=6\\ \Leftrightarrow m=3\)