Một mật khẩu gồm 10 kí tự bao gồm chữ số từ 0-9, 26 chữ cái trong bảng chữ cái tiếng Anh (có thể viết hoa và viết thường). Nếu 1 kẻ gian mất 1 giây để thử 1 mật khẩu thì trong trường hợp xấu nhất phải mất bao lâu để phá mật khẩu?
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


- Số 1 có 1 ước nguyên dương duy nhất là chính nó, mặt khác:
+, Số nguyên tố là số có 2 ước nguyên dương là 1 và chính nó nên 1 không là số nguyên tố
+, Hợp số là số có 2 ước nguyên dương trở lên
Do đó, mệnh đề "1 không là số nguyên tố cũng không là hợp số" là 1 mệnh đề đúng.
*Bạn xem lại đề nha.

a) Với `m=-1` ta có:
\(\dfrac{2x-1}{2-x}+\dfrac{2x+1}{2+x}=\dfrac{4}{4-x^2}\left(x\ne\pm2\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2+x\right)}{\left(2-x\right)\left(2+x\right)}+\dfrac{\left(2x+1\right)\left(2-x\right)}{\left(2-x\right)\left(2+x\right)}=\dfrac{4}{\left(2-x\right)\left(2+x\right)}\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)\left(2+x\right)+\left(2x+1\right)\left(2-x\right)=4\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(4x+2x^2-2-x\right)+\left(4x-2x^2+2-x\right)=4\\ \Leftrightarrow3x+2x^2-2+3x-2x^2+2=4\\ \Leftrightarrow6x=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{4}{6}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{2}{3}\left(tm\right)\)
b) Vì pt có nghiệm `x=1` nên thay `x=1` vào pt ta có:
\(\dfrac{2\cdot1+m}{2-1}+\dfrac{2\cdot1-m}{2+1}=\dfrac{4}{4-1^2}\\ \Leftrightarrow2+m+\dfrac{2-m}{3}=\dfrac{4}{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(2+m\right)+2-m}{3}=\dfrac{4}{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow3\left(2+m\right)+2-m=4\\ \Leftrightarrow6+3m+2-m=4\\ \Leftrightarrow8-2m=4\\ \Leftrightarrow2m=6\\ \Leftrightarrow m=3\)

TK ạ
Nếu chỉ có hai lực tác dụng vào cùng một vật mà vật vẫn đứng yên thì hai lực đó là hai lực cân bằng.
Ví dụ: Hai đội kéo co cùng kéo sợi dây. Nếu hai đội mạnh ngang nhau thì họ sẽ tác dụng lên dây hai lực cân bằng. Sợi dây chịu tác dụng của hai lực cân bằng thì sẽ đứng yên. Hai vecto→u𝑢→ và →v𝑣→ biểu diễn cho hai vecto cân bằng thì hai vecto này có chung gốc, ngược hướng và có độ lớn (hay độ dài) bằng nhau.
Hai lực cân bằng là hai lực có cùng phương, ngược chiều, cùng độ lớn và có cùng điểm đặt (tác động vào cùng một điểm).
Nếu biểu diễn bằng vector thì 2 vector này cùng phương, ngược chiều, có độ dài bằng nhau và có chung điểm gốc.

Bài 1:
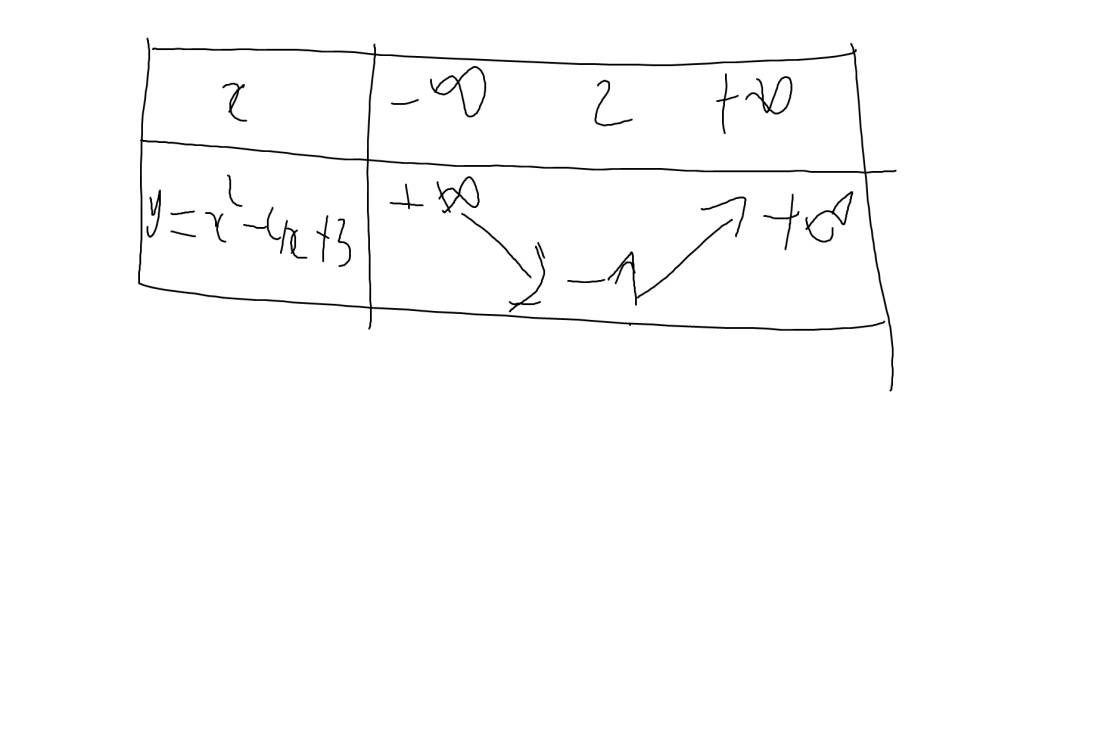
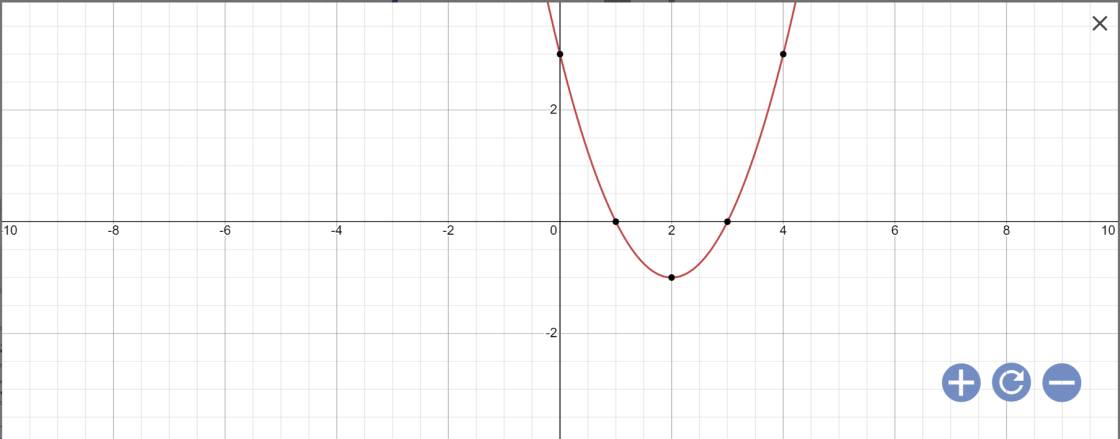
a: \(y=x^2-4x+3\)
Vì a=1>0 nên hàm số đồng biến khi \(x>-\dfrac{b}{2a}=\dfrac{4}{2}=2\) và nghịch biến khi x<2
Khi x=2 thì \(y=2^2-4\cdot2+3=4-8+3=-1\)
Bảng biến thiên:
Vẽ đồ thị:
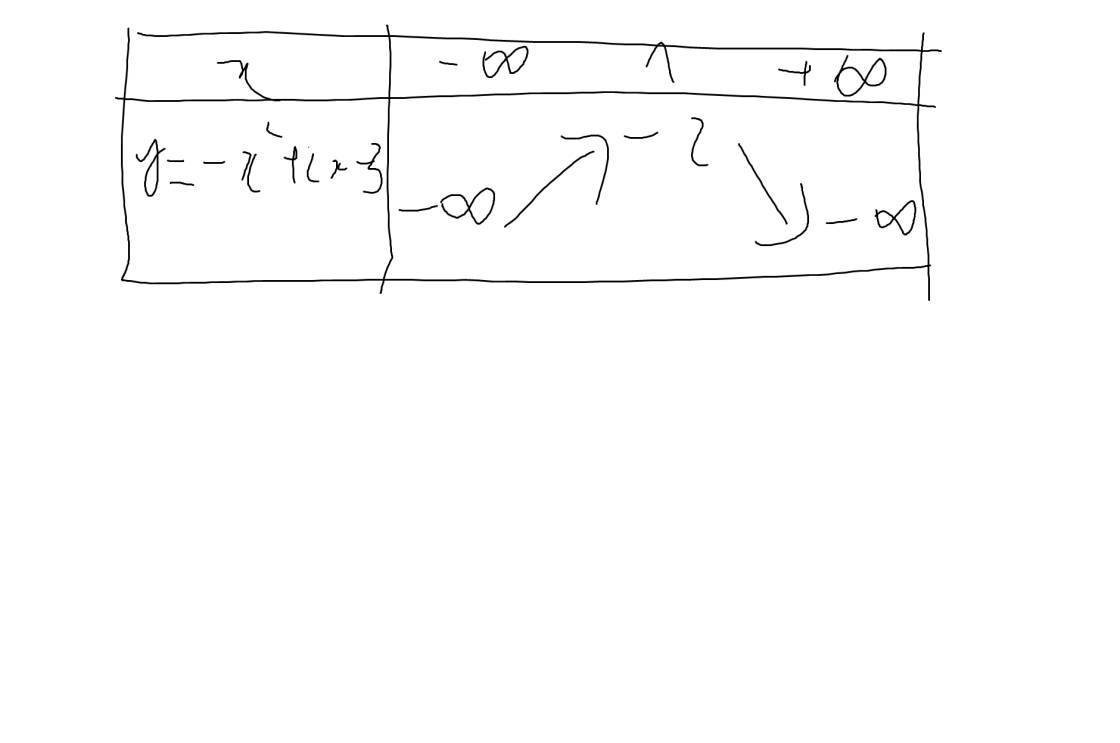
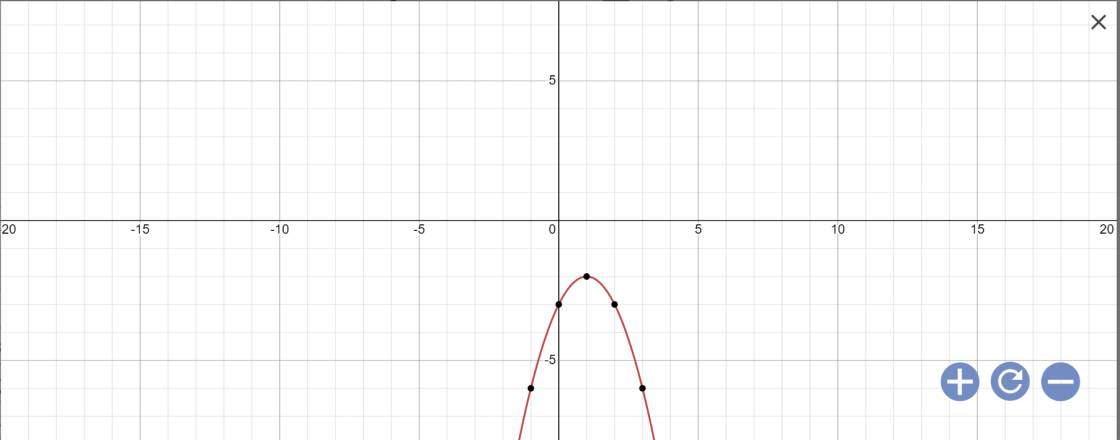
b: \(y=-x^2+2x-3\)
Vì a=-1<0 nên hàm số đồng biến khi \(x< -\dfrac{b}{2a}=\dfrac{-2}{2\cdot\left(-1\right)}=1\) và nghịch biến khi x>1
Khi x=1 thì \(y=-1^2+2\cdot1-3=-1+2-3=-2\)
Bảng biến thiên:
Vẽ đồ thị:
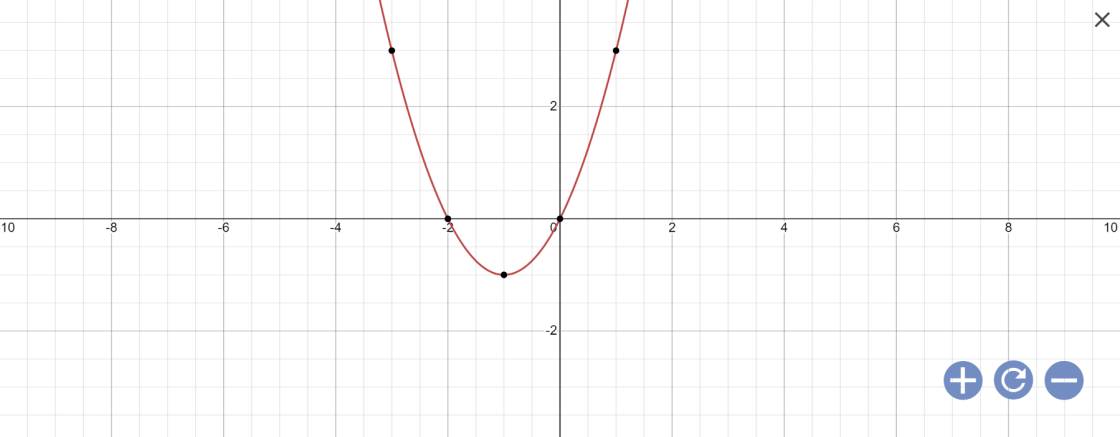
c: \(y=x^2+2x\)
Vì a=1>0 nên hàm số đồng biến khi \(x>-\dfrac{b}{2a}=\dfrac{-2}{2}=-1\); hàm số nghịch biến khi x<-1
Khi x=-1 thì \(y=\left(-1\right)^2+2\cdot\left(-1\right)=1-2=-1\)
Bảng biến thiên:
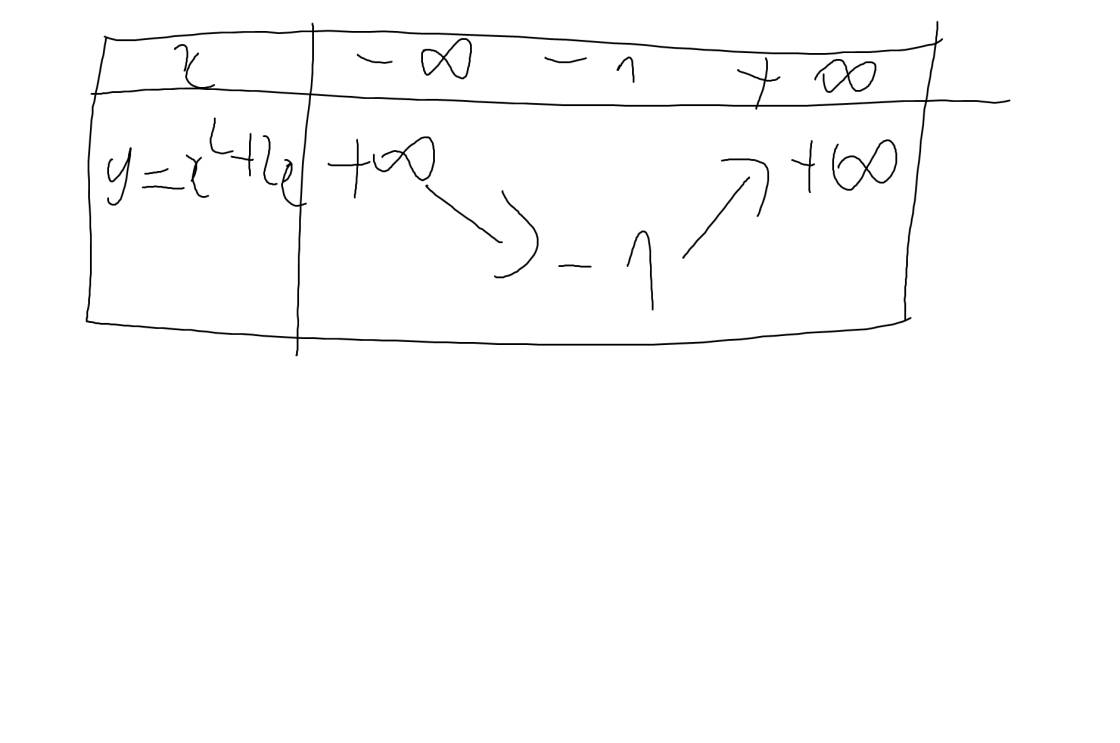
vẽ đồ thị:
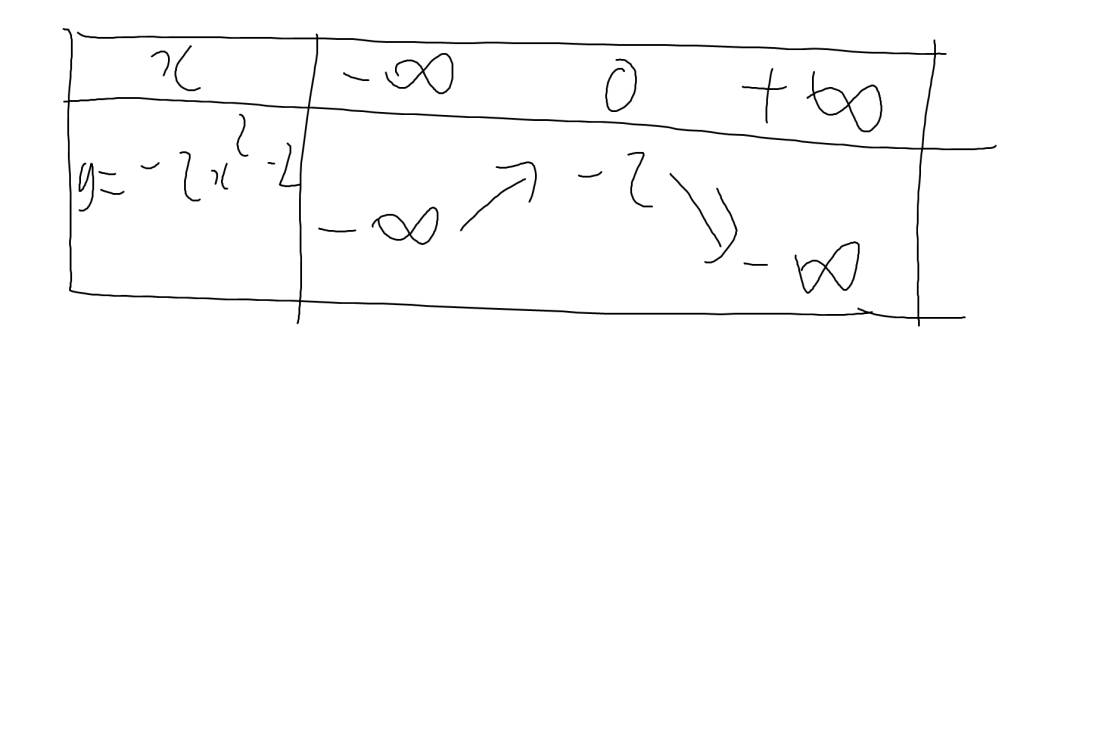
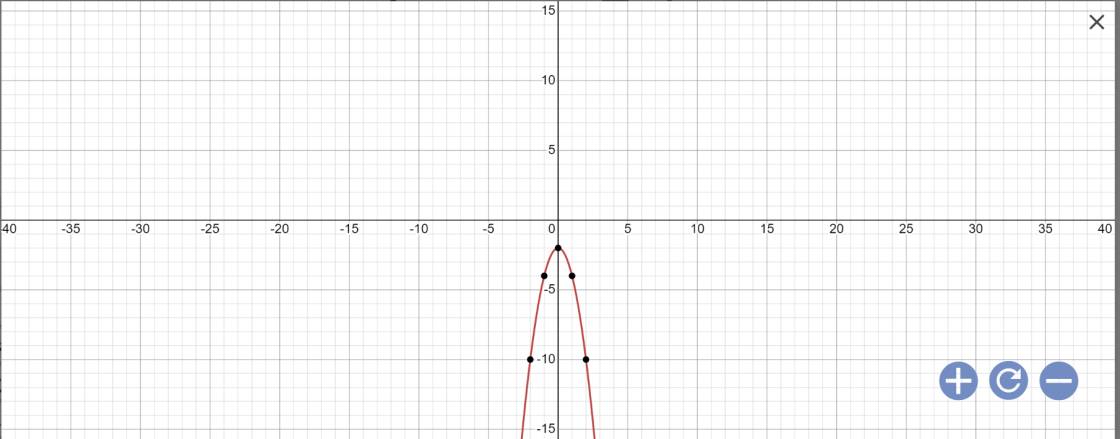
d: \(y=-2x^2-2\)
Vì a=-2<0
nên hàm số đồng biến khi \(x< -\dfrac{b}{2a}=0\) và nghịch biến khi x>0
Khi x=0 thì \(y=-2\cdot0^2-2=-2\)
Bảng biến thiên:
Vẽ đồ thị:

 Mọi người cho mình hỏi câu nào đúng được không ạ
Mọi người cho mình hỏi câu nào đúng được không ạ
Mỗi kí tự có 10 cách chọn số, 26 cách chọn chữ in hoa và 26 cách chọn chữ in thường. Do đó mỗi kí tự có \(10+2.26=62\) cách chọn. Khi đó số mật khẩu có thể là \(62^{10}\)
Trong trường hợp xấu nhất, kẻ gian sẽ mất \(62^{10}\) giây, để cho gọn hơn thì là \(62^{10}:60:60:24:365:100=266140083\) thể kỷ
P/S: Đó là khi kẻ gian không chết trước khi phá được mật khẩu.