
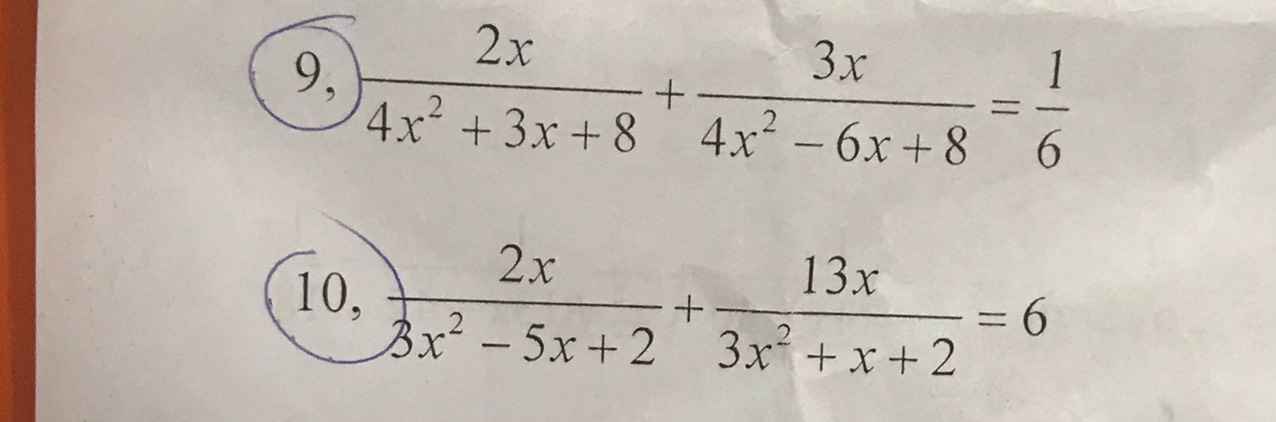 giải phương trình
giải phương trình
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bạn bấm vào biểu tượng ![]() để nhập các công thức toán học cho rõ ràng nhé!
để nhập các công thức toán học cho rõ ràng nhé!
Vd:\(3^{10}\)

Before my sister went on holiday, she had packed some boots and plenty of warm clothes.

Lấy điểm A bất kì nằm trên đường tròn đáy.
Khi đó góc tạo bởi đường sinh và mặt phẳng đáy chính là \(\widehat{SAO}=45^o\)
Do đó \(h=r=\dfrac{a}{\sqrt{2}}\)
\(\Rightarrow S_{xq}=\pi rl=\pi.\dfrac{a}{\sqrt{2}}.a=\dfrac{\pi a^2}{\sqrt{2}}\)
\(S_{tp}=S_{xq}+\pi r^2=\dfrac{\pi a^2}{\sqrt{2}}+\pi\left(\dfrac{a}{\sqrt{2}}\right)^2=\dfrac{\pi a^2\sqrt{2}+\pi a^2}{2}\)

Thay n = 100 vào biểu thức , ta được;
\(N=156-224:100\)
\(=156-22,4\)
\(=133,6\)

222 + 333 - 111 - 444 + 111
= 555 - 111 - 444 + 111
= 444 - 444 + 111
= 0 + 111
= 111

a/
$\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{y}=\frac{1}{5}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{x+y}{xy}=\frac{1}{5}$
$\Rightarrow 5(x+y)=xy$
$\Rightarrow 5x+5y-xy=0$
$\Rightarrow x(5-y)+5y=0$
$\Rightarrow x(5-y)-5(5-y)=-25$
$\Rightarrow (x-5)(5-y)=-25$
$\Rightarrow (x-5)(y-5)=25$
Do $x,y$ nguyên nên $x-5,y-5$ nguyên. Mà tích $(x-5)(y-5)=25$ nên xảy ra các TH sau đây:
TH1: $x-5=1, y-5=25\Rightarrow x=6; y=30$
TH2: $x-5=-1, y-5=-25\Rightarrow x=4; y=-20$
TH3: $x-5=25, y-5=1\Rightarrow x=30; y=6$
TH4: $x-5=-25, y-5=-1\Rightarrow x=-20; y=4$
TH5: $x-5=5, y-5=5\Rightarrow x=10; y=10$
TH6: $x-5=-5, y-5=-5\Rightarrow x=0; y=0$
b/
$\frac{2}{x}+\frac{1}{y}=3$
$\Rightarrow \frac{x+2y}{xy}=3$
$\Rightarrow x+2y=3xy$
$\Rightarrow 3xy-x-2y=0$
$\Rightarrow x(3y-1)-2y=0$
$\Rightarrow 3x(3y-1)-6y=0$
$\Rightarrow 3x(3y-1)-2(3y-1)=2$
$\Rightarrow (3x-2)(3y-1)=2$
Do $x,y$ nguyên nên $3x-2, 3y-1$ cũng là số nguyên. Mà tích của chúng bằng 2 nên ta xét các TH sau:
TH1: $3x-2=1, 3y-1=2\Rightarrow x=y=1$
TH2: $3x-2=2, 3y-1=1\Rightarrow x=\frac{4}{3}$ (loại)
TH3: $3x-2=-1, 3y-1=-2\Rightarrow x=\frac{1}{3}$ (loại)
TH4: $3x-2=-2, 3y-1=-1\Rightarrow x=y=0$ (loại do $x,y\neq 0$)
Vậy $x=y=1$
Bài 4:
d:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;-1;2;-2\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x+4}{x-1}+\dfrac{x-4}{x+1}=\dfrac{x+8}{x-2}+\dfrac{x-8}{x+2}+6\)
=>\(\dfrac{\left(x+4\right)\left(x+1\right)+\left(x-4\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x+8\right)\left(x+2\right)+\left(x-8\right)\left(x-2\right)+6\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x^2+8}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x^2+32+6x^2-24}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x^2+8}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{8x^2+8}{x^2-4}\)
=>\(\left(2x^2+8\right)\left(x^2-4\right)=\left(8x^2+8\right)\left(x^2-1\right)\)
=>\(2x^4-32=8x^4-8\)
=>\(-6x^4=24\)
=>\(x^4=-4\left(loại\right)\)
Vậy: Phương trình vô nghiệm
c:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-1;-3;-8;-10\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{2}{x^2+4x+3}+\dfrac{5}{x^2+11x+24}+\dfrac{2}{x^2+18x+80}=\dfrac{9}{52}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\dfrac{5}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+8\right)}+\dfrac{2}{\left(x+8\right)\left(x+10\right)}=\dfrac{9}{52}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{x+1}-\dfrac{1}{x+3}+\dfrac{1}{x+3}-\dfrac{1}{x+8}+\dfrac{1}{x+8}-\dfrac{1}{x+10}=\dfrac{9}{52}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{x+1}-\dfrac{1}{x+10}=\dfrac{9}{52}\)
=>\(\dfrac{9}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+10\right)}=\dfrac{9}{52}\)
=>(x+1)(x+10)=52
=>\(x^2+11x-42=0\)
=>(x+14)(x-3)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-14\left(nhận\right)\\x=3\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
b:
ĐXKĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-2;-3;-4;-5;-6\right\}\)\(\dfrac{1}{x^2+5x+6}+\dfrac{1}{x^2+7x+12}+\dfrac{1}{x^2+9x+20}+\dfrac{1}{x^2+11x+30}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+4\right)\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+5\right)\left(x+6\right)}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{x+2}-\dfrac{1}{x+3}+\dfrac{1}{x+3}-\dfrac{1}{x+4}+\dfrac{1}{x+4}-\dfrac{1}{x+5}+\dfrac{1}{x+5}-\dfrac{1}{x+6}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{x+2}-\dfrac{1}{x+6}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+6-x-2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+6\right)}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>(x+2)(x+6)=32
=>\(x^2+8x-20=0\)
=>(x+10)(x-2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-10\left(nhận\right)\\x=2\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
a: \(\dfrac{x^2}{x^2+2x+2}+\dfrac{x^2}{x^2-2x+2}-\dfrac{4x^2-20}{x^4+4}=\dfrac{322}{65}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x^2\left(x^2-2x+2\right)+x^2\left(x^2+2x+2\right)-4x^2+20}{\left(x^2+2x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+2\right)}=\dfrac{322}{65}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x^4-2x^3+2x^2+x^4+2x^3+2x^2-4x^2+20}{x^4+4}=\dfrac{322}{65}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x^4+20}{x^4+4}=\dfrac{322}{65}\)
=>\(322\left(x^4+4\right)=65\left(2x^4+20\right)\)
=>\(322x^4+1288-130x^4-1300=0\)
=>\(192x^4=12\)
=>\(x^4=\dfrac{1}{16}\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(nhận\right)\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)