![]() sáng nay e mới thi toán. Cho e hoir là vex hình mà kí hiệu bằng nhau như này được không ạ?
sáng nay e mới thi toán. Cho e hoir là vex hình mà kí hiệu bằng nhau như này được không ạ?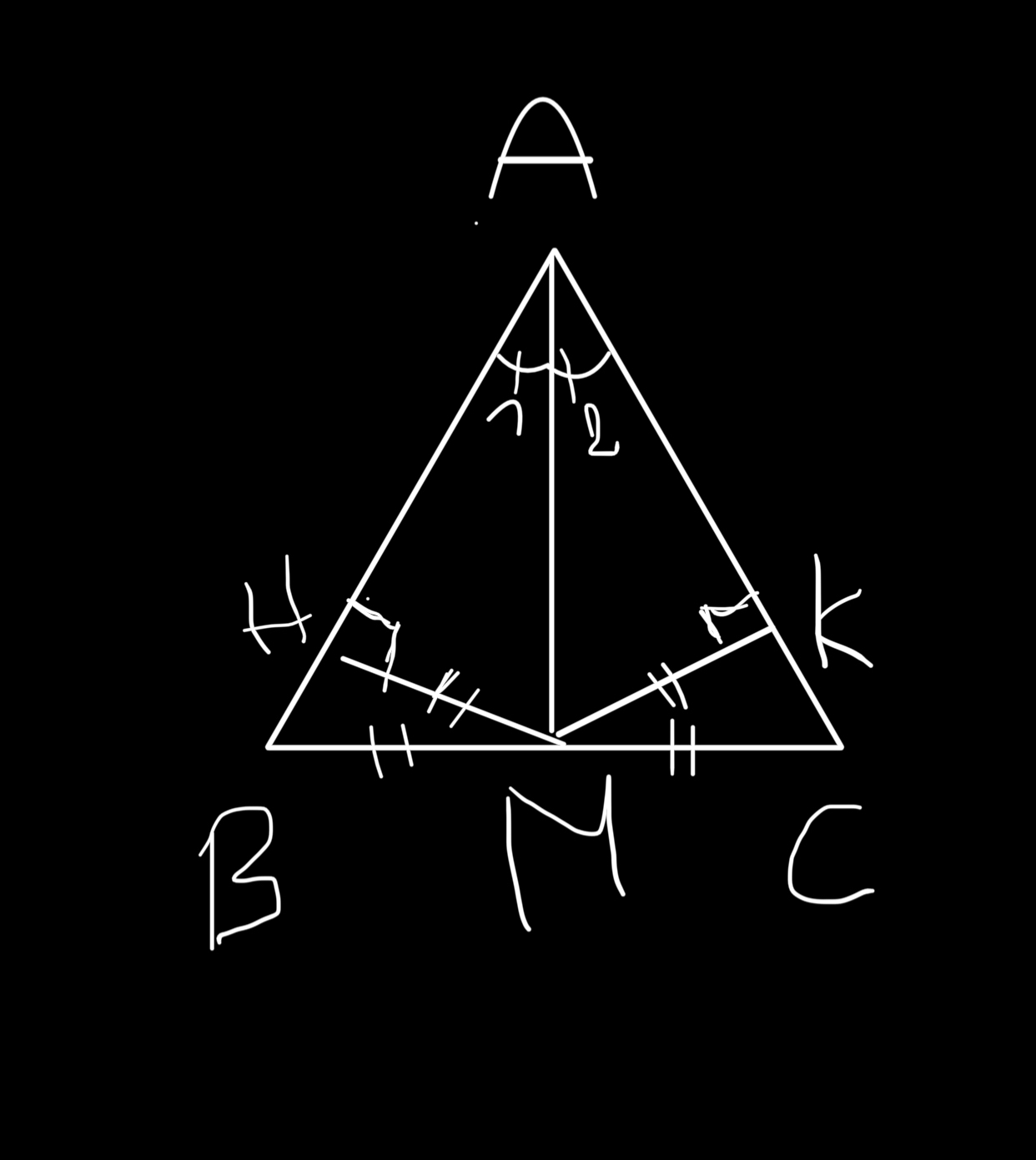
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

5x/7 = 10/-3
=> 5x.(-3) = 7.10
5x.(-3) = 70
5x = 70/-3
x = -70/3 : 5
x = -14/3
Vậy x = -14/3
#ngophuongloan(chipcuti)
Chúc bạn học tốt hjhj!!
Vì \(\frac{5x}{7}=\frac{10}{-3}\) là một tỉ lệ thức
\(\Rightarrow5x.\left(-3\right)=7.10\)
\(5x.\left(-3\right)=70\)
\(5x=70:\left(-3\right)\)
\(5x=\frac{-70}{3}\)
\(x=\left(-\frac{70}{3}\right):5\)
\(x=-\frac{14}{13}\)
Vậy \(x=-\frac{14}{13}\)

Diện tích mảnh vườn hình chữ nhật là : 35 . 28 = 980 (\(m^2\))
Số ki-lô-gam cà chua thu hoạch được trên cả mảnh vườn là :
980 : 4 . 3 = 735 (kg)
Đ/s : 735 kg
giải
Diện tích mảnh vườn hình chữ nhật là:
35 . 28 =980 (m2)
Tổng số kg cà chua thu hoạch được trên mảnh vườn là:
980:4= 254 (kg)
sai cho tớ xl ạ

\(\dfrac{x}{4}=\dfrac{x\cdot2}{4\cdot2}=\dfrac{2x}{8}\)
áp dụng tính chất của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có:
\(\dfrac{2x}{8}=\dfrac{y}{5}=\dfrac{2x-y}{8-5}=\dfrac{12}{3}=4\\ \dfrac{2x}{8}=4\Rightarrow x=16\\ \dfrac{y}{5}=4\Rightarrow y=20\)
vậy x = 16; y = 20
có x/4=y/5 suy ra 2x/8= y/5
áp dụng t/c của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có
2x/8=y/5=2x-y/8-5=4
suy ra
2x/8=4 y/5=4
x=16 y=20

Giải:
Gọi số vở của ba lớp 7A; 7B; 7C lần lượt là: \(x;y;z\) (\(x;y;z\in N\) *)
Theo bài ra ta có: \(\frac{x}{10}\) = \(\frac{y}{14}\) = \(\frac{z}{13}\)
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có:
\(\frac{x}{10}\) = \(\frac{y}{14}=\frac{z}{13}\) = \(\frac{z-x}{13-10}\) = \(\frac{30}{3}\) = 10
\(x\) = 10 x 10 = 100(quyển)
y = 10 x 14 = 140 (quyển)
z = 10 x 13 = 130 (quyển)
Kết luận số vở lớp 7A; 7B; 7C góp được lần lượt là:
100; 130; 140 quyển

Giải:
Theo bài ra ta có:
\(\frac{A}{3}=\frac{B}{5}=\frac{C}{7}\)
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có:
\(\frac{A}{3}=\frac{B}{5}=\frac{C}{7}\) = \(\frac{A+B+C}{3+5+7}\) = \(\frac{180}{15}\) = 12\(^0\)
A = 12\(^0\) x 3 = 36\(^0\)
B = 12\(^0\) x 5 = 60\(^0\)
C = 12\(^0\) x 7 = 84\(^0\)
Gọi ba góc $\widehat {A} ; \widehat {B} ; \widehat {C}` trong $\triangleABC$ lần lượt là $x;y;z (x;y;z \in N$$***$`)`
Theo đề bài , các góc $\widehat {A} ; \widehat {B} ; \widehat {C}$ tỉ lệ với các số `3,5,7`
$\Rightarrow$$\frac{x}{3} = \frac {y}{5} = \frac {z}{7}$
Trong một tam giác , tổng cả ba góc trong tam giác bằng $180^\circ$
$\Rightarrow$$x+y+z = 180^\circ$
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau , ta có :
$\frac{x}{3} = \frac {y}{5} = \frac {z}{7} = \frac {x+y+z}{3+5+7} = \frac {180^\circ}{15} = 12^\circ$
Khi đó :
$\frac {x}{3} = 12^\circ \Rightarrow x = 12^\circ . 3 = 36^\circ$
$\frac {y}{5} = 12^\circ \ Rightarrow y = 12^\circ . 5 = 60^\circ$
$\frac {z}{7} = 12^\circ \Rightarrow z = 12^\circ . 7 = 84^\circ$
Vậy số đo $\widehat {A} ; \widehat {B} ; \widehat {C}$ trong $\triangle ABC$ lần lượt là : $36^\circ ; 60^\circ ; 84^\circ$

Giải:
Theo bài ra ta có:
\(\frac{A}{3}=\frac{B}{5}=\frac{C}{7}\)
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có:
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có:
\(\frac{A}{3}=\frac{B}{5}=\frac{C}{7}\) = = \(\frac{A+B+C}{3+5+7}\) = \(\frac{180}{15}\) = 12\(^0\)
A = 12\(^0\) x 3 = 36\(^0\)
B = 12\(^0\) x 5 = 60\(^0\)
C = 12\(^0\) x 7 = 84\(^0\)
Ký hiệu vậy chưa được em. Vì em ký hiệu vậy nghĩa là BM = CM = HM = KM
Trong khi chỉ có BM = CM; HM = KM
Cho mình xin đề bài đk ạ?