Mọi người giúp mik gấp vs:
Bài 1: Tìm giá trị nguyên của n để phân số sau nhận giá trị nguyên:
A=3n+9/n-4 B=6n+5/2n-1
Bài 2: Tìm GTLN của:
A=3/2-1/2|x-2| D=-2,3|1/2-x| +2
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(12\cdot53+53\cdot47-53\cdot41\)
\(=53\cdot\left(12+47-41\right)\)
\(=53\cdot18=954\)

a: Trên tia Ox, ta có: OA<OB
nên A nằm giữa O và B
b: A nằm giữa O và B
=>OA+AB=OB
=>AB+3=6
=>AB=3(cm)
c: Vì A nằm giữa O và B
nên AO và AB là hai tia đối nhau
=>AO và Ax là hai tia đối nhau
Trên tia AO, ta có: AO<AM
nên O nằm giữa A và M
=>AO+OM=AM
=>OM+3=6
=>OM=3(cm)
=>OM=OA(=3cm)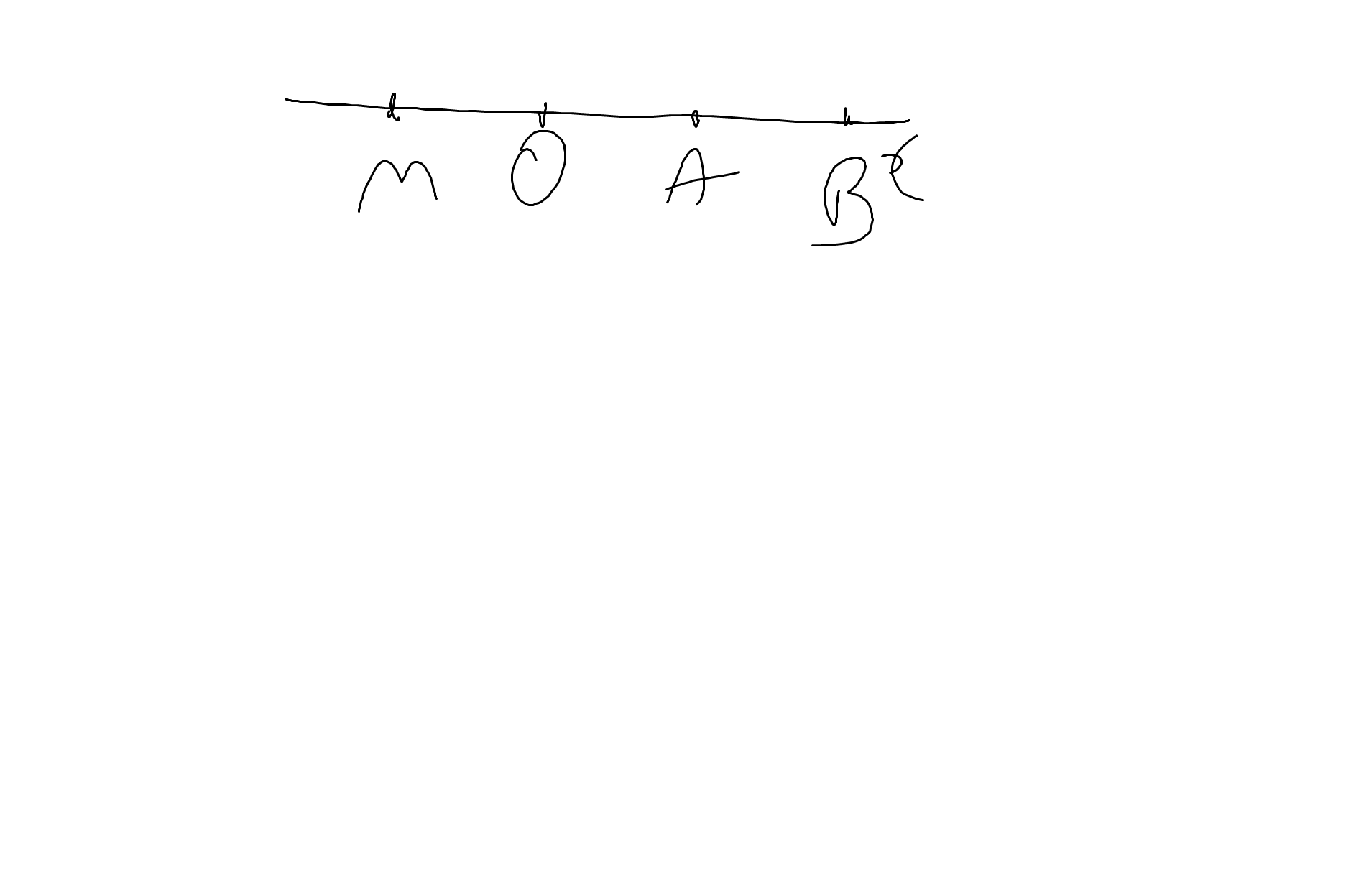

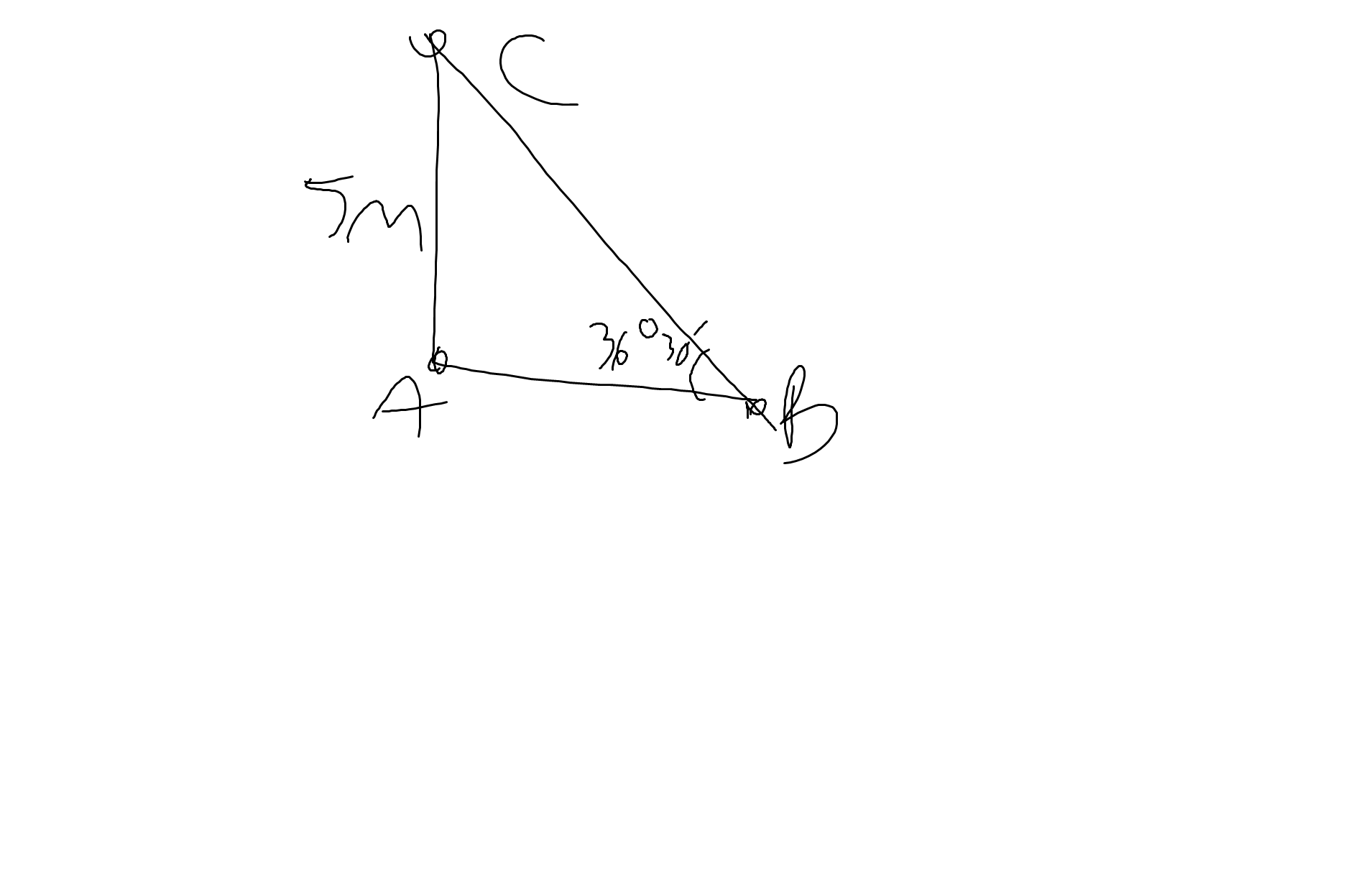
Gọi AC là chiều cao, góc ABC là góc tạo bởi tia sáng mặt trời với mặt đất
Theo đề, ta có: AC=5m; \(\widehat{B}=36^030'\); AC\(\perp\)AB tại A
Xét ΔABC có \(tanB=\dfrac{AC}{AB}\)
=>\(AB=\dfrac{5}{tan36^030'}\simeq6,76\left(m\right)\)

Câu 1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=2\\2x-y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y+2x-y=2+1\\x+y=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x=3\\y=2-x\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=2-1=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>Chọn D
Câu 2:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=1\\x-3y=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y-x+3y=1-2\\x+y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4y=-1\\x=1-y\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{1}{4}\\x=1-\left(-\dfrac{1}{4}\right)=1+\dfrac{1}{4}=\dfrac{5}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>Chọn C
Câu 3:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=3\\x-2y=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2y\\2y+y=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3y=3\\x=2y\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=1\\x=2\cdot1=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>Chọn D
Câu 4:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-y=1\\-3x+y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-y=1\\3x-y=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}0y=0\\y=3x-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>Hệ có vô số nghiệm
=>Chọn D
Câu 5:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-y=3\\x-y=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-y-x+y=3-4\\x-y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}0x=1\\x-y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>Hệ vô nghiệm
=>Chọn A
Câu 6:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2y=3\\2x-y=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+4y=6\\2x-y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+4y-2x+y=6-1\\2x-y=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=1\\2x=y+1=1+1=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>x=1;y=1
=>Chọn B

Vì nếu tăng chiều rộng thêm 20m thì hình chữ nhật trở thành hình vuông nên chiều dài hơn chiều rộng 20m.
Coi chiều dài là 3 phần, chiều rộng là 2 phần, khi đó hiệu số phần bằng nhau là:
$3-2=1$ (phần)
Chiều dài hình chữ nhật là:
$20:1\times3=60(m)$
Chiều rộng hình chữ nhật là:
$60-20=40(m)$
Diện tích hình chữ nhật là:
$60\times40=2400(m^2)$

|3x+4|=x+2
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2>=0\\\left(3x+4\right)^2=\left(x+2\right)^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-2\\\left(3x+4-x-2\right)\left(3x+4+x+2\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-2\\\left(2x+2\right)\left(4x+6\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-2\\x\in\left\{-1;-\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-1;-\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
|5x-6|=4-x
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4-x>=0\\\left(5x-6\right)^2=\left(4-x\right)^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =4\\\left(5x-6-4+x\right)\left(5x-6+4-x\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =4\\\left(6x-10\right)\left(4x-2\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{\dfrac{5}{3};\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
|5-2x|=x-3
=>|2x-5|=x-3
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3>=0\\\left(2x-5\right)^2=\left(x-3\right)^2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=3\\\left(2x-5\right)^2-\left(x-3\right)^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=3\\\left(2x-5-x+3\right)\left(2x-5+x-3\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=3\\\left(x-2\right)\left(3x-8\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in\varnothing\)
|3-2x|=6+4x
=>|2x-3|=4x+6
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x+6>=0\\\left(4x+6\right)^2=\left(2x-3\right)^2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-\dfrac{3}{2}\\\left(4x+6-2x+3\right)\left(4x+6+2x-3\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-\dfrac{3}{2}\\\left(2x+9\right)\left(6x+3\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
|6-3x|=3x
=>|3x-6|=3x
=>|x-2|=x
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=0\\\left(x-2\right)^2=x^2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=0\\-4x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Nguyễn Mai Phương ơi câu hỏi đấy ở trong sách 250 bài toán chọn lọc lớp 4 của thầy trần nhật minh đó


a: Trên tia Ox, ta có: OA<OB
nên A nằm giữa O và B
b: A nằm giữa O và B
=>OA+AB=OB
=>AB+3=6
=>AB=3(cm)
c: Vì A nằm giữa O và B
nên AO và AB là hai tia đối nhau
=>AO và Ax là hai tia đối nhau
Trên tia AO, ta có: AO<AM
nên O nằm giữa A và M
=>AO+OM=AM
=>OM+3=6
=>OM=3(cm)
=>OM=OA(=3cm)

Vậy \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}Min\left(y\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\pi\end{matrix}\right.\\Max\left(y\right)=\dfrac{2\sqrt{2}}{3}\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{4}\\x=\dfrac{3\pi}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bài 1
a: ĐKXĐ: \(n\ne4\)
Để A nguyên thì \(3n+9⋮n-4\)
=>\(3n-12+21⋮n-4\)
=>\(21⋮n-4\)
=>\(n-4\in\left\{1;-1;3;-3;7;-7;21;-21\right\}\)
=>\(n\in\left\{5;3;7;1;11;-3;25;-17\right\}\)
b: ĐKXĐ: n<>1/2
Để B nguyên thì \(6n+5⋮2n-1\)
=>\(6n-3+8⋮2n-1\)
=>\(8⋮2n-1\)
mà 2n-1 lẻ(do n nguyên)
nên \(2n-1\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
=>\(n\in\left\{1;0\right\}\)
Bài 2:
a: \(\left|x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right|>=0\forall x\)
=>\(-\dfrac{1}{2}\left|x-2\right|< =0\forall x\)
=>\(A=-\dfrac{1}{2}\left|x-2\right|+\dfrac{3}{2}< =\dfrac{3}{2}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x-2=0
=>x=2
b: \(\left|\dfrac{1}{2}-x\right|>=0\forall x\)
=>\(-2,3\left|\dfrac{1}{2}-x\right|< =0\forall x\)
=>\(D=-2,3\left|\dfrac{1}{2}-x\right|+2< =2\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi 1/2-x=0
=>x=1/2
Bài 1:
\(A=\dfrac{3n+9}{n-4}=\dfrac{3n-12}{n-4}+\dfrac{21}{n-4}=3+\dfrac{21}{n-4}\)
Để A nguyên thì \(\dfrac{21}{n-4}\) phải nguyên hay \(\left(n-4\right)\inƯ\left(21\right)=\left\{1;-1;3;-3;7;-7;21;-21\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow n\in\left\{5;3;7;1;11;-3;25;-17\right\}\) (thoả mãn điều kiện)
Vậy...
\(B=\dfrac{6n+5}{2n-1}=\dfrac{6n-3}{2n-1}+\dfrac{8}{2n-1}=3+\dfrac{8}{2n-1}\)
Để B nguyên thì \(\dfrac{8}{2n-1}\) phải nguyên hay \(\left(2n-1\right)\inƯ\left(8\right)=\left\{1;-1;2;-2;4;-4;8;-8\right\}\)
Mặt khác: Vì n nguyên nên 2n-1 là số lẻ
Do đó: \(\left(2n-1\right)\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow n\in\left\{1;0\right\}\)
Vậy....