(√m+1)x^2 - 2 (√m+1)x + 1 = 0 tìm m để phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt (m là một thanh số)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Thời gian(phút) | [0;5) | [0;5) | [0;5) | [0;5) |
Tần số(n) | 9,375% | 9,375% | 9,375% | 9,375% |
biểu đồ của em là :
Thời gian(phút) | [0;5) | [0;5) | [0;5) | [0;5) |
Tần số(n) | 9,375% | 9,375% | 9,375% | 9,375% |

Bài 1:
a: vẽ đồ thị:
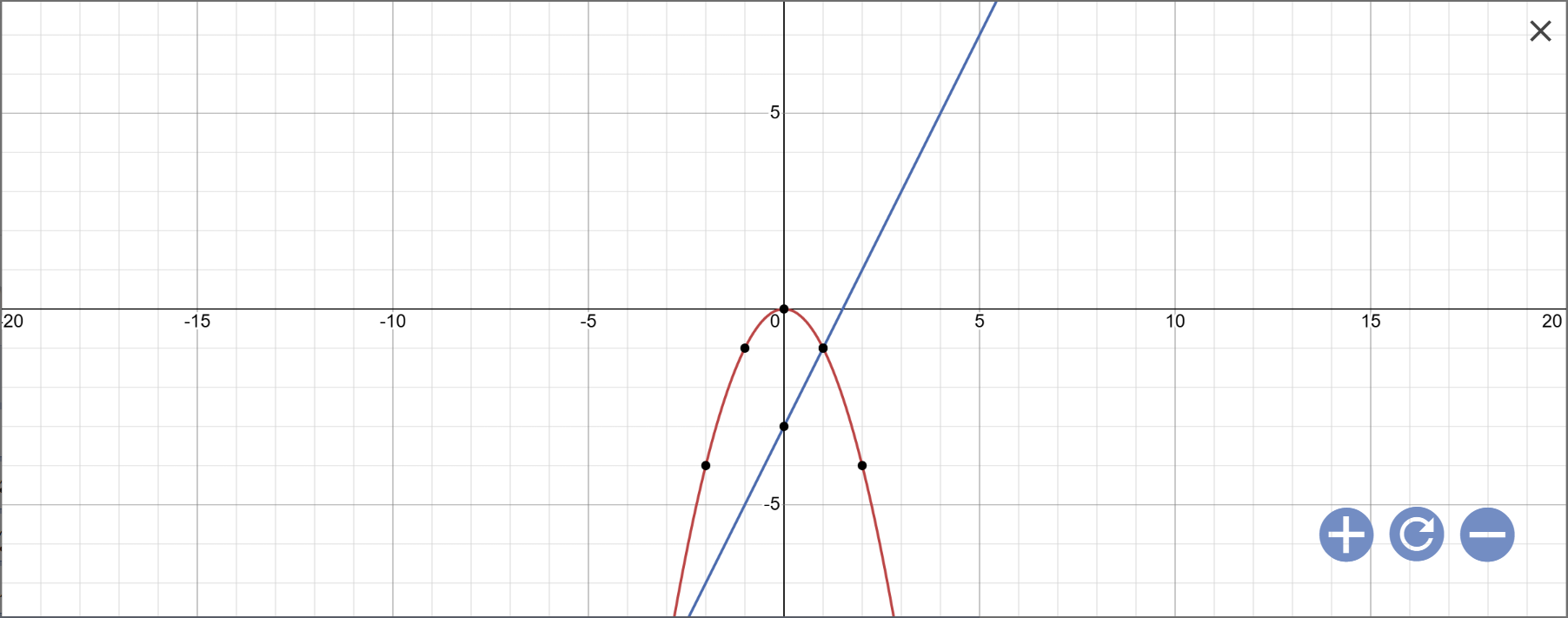
b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(-x^2=2x-3\)
=>\(x^2+2x-3=0\)
=>(x+3)(x-1)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi x=-3 thì \(y=-x^2=-\left(-3\right)^2=-9\)
Khi x=1 thì \(y=-1^2=-1\)
Vậy: (P) cắt (d) tại A(-3;-9); B(1;-1)
Bài 2:
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(x^2=2x+8\)
=>\(x^2-2x-8=0\)
=>(x-4)(x+2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi x=4 thì \(y=x^2=4^2=16\)
Khi x=-2 thì \(y=\left(-2\right)^2=4\)
Vậy: Tọa độ giao điểm là C(4;16); D(-2;4)
Bài 3:
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(3x^2=2x+1\)
=>\(3x^2-2x-1=0\)
=>\(3x^2-3x+x-1=0\)
=>(x-1)(3x+1)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\3x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi x=1 thì \(y=3\cdot1^2=3\)
Khi x=-1/3 thì \(y=3\cdot\left(-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)^2=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
vậy: Tọa độ giao điểm là A(1;3); B(-1/3;1/3)
Bài 4:
a: Vẽ đồ thị:
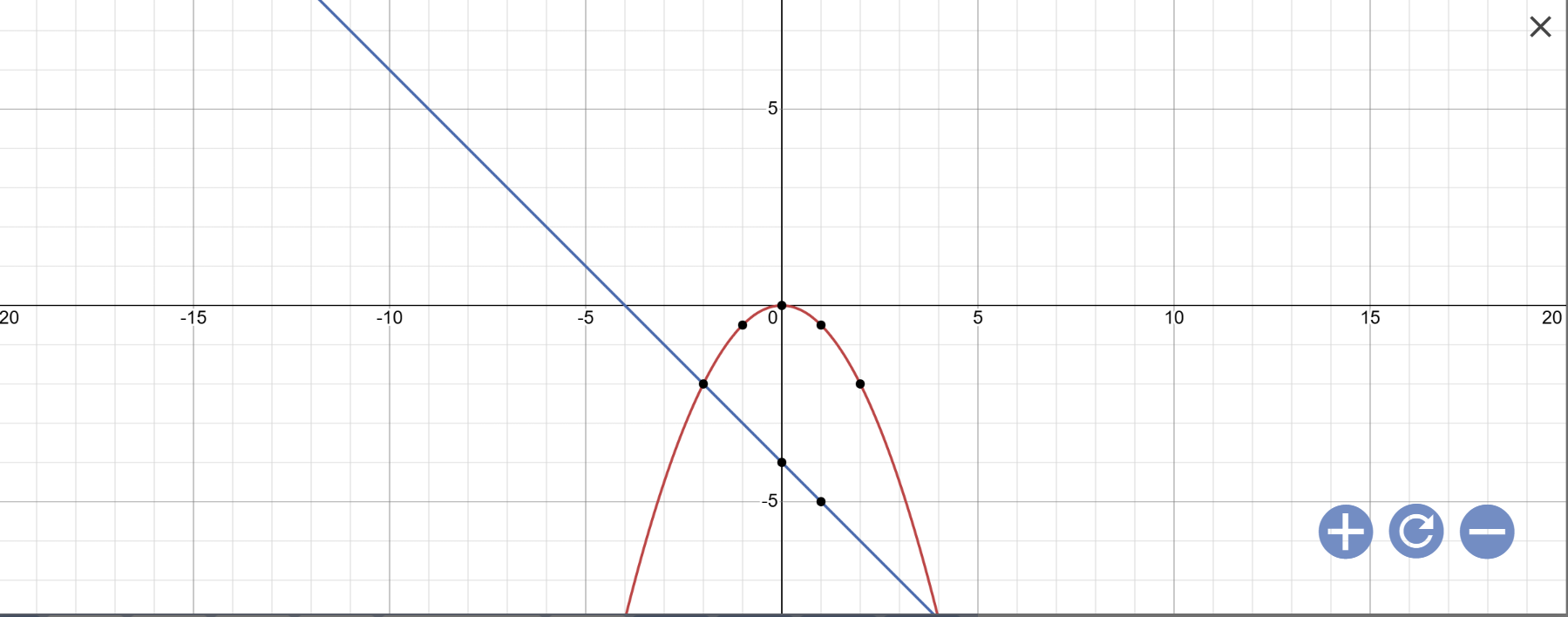
b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(-\dfrac{x^2}{2}=-x-4\)
=>\(x^2=2x+8\)
=>\(x^2-2x-8=0\)
=>(x-4)(x+2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4=0\\x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi x=4 thì \(y=-x-4=-4-4=-8\)
Khi x=-2 thì y=-x-4=-(-2)-4=2-4=-2
Vậy: (P) cắt (d) tại A(4;-8); B(-2;-2)
Bài 5:
a: Vẽ đồ thị
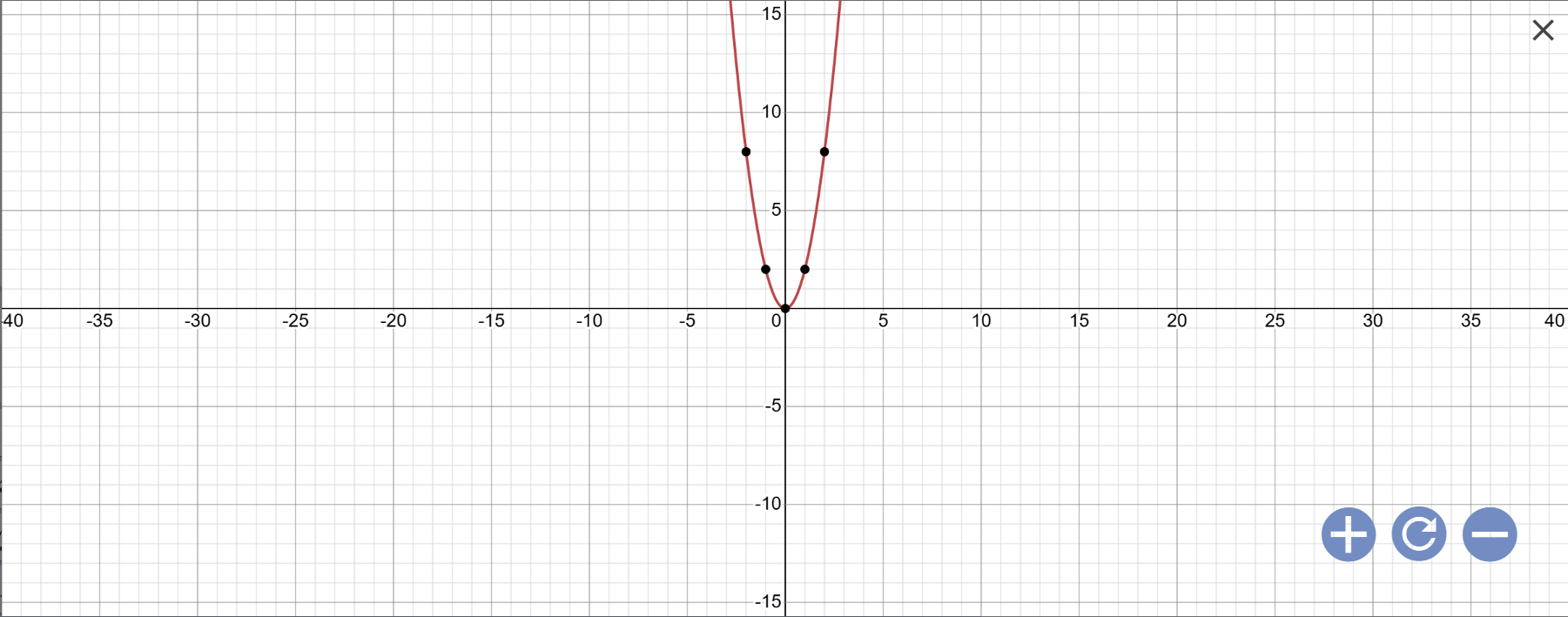
b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(2x^2=5x-3\)
=>\(2x^2-5x+3=0\)
=>\(2x^2-2x-3x+3=0\)
=>(x-1)(2x-3)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\2x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi x=1 thì \(y=2\cdot1^2=2\)
Khi x=3/2 thì \(y=2\cdot\left(\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2=2\cdot\dfrac{9}{4}=\dfrac{9}{2}\)
Vậy: (d) cắt (P) tại A(1;2); \(B\left(\dfrac{3}{2};\dfrac{9}{2}\right)\)

Olm chào em, em cần đăng đầy đủ nội dung câu hỏi đó lên trên n này thì thầy cô mới có thể giải thích cho em tại sao lại có dòng:
- 4 x 1 x 2 em nhé.


Định lý Bézout (hay Định lý Bézout về các ước chung) là một kết quả quan trọng trong đại số và lý thuyết số, liên quan đến các đa thức và số nguyên.
Định lý Bézout cho rằng:
- Với hai đa thức f(x)f(x) và g(x)g(x) trong K[x]K[x] (với KK là một trường, ví dụ như RR hay CC), nếu d=gcd(f(x),g(x))d=gcd(f(x),g(x)) là ước chung lớn nhất của f(x)f(x) và g(x)g(x), thì tồn tại hai đa thức u(x)u(x) và v(x)v(x) sao cho:
d(x)=u(x)f(x)+v(x)g(x)d(x)=u(x)f(x)+v(x)g(x)
- Nếu f(x)f(x) và g(x)g(x) là hai số nguyên, định lý này nói rằng với bất kỳ cặp số nguyên aa và bb, sẽ luôn tồn tại các số nguyên xx và yy sao cho:
ax+by=gcd(a,b)ax+by=gcd(a,b)
Đây là dạng cơ bản của định lý Bézout trong lý thuyết số. Định lý này được sử dụng rộng rãi trong việc tìm ước chung lớn nhất của hai số, giải quyết các phương trình Diophantine, và trong các ứng dụng mã hóa (như RSA).
Về bản chất, định lý Bézout cho phép ta biểu diễn ước chung lớn nhất của hai đa thức hoặc số nguyên dưới dạng một tổ hợp tuyến tính của chúng.
mình cần Định lý bezout về số phép chia đa thức, chứ không phải là số dư đa thức ạ.

Để phương trình là phương trình bậc hai thì \(\sqrt{m}>=0\)
=>m>=0
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì \(\left[-2\left(\sqrt{m}+1\right)\right]^2-4\left(\sqrt{m}+1\right)>0\)
=>\(4\left(m+2\sqrt{m}+1\right)-4\left(\sqrt{m}+1\right)>0\)
=>\(4\left(m+\sqrt{m}\right)>0\)(luôn đúng khi m>=0)
Điều kiện: `m >= 0`
Phương trình đã cho có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
`<=> Δ' > 0`
`<=> (sqrt{m} + 1)^2 - (sqrt{m} + 1).1 > 0`
`<=> m^2 + 2sqrt{m} + 1 - sqrt{m} - 1 > 0`
`<=> m^2 + sqrt{m} >= 0` (Thỏa mãn với mọi `m >= 0)`