x-1/x-1/x+1=2x-1/x2+x
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: ΔABC cân tại A
mà AM là phân giác
nên AM vuôg góc BC và M là trung điểm của BC
\(BM=CM=\dfrac{60}{2}=30\left(cm\right)\)
\(AM=\sqrt{50^2-30^2}=40\left(cm\right)\)
\(S_{ABC}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot40\cdot60=20\cdot60=1200\left(cm^2\right)\)
b: Xét ΔOAK và ΔOCM có
OA=OC
góc AOK=góc COM
OK=OM
=>ΔOAK=ΔOCM
=>góc OAK=góc OCM
=>AK//CM
b: Xét tứ giác AMCK có
AK//CM
AK=CM
góc AMC=90 độ
=>AMCK là hfinh chữ nhật
d: Để AMCK là hình vuông thì AM=CM=BC/2
=>ΔABC vuông tại A

Lời giải:
$x^2+2x+4^n-2^{n+2}+5=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x^2+2x+1)+(4^n-2^{n+2}+4)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+1)^2+[(2^n)^2-4.2^n+4]=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+1)^2+(2^n-2)^2=0$
Vì $(x+1)^2\geq 0; (2^n-2)^2\geq 0$ với mọi $x\in\mathbb{R}; n\in\mathbb{N}$
Do đó để tổng của chúng bằng $0$ thì $(x+1)^2=(2^n-2)^2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=-1; n=1$

a^2+b^2/2=(a-b/2)^2
=>a^2+b^2/2=(a-b)^2/4
=>4(a^2+b^2)=2(a^2-2ab+b^2)
=>2a^2+2b^2=a^2-2ab+b^2
=>a^2+2ab+b^2=0
=>(a+b)^2=0
=>a=-b
(a+b)^3+2=0^3+2=2



`12(5^2+1)(5^4+1)(5^8 +1)(5^16 +1) =1/2(5^n-1)(n in NN)`
`<=> 24(5^2+1)(5^4+1)(5^8 +1)(5^16 +1) =5^n-1`
`<=> (25-1)(5^2+1)(5^4+1)(5^8 +1)(5^16 +1) =5^n-1`
`<=> (5^2 -1)(5^2+1)(5^4+1)(5^8 +1)(5^16 +1) =5^n-1`
`<=> (5^4-1)(5^4+1)(5^8 +1)(5^16 +1) =5^n-1`
`<=> (5^8-1)(5^8+1)(5^16+1) =5^n-1`
`<=> (5^16-1)(5^16+1) = 5^n-1`
`<=> 5^32-1 =5^n-1`
`=> n =32(t//m)`
Thay `n=32` vào biểu thức ta đc
`2*32 -3 = 64-3 =61`
Vậy biểu thức có gt là 61 khi `n=32`
=>24(5^2+1)(5^4+1)(5^8+1)(5^16+1)=5^n-1
=>(5^4-1)(5^4+1)(5^8+1)(5^16+1)=5^n-1
=>5^n-1=(5^8-1)(5^8+1)(5^16+1)
=>5^n-1=5^32-1
=>n=32
=>2n-3=64-3=61

`x/(2x+6) -x/(2x+2) = (3x+2)/[(x+1)(x+3)] (đk : x ne -1 ; x ne -3)`
`<=>`\(\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)}-\dfrac{x\left(x+3\right)}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(3x+2\right)}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
`=> x^2 +x -x^2 -3x = 6x +6`
`<=> x -3x-6x =6`
`<=> -8x =6`
`<=> x =-3/4(t//m)`
Vậy `S={-3/4}`
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)-x\left(x+3\right)=6x+4\)
=>6x+4=x^2+x-x^2-3x=-2x
=>8x=-4
=>x=-1/2(nhận)

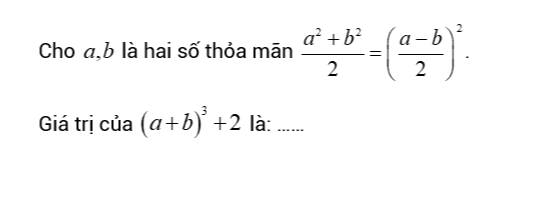
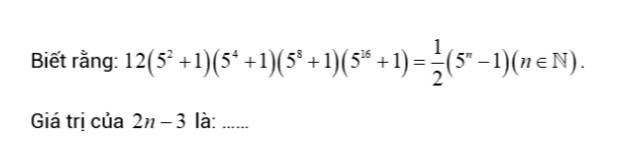
\(\dfrac{x-1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}=\dfrac{2x-1}{x^2+x}\left(dkxd:x\ne0,x\ne-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}-\dfrac{2x-1}{x\left(x+1\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)-x-\left(2x-1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-1-x-2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(l\right)\\x=3\left(n\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)