Tìm x, y và z biết (2x2z2)3 + (-3xy3)2 = 0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


9:
a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;-5\right\}\)
\(P=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{2x+10}+\dfrac{x-5}{x}+\dfrac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{2\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{x-5}{x}+\dfrac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x^2+2x\right)+2\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2-50+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x^2+4x-5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)}{2\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{x-1}{2}\)
b: Khi x=2 thì \(P=\dfrac{2-1}{2}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
c: \(S=P\cdot\dfrac{2}{x-2}=\dfrac{x-1}{2}\cdot\dfrac{2}{x-2}=\dfrac{x-1}{x-2}=\dfrac{x-2+1}{x-2}=1+\dfrac{1}{x-2}\)
Để S là số nguyên thì \(x-2\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{3;1\right\}\)

8)
a) \(A=1-\dfrac{x}{1-\dfrac{x}{x+1}}\left(x\ne-1\right)\)
\(=1-\dfrac{x}{\dfrac{x+1-x}{x+1}}=1-\dfrac{x}{\dfrac{1}{x+1}}=1-x\left(x+1\right)=-x^2-x+1\)
b) \(B=\dfrac{\dfrac{x}{y}+\dfrac{y}{x}}{\dfrac{x-y}{x+y}+\dfrac{x+y}{x-y}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{x^2}{xy}+\dfrac{y^2}{xy}}{\dfrac{\left(x-y\right)^2+\left(x+y\right)^2}{\left(x+y\right)\left(x-y\right)}}\left(x\ne\pm y;x\ne0;y\ne0\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{\dfrac{x^2+y^2}{xy}}{\dfrac{x^2-2xy+y^2+x^2+2xy+y^2}{\left(x+y\right)\left(x-y\right)}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{x^2+y^2}{xy}}{\dfrac{2\left(x^2+y^2\right)}{x^2-y^2}}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+y^2}{xy}\cdot\dfrac{x^2-y^2}{2\left(x^2+y^2\right)}=\dfrac{x^2-y^2}{2xy}\)
10:
a: Thời gian dự định là \(\dfrac{60}{x}\left(giờ\right)\)
b: Thời gian đi nửa quãng đường đầu tiên là: \(\dfrac{60}{2}:\left(x+10\right)=\dfrac{30}{x+10}\left(giờ\right)\)
Thời gian đi nửa quãng đường còn lại là:
\(\dfrac{60-30}{x-6}=\dfrac{30}{x-6}\left(giờ\right)\)
c: Ô tô đến B đúng giờ nên ta có: \(\dfrac{30}{x+10}+\dfrac{30}{x-6}=\dfrac{60}{x}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{x+10}+\dfrac{1}{x-6}=\dfrac{2}{x}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x-6+x+10}{\left(x+10\right)\left(x-6\right)}=\dfrac{2}{x}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x+4}{\left(x+10\right)\left(x-6\right)}=\dfrac{2}{x}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+2}{x^2+4x-60}=\dfrac{1}{x}\)
=>\(x\left(x+2\right)=x^2+4x-60\)
=>\(x^2+2x=x^2+4x-60\)
=>-2x=-60
=>x=30
Vậy: Vận tốc dự định của ô tô là 30km/h
Bài 6:
a: \(A=\dfrac{x-1}{x}-\dfrac{x+1}{x^2-x}+\dfrac{3\left(x-1\right)}{x^2-2x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-1}{x}-\dfrac{x+1}{x\left(x-1\right)}+\dfrac{3}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-1\right)-x-1+3x}{\left(x-1\right)\cdot x}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-2x+1+2x-1}{x\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2}{x\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x}{x-1}\)
b: \(B=\dfrac{x+y}{2\left(x-y\right)}-\dfrac{x-y}{2\left(x+y\right)}+\dfrac{2y^2}{x^2-y^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+y\right)^2-\left(x-y\right)^2+4y^2}{2\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+2xy+y^2-x^2+2xy-y^2+4y^2}{2\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}=\dfrac{4y^2+4xy}{2\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2y\left(x+y\right)}{2\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}=\dfrac{y}{x-y}\)

a: Xét tứ giác ABDC có
M là trung điểm chung của AD và BC
=>ABDC là hình bình hành
Hình bình hành ABDC có \(\widehat{BAC}=90^0\)
nên ABDC là hình chữ nhật
b: E đối xứng M qua AC
=>AC là đường trung trực của EM
=>AE=AM; CE=CM
ΔBAC vuông tại A
mà AM là đường trung tuyến
nên AM=CM=MB
AM=CM
AE=AM
CE=CM
Do đó: AM=MC=CE=AE
=>AMCE là hình thoi
c: AMCE là hình thoi
=>AE//CM
=>AE//BM
Xét tứ giác ABME có
AE//BM
AE=BM
Do đó: ABME là hình bình hành
=>AM cắt BE tại trung điểm của mỗi đường
mà I là trung điểm của AM
nên I là trung điểm của BE
=>B,I,E thẳng hàng

a: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}1,7x-2y=3,8\\2,1x+5y=0,4\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}8,5x-10y=19\\4,2x+10y=0,8\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}12,7x=19,8\\1,7x-2y=3,8\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{198}{127}\\2y=1,7x-3,8=-\dfrac{146}{127}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{198}{127}\\y=-\dfrac{73}{127}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(\sqrt{5}+2\right)x+y=3-\sqrt{5}\\-x+2y=6-2\sqrt{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(2\sqrt{5}+4\right)x+2y=6-2\sqrt{5}\\-x+2y=6-2\sqrt{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\left(2\sqrt{5}+4+1\right)=0\\2y=x+6-2\sqrt{5}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\2y=6-2\sqrt{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=3-\sqrt{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Gọi vận tốc trung bình ở lượt đi của nhóm bạn là: x (km/giờ) (ĐK:x>4)
=> vận tốc trung bình ở lượt về của nhóm bạn là: x-4 (km/giờ)
Thời gian lúc đi từ A đến B là: 24/x (giờ)
Thời gian lúc về từ B về A là: 24/x-4 (giờ)
Theo đề: Thời gian về lâu hơn thời gian đi 1 giờ nên ta có pt:
\(\dfrac{24}{x-4}-\dfrac{24}{x}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{24x-24\left(x-4\right)}{x\left(x-4\right)}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow24x-24x+96=x\left(x-4\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-4x=96\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-4x-96=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-12\right)\left(x+8\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-12=0\\x+8=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=12\left(nhận\right)\\x=-8\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy vận tốc tb ở lượt đi là: 12km/h
Đáp án: 12km/h
Giải thích các bước giải:
gọi x là tốc độ trung bình bàn đầu (km/h)
-> tốc độ trung bình lúc sau: x-4 (km/h)
vì thời gian xe đi từ B về A chậm hơn 1 giờ nên ta có phương trình:
24/x-4 - 24/x = 1
( bạn tự tính giúp mình, mình bấm máy thôi)
-> x= 12
-> tốc độ tb ban đầu là 12 km/h


1: Xét ΔEBA vuông tại B và ΔEDF vuông tại D có
\(\widehat{BEA}\) chung
Do đó: ΔEBA~ΔEDF
2: Xét ΔIDA vuông tại D và ΔIBF vuông tại B có
\(\widehat{DIA}=\widehat{BIF}\)(hai góc đối đỉnh)
Do đó: ΔIDA~ΔIBF
=>\(\dfrac{ID}{IB}=\dfrac{IA}{IF}\)
=>\(ID\cdot IF=IA\cdot IB\)


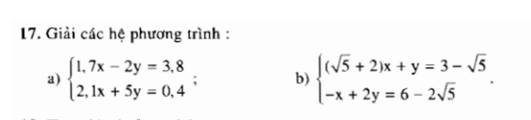

\(\left(2x^2z^2\right)^3+\left(-3xy^3\right)^2=0\)
=>\(8x^6z^6+9x^2y^6=0\)
=>\(x^2\left(8x^4z^6+9y^6\right)=0\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2=0\\8x^4z^6+9y^6=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>x=y=0