cho hàm số y=(3-m)x+3m+2.Tìm giá trị của m để đồ thị của hàm số đã cho song song với đường thẳng y=5x-4
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(f\left(x\right)=\left(x^2-3x+3\right)\left(x^2-2x+3\right)-2x^2\)
\(=\left(x^2-2x+3-x\right)\left(x^2-2x+3\right)-2x^2\)
\(=\left(x^2-2x+3\right)^2-x\left(x^2-2x+3\right)-2x^2\)
\(=\left(x^2-x+3-2x\right)\left(x^2-x+3+x\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-4x+3\right)\left(x^2+3\right)\)
Đặt f(x)=0
=>\(\left(x^2-4x+3\right)\left(x^2+3\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2+3>0\forall x\)
nên \(x^2-4x+3=0\)
=>(x-1)(x-3)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)

Bài 2:
a: Khi x=4 thì \(M=\dfrac{4+3}{4-2}=\dfrac{7}{2}\)
b: \(M=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+3}{x-2}=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
=>3(x+3)=2(x-2)
=>3x+9=2x-4
=>3x-2x=-4-9
=>x=-13(nhận)
c: Để M là số nguyên dương thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+3⋮x-2\\M>0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2+5⋮x-2\\\dfrac{x+3}{x-2}>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5⋮x-2\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>2\\x< -3\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2\in\left\{1;-1;5;-5\right\}\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>2\\x< -3\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(x\in\left\{3;7\right\}\)
Bài 3:
ΔMIN vuông tại I
=>\(IM^2+IN^2=MN^2\)
=>\(x=MI=\sqrt{12^2-5^2}=\sqrt{144-25}=\sqrt{119}\left(cm\right)\)
ΔMIP vuông tại I
=>\(IM^2+IP^2=PM^2\)
=>\(y=\sqrt{119+100}=\sqrt{219}\left(cm\right)\)
Bài 4:
a: Xét ΔBAC vuông tại A và ΔBHA vuông tại H có
\(\widehat{ABC}\) chung
Do đó: ΔBAC~ΔBHA
b: Xét ΔHBA vuông tại H và ΔHAC vuông tại H có
\(\widehat{HBA}=\widehat{HAC}\left(=90^0-\widehat{HAB}\right)\)
Do đó: ΔHBA~ΔHAC
=>\(\dfrac{HB}{HA}=\dfrac{HA}{HC}\)
=>\(HA^2=HB\cdot HC\)
c: Xét tứ giác AIHK có \(\widehat{AIH}=\widehat{AKH}=\widehat{KAI}=90^0\)
nên AIHK là hình chữ nhật
=>\(\widehat{AKI}=\widehat{AHI}\)
mà \(\widehat{AHI}=\widehat{ABC}\left(=90^0-\widehat{HAB}\right)\)
nên \(\widehat{AKI}=\widehat{ABC}\)
ΔABC vuông tại A
mà AM là đường trung tuyến
nên MA=MC
=>ΔMAC cân tại M
=>\(\widehat{MAC}=\widehat{MCA}\)
\(\widehat{AKI}+\widehat{MAC}=\widehat{ABC}+\widehat{ACB}=90^0\)
=>AM\(\perp\)IK

\(x^2-5x+3=0\\ \Delta=b^2-4ac=\left(-5\right)^2-4\cdot1\cdot3=13>0\\ x_1=\dfrac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{-\left(-5\right)-\sqrt{13}}{2\cdot1}=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{13}}{2}\\ x_2=\dfrac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{-\left(-5\right)+\sqrt{13}}{2\cdot1}=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{13}}{2}\\ \text{vậy phương trình có 2 nghiệm là }x_1=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{13}}{2};x_2=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{13}}{2}\)

\(\left(x^2-y^2\right)^2+4x^2y^2+x^2-2y^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^4+y^4-2x^2y^2+4x^2y^2+x^2-2y^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^4+y^4+2x^2y^2+x^2-2y^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x^2+y^2\right)^2-2\left(x^2+y^2\right)+3x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+y^2-1\right)^2=1-3x^2\le1\)
\(\Rightarrow-1\le x^2+y^2-1\le1\)
\(\Rightarrow0\le x^2+y^2\le2\)
\(\Rightarrow A_{min}=0\) khi \(x=y=0\)
\(A_{max}=2\) khi \(x=0;y=\pm\sqrt{2}\)

\(P=\dfrac{x+1}{x^3-1}\left[\left(4x^2-1\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{2x-1}-\dfrac{1}{2x+1}+1\right)-5\right]\)
\(=\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\cdot\left[\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)\cdot\dfrac{2x+1-2x+1+4x^2-1}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}-5\right]\)
\(=\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\cdot\left(4x^2+1-5\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\cdot\left(4x^2-4\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\cdot4\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{4\left(x+1\right)^2}{x^2+x+1}\)

\(B=-3x^2+4x+1\)
\(=-3\left(x^2-\dfrac{4}{3}x-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)\)
\(=-3\left(x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{2}{3}+\dfrac{4}{9}-\dfrac{7}{9}\right)\)
\(=-3\left(x-\dfrac{2}{3}\right)^2+\dfrac{7}{3}< =\dfrac{7}{3}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x-\dfrac{2}{3}=0\)
=>\(x=\dfrac{2}{3}\)

Đặt \(x^2+4=a;1-6x=b\)
=>\(a+b=x^2+4+1-6x=x^2-6x+5\)
\(\left(x^2+4\right)^3+\left(1-6x\right)^3=\left(x^2-6x+5\right)^3\)
=>\(a^3+b^3=\left(a+b\right)^3\)
=>\(\left(a+b\right)^3-\left(a+b\right)^3+3ab\left(a+b\right)=0\)
=>3ab(a+b)=0
=>ab(a+b)=0
=>\(\left(x^2+4\right)\left(1-6x\right)\left(x^2-6x+5\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(1-6x\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x-5\right)=0\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}1-6x=0\\x-1=0\\x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{6}\\x=1\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)


Bài 5:
a: \(D=\dfrac{6x}{4x^2-9}-\dfrac{x}{3-2x}+\dfrac{x}{2x+3}-1\)
\(=\dfrac{6x}{\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x+3\right)}+\dfrac{x}{2x-3}+\dfrac{x}{2x+3}-1\)
\(=\dfrac{6x+x\left(2x+3\right)+x\left(2x-3\right)-4x^2+9}{\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{6x+x\left(2x+3+2x-3\right)-4x^2+9}{\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{6x+9}{\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x+3\right)}=\dfrac{3}{2x-3}\)
b: \(D=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
=>\(\dfrac{3}{2x-3}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
=>2x-3=-6
=>2x=-3
=>\(x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\left(loại\right)\)
c: Để D nguyên thì \(3⋮2x-3\)
=>\(2x-3\in\left\{1;-1;3;-3\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{2;1;3;0\right\}\)
Bài 6:
a: \(P=\left(\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}+\dfrac{x}{x-2}+\dfrac{2x+4}{4-x^2}\right)\cdot\left(1+\dfrac{5}{x-3}\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}+\dfrac{x}{x-2}-\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\right)\cdot\dfrac{x-3+5}{x-3}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}+\dfrac{x}{x-2}-\dfrac{2}{x-2}\right)\cdot\dfrac{x+2}{x-3}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}+1\right)\cdot\dfrac{x+2}{x-3}=\dfrac{x-2+x+2}{x+2}\cdot\dfrac{x+2}{x-3}=\dfrac{2x}{x-3}\)
b: Khi x=-1 thì \(P=\dfrac{2\cdot\left(-1\right)}{-1-3}=\dfrac{-2}{-4}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
c: \(P=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x}{x-3}=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x}{x-3}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
=>3x=x-3
=>2x=-3
=>\(x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)(nhận)
d: Để P là số tự nhiên thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x⋮x-3\\\dfrac{2x}{x-3}>=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-6+6⋮x-3\\\dfrac{x}{x-3}>=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6⋮x-3\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>3\\x< =0\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;3;-3;6;-6\right\}\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>3\\x< =0\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(x\in\left\{4;5;6;0;9;-3\right\}\)
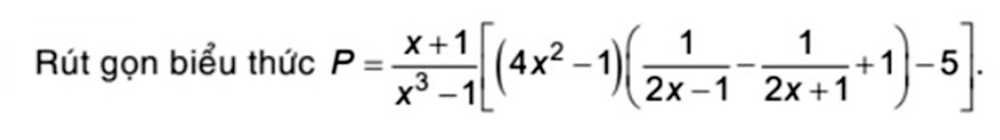

Để đồ thị hàm số y=(3-m)x+3m+2 song song với đường thẳng y=5x-4 thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3-m=5\\3m+2\ne-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=3-5=-2\\3m\ne-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(m\in\varnothing\)