cho tam giác ABC.Điểm D thuộc tia đối của tia BA/BD=BA,M là trung điểm BC.K là giao điểm DM và AC.Chứng minh: AK=2KC
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Dựng đường thẳng qua B và song song với DK cắt AC tại G
Xét tam giác ADK ta có:
AB = BD; BG // DK
⇒ KG = GA = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) AK (định lý 1 đường trung bình của tam giác) (1)
Xét tam giác BCG ta có:
BM = MC; MK // BG
⇒ KC = KG (định lý 1 đường trung bình của tam giác) (2)
Kết hợp (1) và (2) ta có:
KC = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) AK
⇒ AK = 2KC (đpcm)

Bạn nên viết đề cho rõ ràng để mọi người hiểu đề và hỗ trợ bạn tốt hơn. Viết đề díu dít vào nhau và không gõ công thức toán (biểu tượng $\sum$ góc trái khung soạn thảo) khiến bài của bạn có khả năng bị bỏ qua cao hơn nhé.

Ta có:
6x² + 3x - 5 = 3x(2x + 1) - 5
Để M là số nguyên thì (6x² + 3x - 5) ⋮ (2x + 1)
⇒ 5 ⋮ (2x + 1)
⇒ 2x + 1 ∈ Ư(5) = {-5; -1; 1; 5}
⇒ 2x ∈ {-6; -2; 0; 4}
⇒ x ∈ {-3; -1; 0; 2}
Vậy x ∈ {-3; -1; 0; 2} thì M là số nguyên

a) Số sản phẩm công ty sản xuất trong một ngày theo kế hoạch:
10000/x (sản phẩm)
b) Số sản phẩm công ty thực tế đã làm được trong một ngày:
10080/(x - 1) (sản phẩm)
c) Số sản phẩm theo kế hoạch mỗi ngày phải làm:
10000/25 = 400 (sản phẩm)
Số sản phẩm thực tế làm mỗi ngày:
10080/(25 - 1) = 420 (sản phẩm)
Số sản phẩm làm thêm mỗi ngày:
420 - 400 = 20 (sản phẩm)
Bổ sung:
c, Số sản phẩm công ty làm thêm trong một ngày biểu thị theo \(x\) là:
\(\dfrac{10080}{x-1}\) - \(\dfrac{10000}{x}\) = \(\dfrac{80x+10000}{x\left(x-1\right)}\) (sản phẩm)

\(\dfrac{6}{x^2-3x}\) = \(\dfrac{A}{x}\) + \(\dfrac{B}{x-3}\) (nếu đúng với mọi \(x\) ≠0; 3 thì làm như sau)
Đkxđ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-3x\ne0\\x\ne0\\x-3\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\) ⇒ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\left(x-3\right)\ne0\\x\ne0\\x\ne3\end{matrix}\right.\) ⇒ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne0\\x\ne3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{A}{x}\) + \(\dfrac{B}{x-3}\) = \(\dfrac{A.\left(x-3\right)}{x.\left(x-3\right)}\) + \(\dfrac{B.x}{x\left(x-3\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{Ax-3A+Bx}{x\left(x-3\right)}\)
⇒\(\dfrac{6}{x^2-3x}\) = \(\dfrac{6}{x.\left(x-3\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{Ax-3A+Bx}{x.\left(x-3\right)}\)
⇒ \(\dfrac{6}{x\left(x-3\right)}\) - \(\dfrac{Ax-3A+Bx}{x\left(x-3\right)}\) = 0
\(\dfrac{1}{x\left(x-3\right)}\).[6 - (A\(x\) - 3A + B\(x\))] = 0
⇒ 6 - A\(x\) + 3A - B\(x\) = 0
⇒ - \(x\).( A + B) + 6 + 3A = 0 (1)
(1) đúng với ∀ \(x\) ≠0; 3 ⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}A+B=0\\6+3A=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}A=-B\\3A=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}A=-B\\A=-6:3\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}B=-A\\A=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇒ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}B=2\\A=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy A = -2; B = 2
\(\dfrac{6}{x^2-3x}=\dfrac{A}{x}+\dfrac{B}{x-3}\left(x\ne0;x\ne3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{6}{x\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{A\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{Bx}{x\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6=A\left(x-3\right)+Bx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6=Ax-3A+Bx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x+6=\left(A+B\right)x-3A\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}A+B=0\\-3A=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}A=-B\\A=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}B=2\\A=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)

Bài 3:
a, rút gọn P = \(\dfrac{x^2}{x+1}\) + \(\dfrac{2.\left(x-1\right)}{x}\) + \(\dfrac{x+2}{x^2+x}\) với \(x\ne0;x\ne-1\)
P = \(\dfrac{x^2}{x+1}\) + \(\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)}{x}\) + \(\dfrac{x+2}{x.\left(x+1\right)}\)
P = \(\dfrac{x^2.x}{\left(x+1\right).x}\) + \(\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x.\left(x+1\right)}\) + \(\dfrac{x+2}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
P = \(\dfrac{x^3}{x\left(x+1\right)}\) + \(\dfrac{2\left(x^2-1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}\) + \(\dfrac{x+2}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
P = \(\dfrac{x^3+2x^2-2+x+2}{x.\left(x+1\right)}\)
P = \(\dfrac{x^3+2x^2+x-\left(2-2\right)}{x.\left(x+1\right)}\)
P = \(\dfrac{x^3+2x^2+x}{x.\left(x+1\right)}\)
P = \(\dfrac{x\left(x^2+2x+1\right)}{x.\left(x+1\right)}\)
P = \(\dfrac{x.\left(x+1\right)^2}{x.\left(x+1\right)}\)
P = \(x\) + 1
b, Thay \(x\) = 1 vào biểu thức P = \(x\) + 1 ta có:
P = 1 + 1
P = 2

a) \(A+\dfrac{1}{x+1}=\dfrac{3x+1}{x^2-2x+1}-\dfrac{x+3}{x^2-1}\left(x\ne\pm1\right)\)
\(A=\dfrac{3x+1}{\left(x-1\right)^2}-\dfrac{x+3}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}\)
\(A=\dfrac{\left(3x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{3x^2+3x+x+1-x^2+x-3x+3-x^2+2x-1}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x^2+4x+3}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x+3}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x+3}{x^2-2x+1}\)
b) \(\dfrac{4}{x^2+x+1}-P=\dfrac{2}{1-x}+\dfrac{2x^2+4x}{x^3-1}\)
\(P=\dfrac{4}{x^2+x+1}-\dfrac{2}{1-x}-\dfrac{2x^2+4x}{x^3-1}\)
\(P=\dfrac{4}{x^2+x+1}+\dfrac{2}{x-1}-\dfrac{2x^2+4x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{4\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}+\dfrac{2\left(x^2+x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}-\dfrac{2x^2+4x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{4x-4+2x^2+2x+2-2x^2-4x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{2x-2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{2}{x^2+x+1}\)

a, \(\dfrac{x+3}{3x-3}\) + \(\dfrac{2-x}{4x-4}\)
đkxđ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-3\ne0\\4x-4\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\) ⇒ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3.\left(x-1\right)\ne0\\4.\left(x-1\right)\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\) ⇒ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-1\ne0\\x-1\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\) ⇒ \(x\) ≠1
A = \(\dfrac{x+3}{3x-3}\) + \(\dfrac{2-x}{4x-4}\)
A = \(\dfrac{x+3}{3.\left(x-1\right)}\) + \(\dfrac{2-x}{4.\left(x-1\right)}\)
A = \(\dfrac{4.\left(x+3\right)}{4.3.\left(x-1\right)}\) + \(\dfrac{3.\left(2-x\right)}{3.4.\left(x-1\right)}\)
A = \(\dfrac{4x+12}{12\left(x-1\right)}\) + \(\dfrac{6-3x}{12\left(x-1\right)}\)
A = \(\dfrac{4x+12+6-3x}{12\left(x-1\right)}\)
A = \(\dfrac{\left(4x-3x\right)+\left(12+6\right)}{12\left(x-1\right)}\)
A = \(\dfrac{x+18}{12.\left(x-1\right)}\)
b, \(\dfrac{3}{x+2}-\dfrac{6}{x-1}\)
Đkxđ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2\ne0\\x-1\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\) ⇒ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne-2\\x\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\)
B = \(\dfrac{3}{x+2}\) - \(\dfrac{6}{x-1}\)
B = \(\dfrac{3.\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)}\) - \(\dfrac{6.\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
B = \(\dfrac{3x-3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)}\) - \(\dfrac{6x+12}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
B = \(\dfrac{3x-3-\left(6x+12\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
B = \(\dfrac{3x-3-6x-12}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
B = \(\dfrac{\left(3x-6x\right)-\left(12+3\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
B = \(\dfrac{-3x-15}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
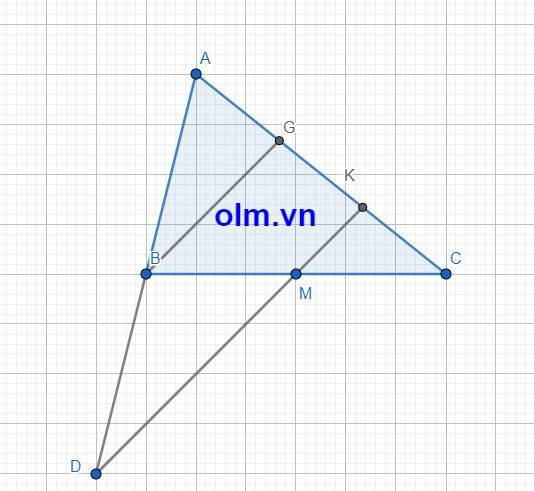
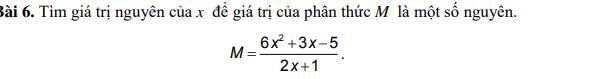


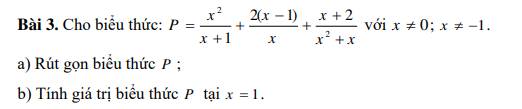


Qua B dựng đường thẳng song song với DK và cắt AC tại G
Xét tam giác ADK ta có: AB = BD; BG//DK
⇒ AG = GK (định lý đường trung bình của tam giâc)
⇒ GK = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) AK (1)
Xét tam giác BCG ta có:
BM = MC; MK // BG
⇒ GK = KC (định lý 1 đường trung bình của tam giác) (2)
Kết hợp (1) và (2) ta có:
KC = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) AK
⇒ AK = 2KC (đpcm)