Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



Biện pháp nghệ thuật nào được sử dụng trong câu văn sau: "Hoa phượng màu hồng pha da cam chứ không đỏ gắt như vông, như gạo. Đến cái anh bằng lăng thì đã vừa hồng vừa tím.”
C, Nhân hoá
1 like

Olm chào em. Để nhận được coin của olm em cần tham gia các cuộc thi của olm em nhé.
Hoặc em cần tham gia các sự kiện của olm để trúng thưởng bằng coin.
Cảm ơn em đã lựa chọn đồng hành cùng olm trên hành trình tri thức.
Chúc em học tập vui vẻ và hiệu quả cùng olm.

43. We are planning to play basketball at the weekend.
44. Campers don’t need to pack a first aid kit.
45. You must switch off your mobile phones during the exam.
46. Because it’s raining heavily, we are staying at home.
47. Amanda is planning to go to Bali next summer.
48. Today, Cathy is wearing a red T-shirt and blue jeans.
49. Mum is putting sausages on the barbecue right now.
50. Is Jackson going to come with us to the cinema tomorrow ?
43. Rewrite the following sentences without changing their meaning.
We intend to play basketball at the weekend.
→ We are.............going to play basketball at the weekend................
44. Rewrite the following sentences without changing their meaning.
It isn’t necessary for campers to pack a first aid kit.
→ Campers don’t..........have to pack a first aid kit....................
45. Rewrite the following sentences without changing their meaning.
It’s the rule that you switch off your mobile phones during the exam.
→ You.........must switch off your mobile phones during the exam....................
46. Rewrite the following sentences without changing their meaning.
It’s raining heavily, so we are staying at home.
→ Because......it's raining heavily, we are staying at home. .......................
47. Rewrite the following sentences without changing their meaning.
Amanda has a plan to go to Bali next summer.
→ Amanda is.....going to Bali next summer.........................
48. Use the given words to make complete sentences.
Today/ Cathy/ wear/ red T-shirt/ blue jeans.
→ ......Today Cathy is wearing a red T-shirt and blue jeans.......................
49. Use the given words to make complete sentences.
Mum/ put/ sausages/ the barbecue/ right now.
→ ......Mum is putting sausages on the barbecue right now.......................
50. Use the given words to make complete sentences.
Jackson/ going/ come/ us/ the cinema/ tomorrow?
→ ........Is Jackson going to come with us to the cinema tomorrow? .....................

Although Daniel tried his best, he couldn't repair his motorbike.
Although Daniel tried his best, he couldn't repair his motorbike
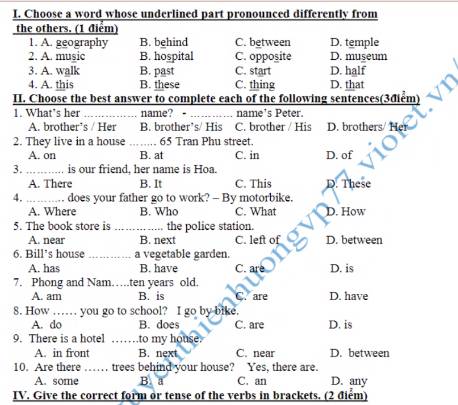
1D
2B
3A
4C
II
1 B
2 B
3 C
4 D
5 A
6 A
7 C
8 A
9B
10 D
1 D
2 B
3 A
II
1B
2 B
3 C
4 D
5 A
6 A
7 C
8 A
9 B
10 D