Bài học cùng chủ đề
Báo cáo học liệu
Mua học liệu
Mua học liệu:
-
Số dư ví của bạn: 0 coin - 0 Xu
-
Nếu mua học liệu này bạn sẽ bị trừ: 2 coin\Xu
Để nhận Coin\Xu, bạn có thể:

Luyện tập SVIP
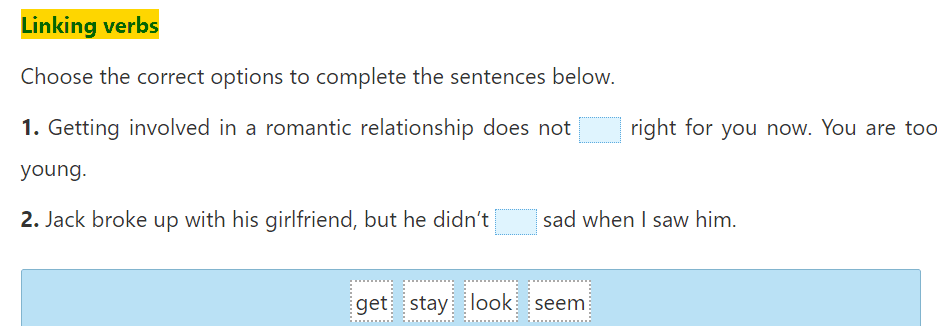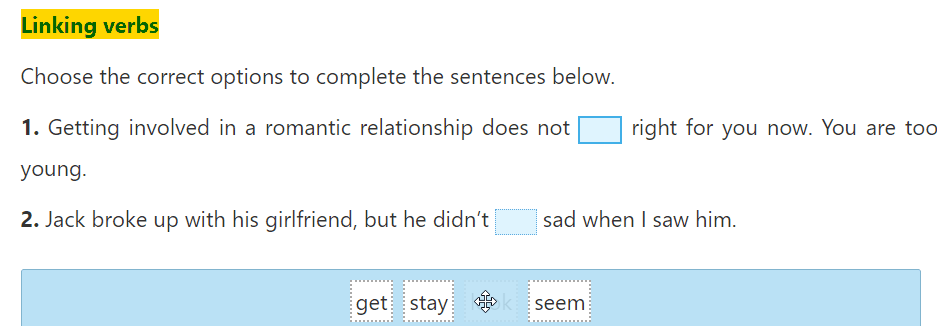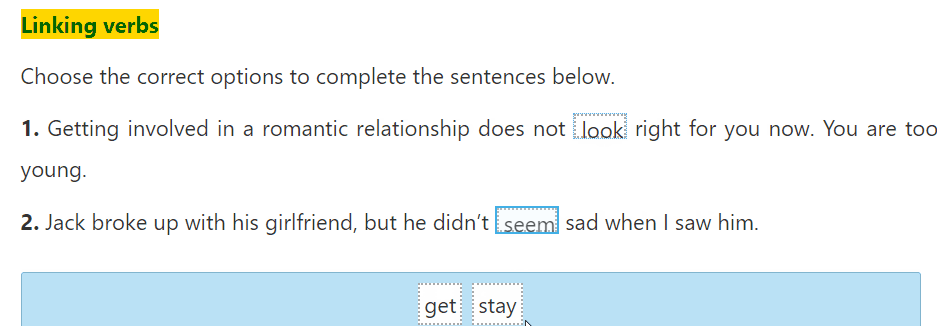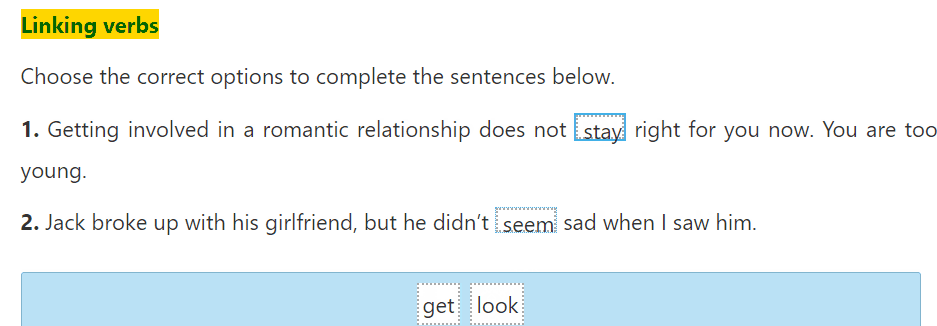
Communication
Label the diagram of Viet Nam's education system after primary school, using the words in the box.

1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
(Kéo thả hoặc click vào để điền)
COMMUNICATION
Listen to an overview of Viet Nam's higher education. Decide if the following statements are true (T) or false (F). Tick the correct boxes.
(Nhấp vào dòng để chọn đúng / sai)
| 1. Most Vietnamese families want their children to take vocational courses. |
|
| 2. Viet Nam has only developed its vocational education system recently. |
|
| 3. It often takes three years to graduate from a college. |
|
| 4. Students often have to pass three examinations before they can enter university. |
|
| 5. Students can only use their personal funds to pay for their studies abroad. |
|
Communication
Give your opinion about higher education and suggest what should be done to help students to pursue academic or professional degrees.
Culture
Look at Singapore's education journey. Briefly describe the stages following secondary education.

Culture
Read the text and answer the questions.
Singapore's secondary and further education
One of the main aims of the Singapore's education system is to help students to discover their talents and develop a passion for learning.
During secondary education, which lasts four to five years, students have opportunities to take various courses, build their strengths and develop their talents in both academic and non-academic areas. For example, after passing standardised examinations, students can enrol on courses in specialised independent schools such as NUS High School of Mathematics and Science, Singapore Sports School, School of the Arts, or School of Science and Technology. They can further their study and interests at junior colleges and polytechnics through direct admission. These are flexible ways that allow students to continue their education journey at a post-secondary institution.
After leaving secondary school, students can pursue either pre-university education or technical education. A pre-university course provides students with essential skills and knowledge for higher education. They can realise their potential through a wide range of subjects from academic areas such as Humanities, Arts, Languages, Mathematics, and Science. Alternatively, technical education, through collaboration with companies and other organisations, can equip students with professional, technical skills and working experience. They can select engineering, technical, business or service skills areas to prepare themselves for their work environment.
If they want to pursue higher education, students can do that at one of the four publicly-funded local universities with degree programmes. All of them have global partnerships with leading universities and educational institutions overseas to ensure the best quality and future for the graduates.

1. Name one of the important targets of Singapore's education.
2. What is the requirement for enrolling on special courses in secondary education?
3. How can secondary education prepare students for further education?
4. What are the choices for secondary school leavers?
5. How many local institutions provide higher education in Singapore?

Bạn có thể đăng câu hỏi về bài học này ở đây
